What is the nurse's priority concern when actively proning a patient?
Airway
What type of penetrating trauma has the highest probability for extensive internal organ damage?
GSW
Following placement of a Nasogastic Tube, what is the nest priority step?
CXR
The primary purpose of a pulmonary artery catheter is to best assess what?
Fluid Volume Status
A patient with a Hgb of 5.5 receives 2 units of PRBCs. What is the anticipated post-infusion Hgb value?
7.5
What EKG Finding AND Lab Value would indicate the patient is experiencing a STEMI?
ST elevation
+ Troponin (Trop > 0.035)
For a patient in Rhabdomyolysis, fluid replacement should be given to achieve a minimum urine output of what?
100mL/hr
In what 3 ways does HHS differ from DKA?
No acidosis
No ketones
More fluid loss
Higher BGL
For a patient with severe sepsis, what order would you anticipate receiving and initiating first (be as specific as possible):
30mL/kg bolus of NS
When initiating ventilations on an intubated patient during an ACLS code, the nurse would deliver breaths following what guideline?
1 breath every 5-6 seconds
do not stop for compressions
The nurse is caring for a patient who is experiencing sudden, severe chest and back pain. What assessment finding would confirm a diagnosis of Aortic Dissection instead of a Myocardial Infarction?
BP difference between R and L arm
4545 (4550) mL / 8hrs = 568 (or 569) mL/hr
Name one cause for each type of AKI:
1. Pre-Renal
2. Intra-Renal
3. Post-Renal
1. hypotension
2. ATN, contrast
3. stones, CA, foley blocked, outlet obstruction, BPH
The nurse is caring for a patient in the CCU following a STEMI. The patient is hypotensive, diaphoretic, tachypneic, and tachycardic. The patient is intubated with a SpO2 or 90% on 70% FiO2. What continuous IV medication would the nurse anticipate being ordered as priority for this patient?
Dobutamine
A 52-year-old male patient with a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) was prescribed prednisone for an acute exacerbation. He has been on prednisone 40 mg daily for the past 3 months. Recently, the patient decided to abruptly stop taking the medication without tapering the dose. He is brought to the emergency department by his family, presenting with severe fatigue, dizziness, nausea, and hypotension. What does the nurse anticipate this patient is experiencing?
Adrenal Crisis
Name 2 ventilator modes that would be inappropriate for a patient with a GCS of 3:
Pressure Support
SIMV
CPAP
For a patient with acute blood loss, what CVP, PAOP, CO, MAP, and Lactic Acid would the nurse expect? (use normal values and < or >)
CVP < 2
MAP < 65
PAOP < 8
CO < 4
Lactic > 2
Name 3 labs that would be altered in Liver Failure (and if they would be high or low):
High LFT
High Billi
High Ammonia
Low Albumin
Prolonged PTT
What CVP, PAOP, CO, and SVR would the nurse anticipate for a patient with severe heart failure following extensive left ventricular myocardial infarction?
(name normal values and if < or >)
CVP > 6
PAOP > 12
CO < 4
SVR > 1200
What is the nurse's priority treatment option for the patient with the following rhythm who is considered stable?
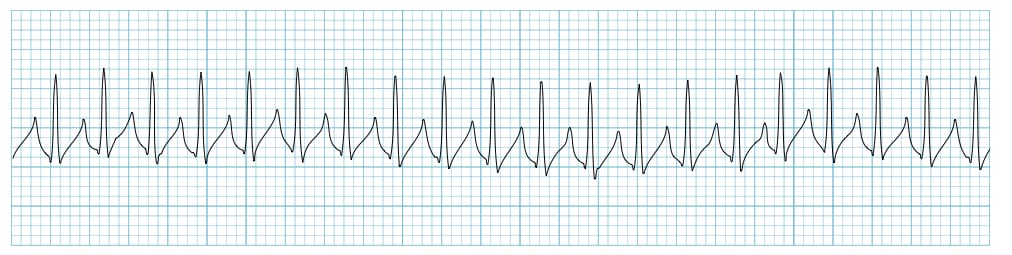
Adenosine 6mg IVP
Name 4 possible causes of ARDS:
Sepsis
Trauma
Pneumonia/Infection
Aspiration
What are the three components of the Triad of Death and how are they related?
Start with: Hemorrhage causes ________ .....
Hemorrhage causes low circulating blood volume which causes low body temperature, low body temperature causes disruption of the coagulation cascade which causes bleeding to continue because you can't clot, when bleeding continues, blood volume is further decreased which causes anaerobic metabolism to ensue because there is low delivery to the tissues, when there is low oxygen delivery, metabolic acidosis (lactic) happens which causes further cardiac dysfunction, which causes decreased cardiac output, which decreased body temperature...
You are caring for a patient who is unable to open their eyes. The patient is unable to follow commands, only mumbles/grunts when speaking, and moves away from you when you pinch their shoulder. What is the priority for this patient based on their GCS?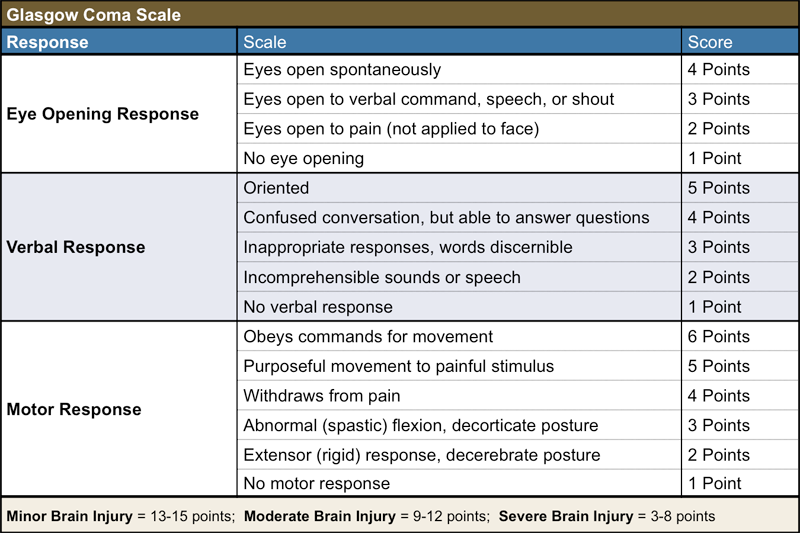
Airway!
After completing a 1L IV NaCL bolus for a patient with severe Diabetes Insipidus, name 1 lab value and 3 nursing assessments that would be used to best assess effectiveness of fluid volume replacement?
Lactic Acid
MAP/HR/BP
UOP
Neuro Status/LOC
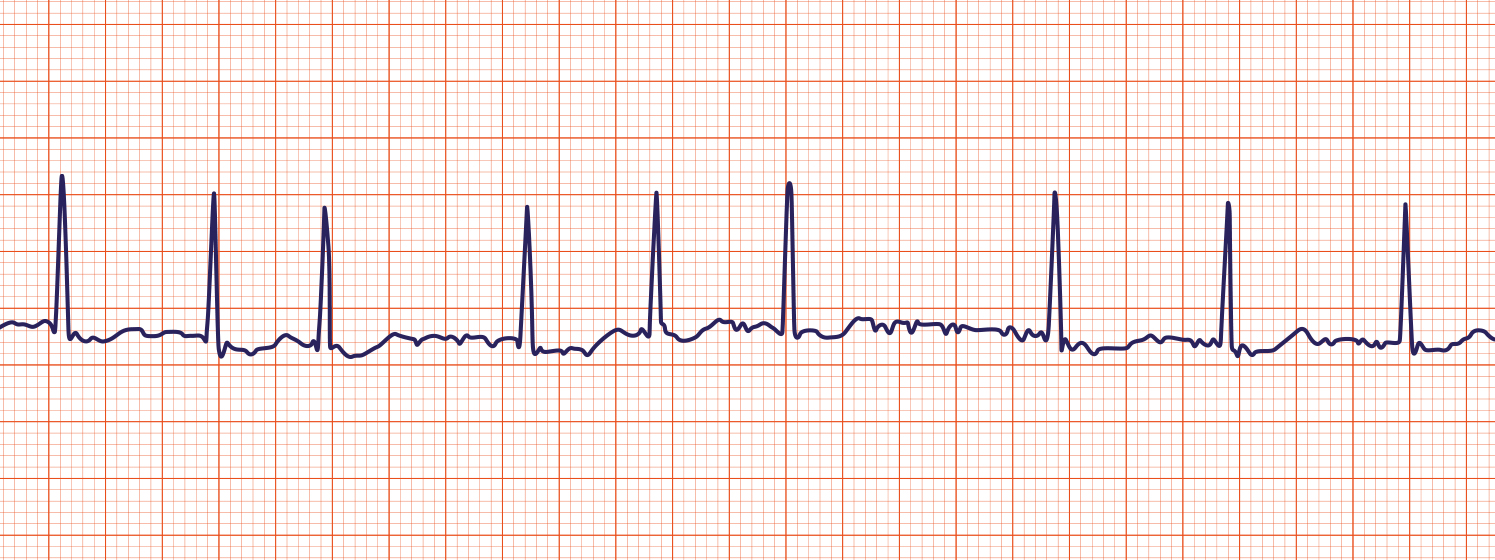
Identify the following rhythms:
1. 
2. 
1. Junctional ryhthm
2. A fib