A TIA is a warning for a ______
A stroke is a warning for a ______
What is Stroke?
What is another Stroke?
External physical force-> potential to cause
mild to complex alterations of brain function
• Variable outcomes
▫ Extent of injury
▫ Other injuries sustained
▫ Management of the injury
What is a Traumatic brain injury TBI?
Complete neurologic recovery by discharge is
less than ___%
What is 1%?
Risk factors modifiable and nonmodifiable
Modifiable
▫ Hypertension
-greater than 160/95 mm/Hg
Decreasing diastolic bp by 5-6mm/hg decreases
risk of stroke by up to 40%
▫ Heart disease
▫ Diabetes
▫ Cigarette smoking
▫ Heavy EToH consumption
▫ High CHO
▫ Illicit drug use
Non-modifiable
▫ Age
▫ Race
▫ Gender
▫ Family history/genetic or congenital conditions
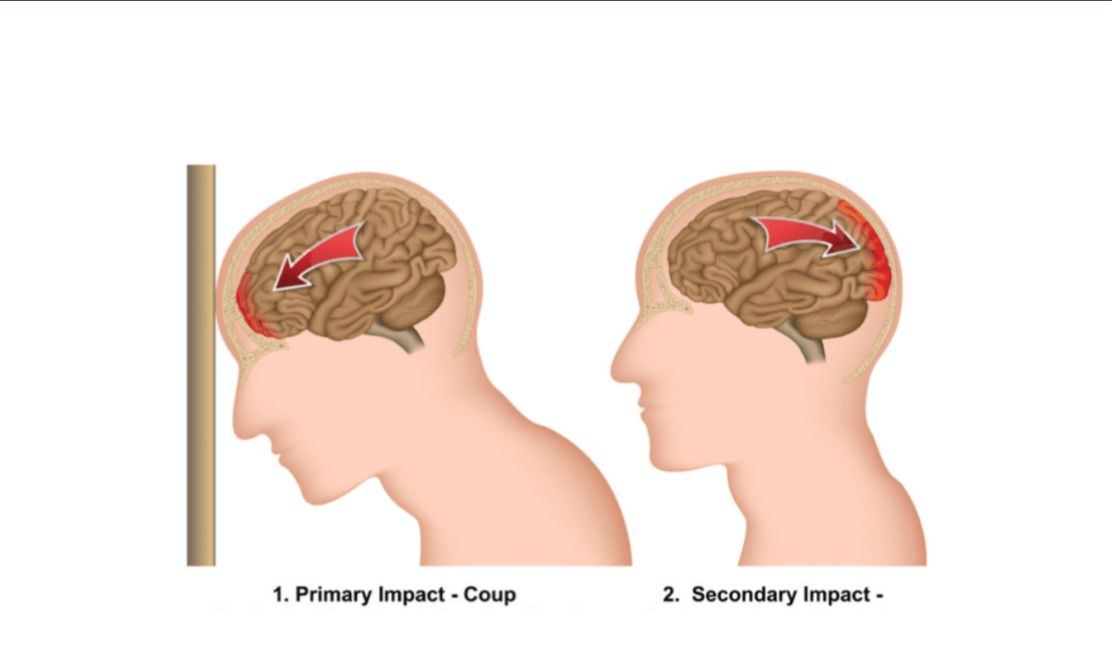
The difference between coup and counter coup as it relates to a Close head injuries.
Absence of skull fracture
Coup injury: initial blow occurs under the point of
impact
Counter coup: brain decelerates against the
contralateral skull, injury occurs on the opposite
side- frequently worse than the underlying impact
Difference between complete and incomplete
spinal cord lesion
may depend on the survival
of a small fraction of axons in the spinal cord!
Important to know!
• Complete
▫ Complete loss of sensory and motor below
level of lesion
• Incomplete
▫ Partial loss of sensory and motor function
below level of injury
Symptoms that occur suddenly
▫ Weakness
▫ Numbness (UE, LE or face)
Primarily unilateral
▫ Confusion
▫ Difficulty speaking/understanding language
▫ Problems with vision
▫ Dizziness/loss of balance
▫ Sudden and severe headache
▫ Occurs within 7-10 days following
concussion
▫ May last 3 months and have signs and
symptoms which resemble concussion
What is Post concussion syndrome?
This is how Level of injury in spinal cord is named
Named according to the level of neurological
impairment
Cervical- tetraplegia: limbs+ trunk
Muscles of respiration
Thoracic and lumbar:-paraplegia: lower limbs
and potentially lower trunk
Primary cause of stroke
85% its a ______
15% its a ______
Cerebral vascular disease
-Intrinsic damage to the vessel
-Clot originates remotely
-Rupture of vessel- sub arachnoid space of intracerebral tissue
85% its a ischemic stroke
15% its a primary hemorrhage intraparenchymal subarachnoid
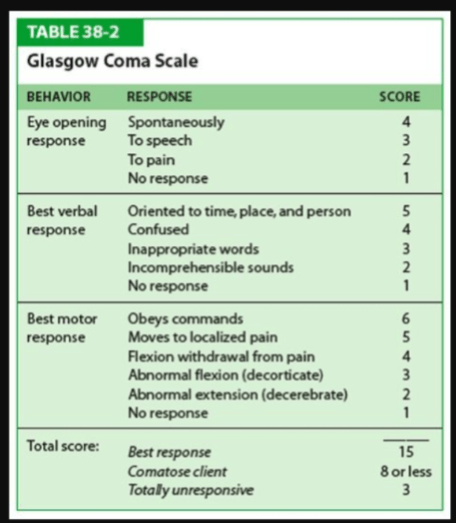
▫ Most widely used instrument for determining
level of consciousness
▫ Used to determine current status and potential
for improvement
What is Glasgow coma scale (GCS)?
ASIA stands for....
American spinal injury association
University of Oxford ABCD scale
a clinical tool used to assess the risk of stroke following a transient ischemic attack (TIA). It is based on 4 factors...
What is
Age
Blood pressure
Clinical features (symptoms)
Duration?
ABCD scales assigns points bases these categories to determine how likely you are to have another stroke
The Difference between Retrograde amnesia and Posttraumatic amnesia...
What is
• Retrograde amnesia- partial or total loss of
ability to recall events that have occurred during
the period immediately preceding head injury
• Posttraumatic amnesia- time lapse between the
injury and the point at which functional memory
returns
a Common symptom after a SCI
Changes in muscle tone
• Paralysis of the voluntary musculature is the most
obvious effect of SCI
• When descending tracts are involved, immediate
flaccidity is present and reflexes are absent at and
below the level of injury
• Spasticity is an inevitable consequence
• Essential/basic spasticity – may be of some benefit
when emptying bladder or flexing hip and knees
• Excess spasticity – due to afferent stimuli
• Spasticity can be made worse by the presence of stress:
constipation, infection, fracture, pressure sores
An occlusion of major arteries leads to...
what is a Secondary vascular responses
• Cerebral artery is occluded-> formation of
thromboembolism begins in the distal vessels
of that artery
▫ Increase in number and continue to impair
blood flow to the brain
Cell death surrounding the area of blocked
blood flow
▫ Cumulative damage from multiple
concussions -> can lead to long-term brain
damage and disability
▫ Formal neuropsychological testing to compare
baseline to continued deficits
Cognitive challenges: attention span, memory,
language, sequencing, problem solving, verbal
and spatial integration tasks
What is Second impact syndrome?
An autonomic nervous system
change described as a lesion to T5 and above
▫ Damage causing simultaneous sympathetic
and parasympathetic activity
What is Autonomic dysreflexia (AD)?
Noxious stimuli- may illicit a sympathetic
response- increase in BP
▫ Usually the sympathetic output compensates
for increased BP by causing vasodilation to
decrease BP- but with SCI they continue to
transmit excitatory responses continuing
vasoconstriction and increased BP
Severe HA, sweating, chills but no fever
Susceptible to subarachnoid hemorrhage, renal
or retinal hemorrhage, seizure or MI
• Syndromes- dysfunctions related to specific areas of the brain
These syndromes are named for the arteries which supply that tissue
List at least 5....
▫ Middle cerebral artery syndrome
▫ Anterior cerebral artery syndrome
▫ Internal carotid artery syndrome
▫ Posterior cerebral artery syndrome
▫ Vertebral and posterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome
▫ Basilar artery syndrome
▫ Superior cerebellar artery syndrome
▫ Anterior inferior cerebellar artery syndrome
▫ Lacunar syndrome
A medical scale used to assess and describe the cognitive and behavioral recovery of patients after a brain injury, particularly traumatic brain injury (TBI) or other neurological conditions.
What is the Rancho Los Amigos scale?
Lesions above ____ can result in paralysis of
the muscles of inspiration
-May require artificial ventilation
-Loss of phrenic nerve innervation
What is spinal level c4?
A stroke in Broca's area will affect the patient this way A stroke in Wernicke's area affect the patient this way
What is...
Wernicke’s area
▫ Understanding written and spoken language
▫ Receptive aphasia
Broca’s area
▫ Speech production
▫ Expressive aphasia
Respiratory changes as a result of a SCI at this specific level are:
Loss of innervation of the muscle of expiration
and abdominal intercostal muscles
▫ Decreased ability to cough and clear
secretions
What are Pulmonary complications: C5-T12?
Stroke pt.s are given this type of medicine to reduce a atherothrombotic stroke recurrence...
What is Anticoagulation medication?
blood thinners
Aspirin- reduce risk of MI and stroke after MI
Warfarin- prevention of CVA with atrial
fibrillation
This type of stroke is describe as bleeding from an artery into the brain. MOST DEADLY
What is a Intracerebral hemorrhage?
--Primary- spontaneous
▫ Hypertension- weakening of arterial walls-
formation of small aneurysmal outpouchings
--Secondary- identifiable cause
▫ Trauma
▫ Impaired coagulation
▫ Toxin exposure
▫ Anatomic lesion
Described as Frank blood in the subarachnoid space
between the arachnoid and pia mater
Can begin with sudden onset of headache
with searing pain (thunder clap headache)
What is a Subarachnoid hemorrhage?