First, what is the good fat? Second, what is the bad fat?
What is the name of this cell?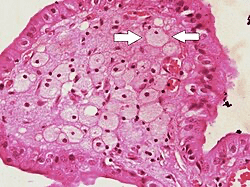
What is a foam cell?
What is narrowing of vessels by fibrous plaque
What are 3 non-modifiable risk factors for developing atherosclerosis?
What are age (increasing), gender (male), family history, and genetics?
List 5 things that make up the necrotic centre of an atherosclerotic plaque.
What are smooth muscle cells, macrophages, foam cells, lymphocytes, cholesterol crystals, calcium, cell debris
List 5 medical complications of atherosclerosis
What are MI, angina (stable & unstable), stroke, intermittent claudication, aortic aneurysm, transient ischaemic attack, ischaemic limb, heart failure secondary to ischaemia, sudden death
What are 5 modifiable risk factors for developing atherosclerosis?
What are dyslipidaemia, smoking, diabetes, hypertension & obesity
What are the steps that lead to the formation of atherosclerosis?
What is
1. ENDOTHELIAL INJURY
2 LDL LEAKS INTO THE INTIMAL LAYER
3 LDL IS OXIDISED AND INDUCES AN IMMUNE RESPONSE
4 MACROPHAGES PHAGOCYTOSE THE LDL PARTICLES AND TURN INTO FOAM CELLS
5 THE DAMAGED ENDOTHELIUM RECRUITS PLATELETS
6 PLATELETS AND ENDOTHELIUM RELEASE GROWTH FACTOR
7 GROWTH FACTOR RECRUITS SMOOTH MUSCLE FROM THE MEDIA TO THE INTIMA
8 SMOOTH MUSCLE CELLS STIMULATE THE PRODUCTION OF ECM
9 A FIBROUS CAP IS FORMED
How does atherosclerosis lead to a AAA?
What is
Degradation of the extracellular matrix: Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) degrade the elastin and collagen fibers making the aortic wall prone to dilation and ballooning under the high-pressure blood flow
Chronic inflammation and oxidative stress: Plaque formation in the inner lining of the vessel (intima) compromises the aorta’s elasticity and structural strength
Loss, death & damage of smooth muscle cells: further reduces the structural stability of the aorta