Nerve impulse speed does this as diameter of a nerve fiber increases.
What is increases (becomes faster)?
Ectodermal cells that remain outside the neural tube are called this.
What is neural crest?
These are the spinal levels which the sympathetic nervous system comes from
What is T1 to L2 or L3?
Gamma motor neurons innervate this type of muscle fibers
What is intrafusal?
The middle cranial fossa is formed by these bones
What are the temporal and sphenoid bones?
This artery supplies blood to the membranous labyrinth of the inner ear through the internal acoustic meatus
What is the labyrinthine artery?
At birth, the spinal cord ends at this spinal level
What is L3?
This is the type of glial cells that can myelinate segments of several axons.
What is oligodendrites?
This is the day when the rostral neuropore should close
What is day 24?
This is the group of nerve fibers that release norepinephrine
What is the postganglionic nerve fibers of the sympathetic nervous system?
What is acetylcholine?
This is the opening through which the internal carotid artery passes to enter the cranial vault
What is the foramen lacerum?
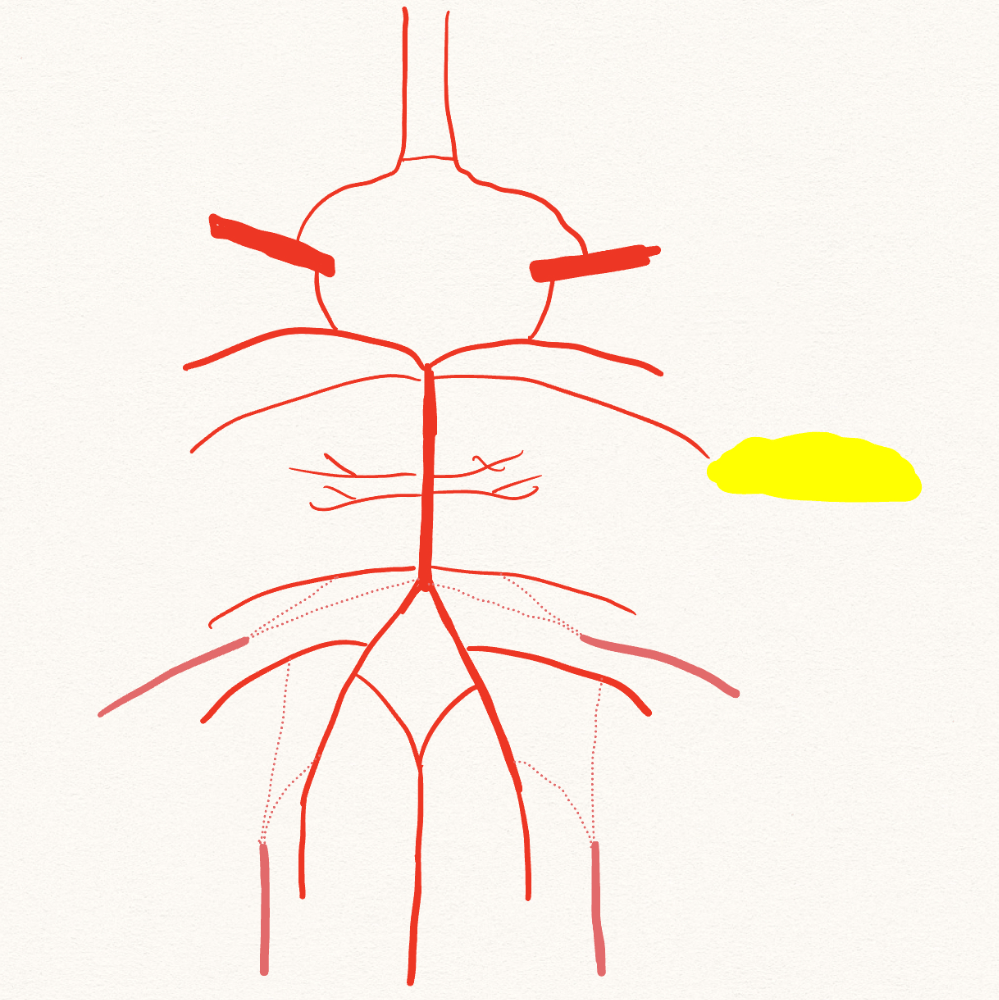 What artery is this?
What artery is this?
What is the superior cerebellar artery?
The spinal cord can be divided into this many segments according to its spinal nerve roots.
What is 31?
Purkinje neurons in the cerebellum are characterized by this feature.
What is treelike dendrites?
This vessicle goes on to develop into the medulla
What is the myelencephalon?
This is the cranial nerve that innervates the superior oblique eye muscle
What is cranial nerve IV (trochlear)?
What are Meissner's corpuscles and pacinian corpuscles. *****
What structure is this?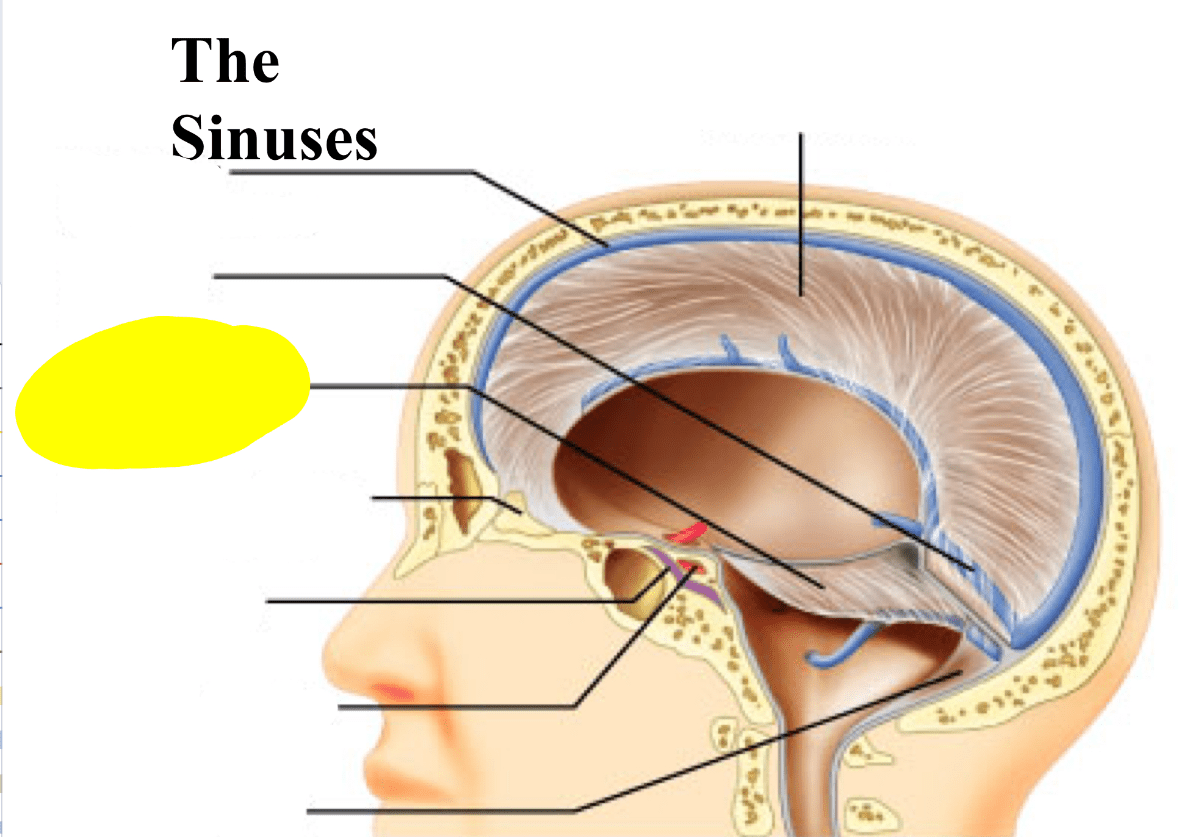
What is the tentorium cerebelli?
This is the structure through which the ophthalmic artery passes through
What is the optic foramen?
Cauda equina is this type of motor neuron
What is lower motor neuron
Most glial cells are created in this germ cell layer.
What is the ectoderm?
Myelination of the CNS should complete by this age.
What is age 10?
Impairment of this CN would result in problems with general sensation, respiratory and GI tract, and visceral sensation.
What is CN X (Vagus)?
This encapsulated sensory nerve responds to muscle tension
What is golgi tendon organ?
These are the exits which CSF flows out from the fourth ventricle
What is the (1) median aperture (2) lateral aperture and (3) and central canal
This is the portion of the spinal cord which the anterior spinal artery supplies blood to
This Lamina is where the origin of the spinothalamic tract is.
What is Lamina IV?
This kind of synapse in the nervous system has a very small gap and is rare in mammalian nervous systems.
What is electrical synapse?
This is a herniation of the posterior cerebellum through the foramen magnum
What is Arnold Chiari malformation?
These are the cell bodies of CN VII (facial).
What are M:Facial Nucleus S:Nucleus Solitarius P Superior Salivatory Nucleus ?
Postganglionic fibers and slow pain receptors are classified as this group of axons.
What is group C (unmyelinated)?
CSF from the superior sagittal sinus drains through several sinuses into this structure
What is the internal jugular vein?
This is the artery that supplies the lateral surface of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes as well as the language areas of the brain.
What is the middle cerebral artery?
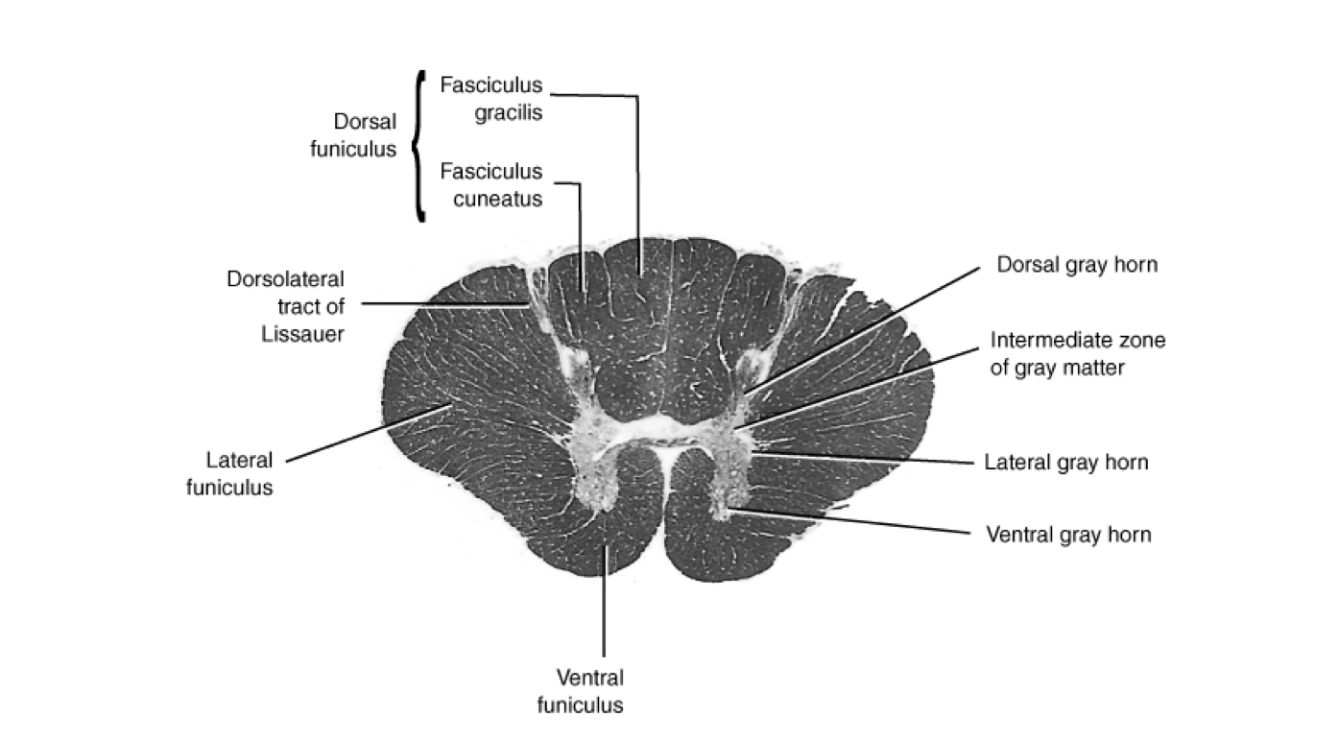
What portion of the spinal cord is this cross section from?