All stars form here
What is a nebula (or interstellar cloud)
What is a main sequence star?
These are the most MASSIVE stars in the Main sequence.
What are blue stars?
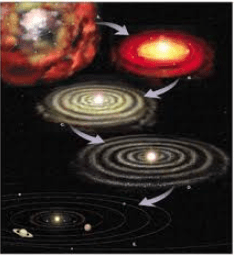
What is nebular theory?
That theory says that everything is going further and further away from each other and eventually the stars will all die.
What is the Big Freeze?
Before a star is a main sequence star it is considered one of these.
What is a protostar?
The next step for our sun will be this.
What is (becoming) a red giant?
These are the least LUMINOUS in the main sequence.
What are the red stars?
These are the two formations that can happen when a supergiant goes supernova
What is a neutron star or black hole?
That is not a Deep Space object
What is a meteor shower?
This is how we know there is a true star. (This has to start)
What is nuclear fusion?
Stars that are red giants will become these next.
What are white dwarfs?
Blue stars like Bellatrix compared to yellow stars like our sun (temperature)
Which stars are higher in temperature?
This is the only time you can see the corona of the sun
What is a solar Eclipse?
That is the correct temperature of Sirius (must include the correct units)
What star has a temperature of 10,000 Kelvin?
Leftover material from a star's formation, planets form here.
What is an accretion disk?
Stars that are Supergiants will ALWAYS do this before their next star step.
What is go supernova?
No this step of the star cycle will NEVER happen to smaller stars like our sun.
What is go supernova? (OR become a supergiant, neutron star, or blackhole)
Our sun's story started about 6 billion years ago with this
what is a neighboring star going supernova?
According to the H-R diagram that is the luminosity of Procyon B.
What star has a luminosity of less than 1/1000 of our sun.
The reason that particles get pulled together forming stars or planets.
What is gravity?
After going supernova these are the 2 things that can happen to supergiants if they are not destroyed in the supernova.
We know stars do not age at the same rate because of this data (from the star in the box).
A star is triggered to go from one type to the next (like from main sequence to a red giant).
What happens when stars run out of one fuel type?
That is the solar radius of B Centari
What star has a solar radius of 11 or 12 that of our sun?