A statement consisting of two clauses, one of which begins with "if" or "when"
What is a Conditional Statement?
A statement formed by interchanging the hypothesis and the conclusion of the conditional. The converse of a true statement is not necessarily true.
Converse of a Conditional Statement
A chain of statements, with justification of each statement, that ends with a desired conclusion.
Proof
A series of implications leading to a conclusion.
Premise of an arguement
The pursuit of logical consequences from a given system of initial universal truths.
Deductive Reasoning
Define a Line
Two Points
The clause following “if”
Hypothesis
Both the conditional statement and its converse are true.
Definition
A form of reasoning in which two statements are made and a conclusion is drawn from them.
Syllogism
A statement proved to be true by reasoning deductively from already accepted statements.
Theorem
A statement proved to be true by reasoning deductively from already accepted statements.
Theorem
Define a plane
The clause following “then”;
Also, the conditional statement using the first hypothesis and last conclusion of a series of premises.
Conclusion
A statement that contains the phrase “if and only if”.”
Bi-conditional Statement
A proof in which the conclusion is drawn directly from previous conclusions, starting with the hypothesis of the first premise and ending with the conclusion of the last premise.
Direct proof
A proof when an assumption is made at the beginning that leads to a contradiction. The contradiction indicates that the assumption is false and desired conclusion is true.
Indirect Proof
A statement that is assumed to be true without proof.
Postulate
The square of the hypotenuse of a right triangle is equal to the squares of the other two sides.
The Pythagorean Theorem
A diagram consisting of two circles to represent a conditional statement with the inside circle representing the hypothesis and the outside circle representing the conclusion.
Euler Diagram
"iff"
If and only if
Reasoning in which a conclusion is reached by stating a general principle and then applying that principle to a specific case.
Deductive Reasoning
Assume the opposite of what you are are trying to prove and start listing every consequence that you can think of. Eventually and error will show up leading to a contradiction and you will be done.
Indirect Proof
a2+b2=c2
Pythagorean Theorem
The sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°
The Triangle Angle Sum Theorem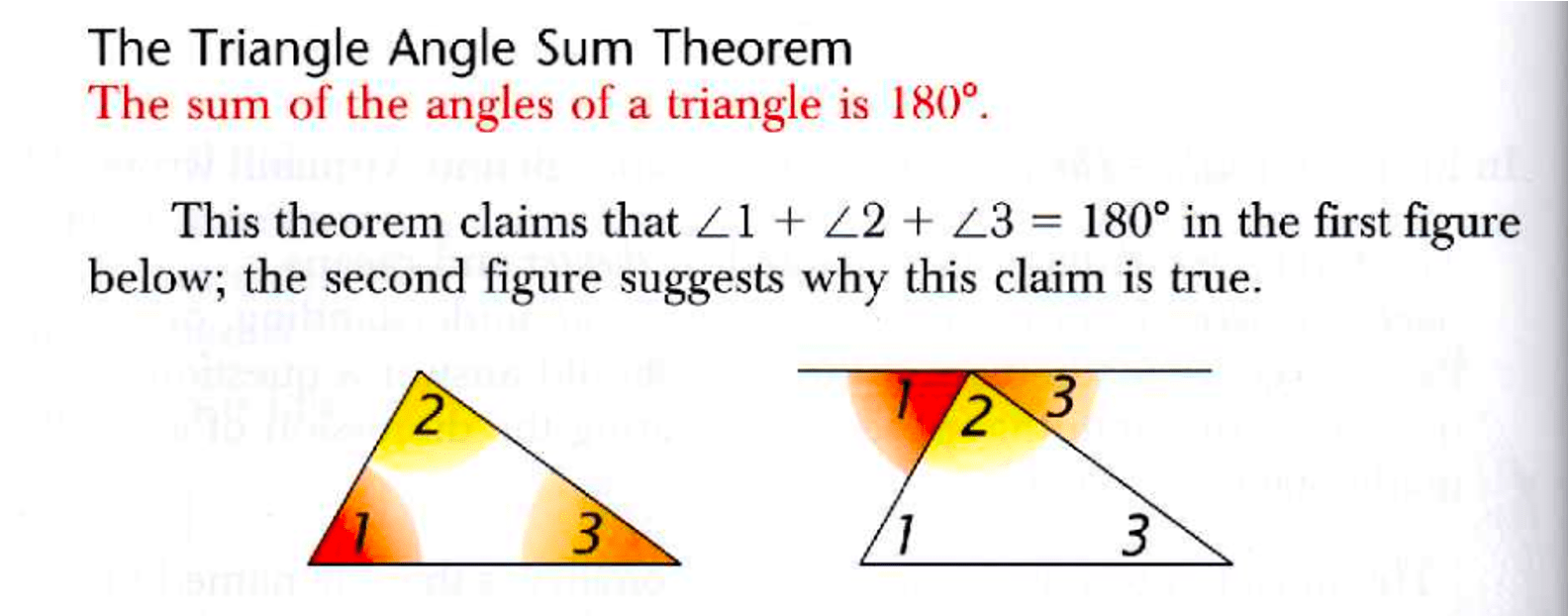
a rarr b
Symbol for conditional statement
a harr b
a If and only if b
a rarr b, brarrc,:. ararrc
Syllogism
180°
The Sum of the Interior Angles of a Triangle
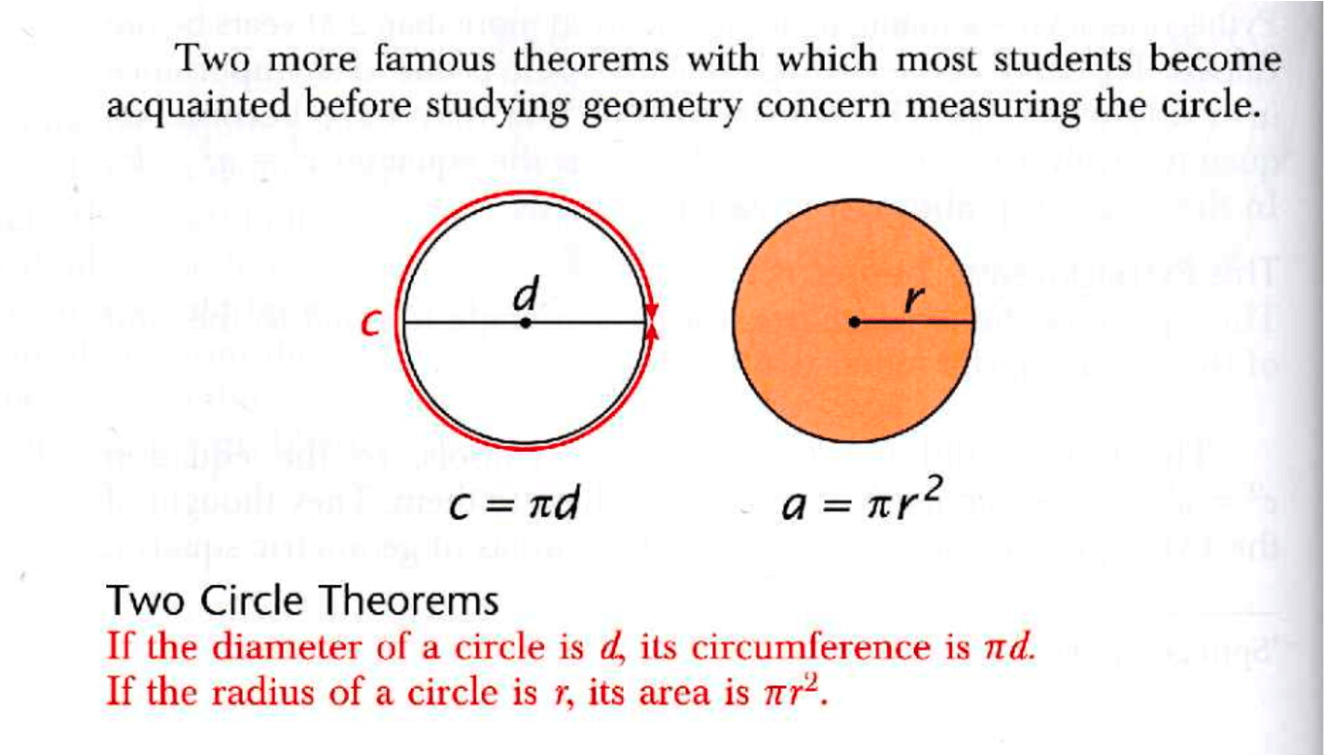
c=2pir
Formula of the Circumference of a circle
c=pird
a=pi r^2