Fill in the blank:
Death rate/Mortality Rate is the number of people who ______ per _________
Die, year
How many types of population pyramid shapes are there?
3
How many stages are in the DTM
5
Fill in the blank:
Immigration - Emigration = ?
Net Migration Rate
Name one of the three countries with the highest population.
India, China, United States
Define Literacy and Illiteracy rate
Literacy Rate: The number of people in the population who can read and write
Illiteracy Rate: The number of people in the population who cannot read and write
What is the term referring to the group of people born within a specific time period. Normally they are presented in 5 year intervals
Age cohort
What are the three line trends shown in the DTM?
BR, DR, Total pop. growth
In percentage (%), what is the total population of those considered in the children age cohort?
0-4: 5%
5-9: 7 %
10-14: 2%
15-19: 4%
20-24: 3%
14%
Give one pull and one push factor to migration
Multiple answers
Define food security
Having reliable access to food for nutrition and dietary needs
Name an infrastructures, a good, and a service that will be needed for a country with a high elderly population
Long-term care homes, canes, adjustable bed, medication, nursing homes, nurses, adult day programs, finance and household support…
Explains what happens in stage 5 of the DTM. Reference the BR, DR, and total population
The BR is lower than the DR and there is a population decline
Calculate the Population Growth Rate in %
NIR: 4.2/1000 NMR: 3.7/1000
PGR = 4.2/1000 + 3.7/1000
PGR = (7.9/1000) x 100
PGR = 0.79%
If many people were moving out of Toronto, what would be a negative consequence?
Multiple answers
Job vacancies, declining economy because of less demand for goods and services, deteriorating infrastructure, lack of necessary services such as healthcare due to lack of workers, etc.
What is the difference between migration, immigration, emigration, and interprovincial migration?
Migration refers to the general movement of people between areas.
Emigration refers to people moving out of an area
Immigration refers to people moving into an area
Interprovincial is another form of internal migration where people move between provinces and territories.
Name the three types of population pyramids and provide one characteristics about the population for each
Expansionary – a large young population, high DR, high BR, higher dependency load…
Restrictive – very low BR, low DR, long life expectancy, higher dependency load…
Stationary – age groups in all categories, long life expectancy…
What does the BR and DR look like in stage 1? Provide a country that might be in stage one right now.
BR and DR are both high. People are having a lot of children but the life expectancy is low as the countries are not well-developed to support population growth (lots of diseases, not enough food, not sanitary, etc.)
There are no countries in stage 1
Calculate the dependency load of this country:
0-10: 500,000
11- 14: 1,200,000
15-25: 2,400,000
25-55: 1,400,000
55-64: 450,000
65-80: 26,000
81+: 15,000
The Dependency Load is 1,741,000 people
In which part of Canada do Canadians settle? Provide one reason why they settle in this area.
Southern part of Canada/Near the U.S-Canadian border
Reason: good land for agriculture, water source, trade, pre-established community and infrastructure
Define demography and identify three concepts within demography that we have learned in class. Provide a definition for each concept.
Demography is the study of human population
Various answers
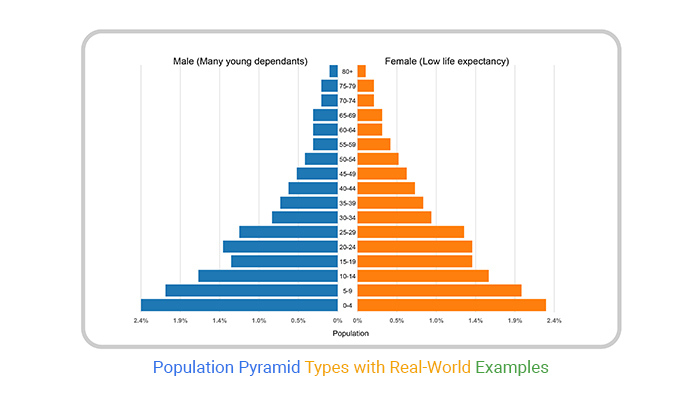
Analyze this pop. pyramid. What type is it? What is the life expectancy? What is the birth rate?
Identify one SPECIFIC thing (specific infrastructure, sector, resource etc.) that the country's government should be worried about and explain why they should be worried.
Expansive. Low life expectancy. Very high birth rate.
Job opportunities as the young population grows. Creation of more houses for the growing population. Education resources, such as more teachers or bigger classrooms because there will be more younger people. Food security because people will need enough food to grow up healthy.
What happens between stage 2 and 3 of the DTM? Explain
In stage two, DR declines because more access to food and improvements in public health.
In stage three, the BR declines because women are more educated (higher literacy rate), lower infant mortality, increasing urbanization, improvements in contraceptives, more female employment
Country F:
BR = 14.2/1000
DR = 10.4/1000
Calculate the Doubling Time for this country only using the natural increase rate
NIR = 14.2/1000 -10.4/1000
NIR = (3.8/1000) x 100
NIR = 0.38
DT = 70/0.38
DT = 184.2 years
What is the current world population (rounded to nearest billion)?
Give one reason why the world population has been growing exponentially.
Is the growth experienced equally in all parts of the world? Explain
8 billion
Reason: Better access to food and water. Better infrastructure such as healthcare. More technological advances in medicine. Industrialization means that there is more food production.
No growth is not experienced equally. More developed countries tend to have lower birth rates.