What is the difference between heterotrophs and autotrophs?
Autotrophs can make their own energy, while heterotrophs must consume other living things for energy.
two or more atoms chemically combined are called________.
compound
what is adhesion?
water sticks to something other than another water molecule
what is the difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
prokaryotes= no nucleus or membrane bound organelles
eukaryotes= nucleus with membrane bound organelles
what molecules make up the cell membrane?
phospholipid
Where is the pigment chlorophyll stored in the leaf?
thylakoid
How is Botox taken into a neuron?
by receptor mediated endocytosis
correctly describe a controlled experiment
An experiment where only one variable is changed at a time
Which organic molecule does not form a POLYMER?
lipids
what is cohesion
water sticks to water
Name 4 things all cells have? (whether prokaryote or eukaryote)
cell membrane
cytoplasm
ribosome
DNA
Cholestrol is in the cell membrane bilayer. Is cholestrol polar or nonpolar.
nonpolar
What is the name of the enzyme that puts the carbon together?
rubisco
When someone drinks a lot of pure water in a very short period of time this condition may occur.
Hyponatremia
What is the difference between a dependent and independent variable in an experiment?
Independent = variable I changed aka the manipulated variable
Dependent= aka the responding variable -what is being measured as a result of what you manipulated
What type of organic molecule is this:
lipid (triglyceride)
why is a water molecule polar
uneven sharing of electrons
what is the function of the golgi apparatus ?
modify and package proteins for shipping out of the cell
What is the difference between passive and active transport?
passive= requires no energy molecules move from H-> L
active= requires energy molecules move from L->H
In the Leaf Chad lab, what molecule produced by photosynthesis caused the chads to rise in the presence of light?
Oxygen
If someone drinks milk and their blood glucose levels do not rise after 30 min are they lactase persistent or lactose intolerant? Explain your answer.
lactose intollerant- because the enzyme lactase is turned off and they cannot breakdown Lactose into Glucose and Galactose! Thereby increasing their blood glucose level.
what is a zygote?
fertilized egg
What are the atoms for:
Carbs
lipids
proteins
Nucleic acids?
Carbs= C,H,O
Lipids= C,H,O
Proteins= C,H,O,N
Nucleic Acid= C,H,O,N,P
what is the bond that allows one water molecule to bond with another water molecule?
hydrogen bond
name the cell support structures (not the cell wall)
cytoskeleton- microtubules and micrfilament
what is facilitated diffusion?
Facilitated diffusion is passive transport of larger molecules that require help getting through the membrane. The help is with transport proteins like a channel protein
What are the 2 reactants in photosynthesis?
CO2 + H2O
Ach is a ligand that enables a muscle cell to contract. Explain how this works.
Ach is released into the snaptic gap and goes into the ligand site on the gated channel protein causing it to open and allow ions to flood the muscle cell which causes a contraction.
What is the difference between the constants and the control in an experiment.
constants= what the experimenter keeps the same in the different setups
control= the variable that is in most natural state. what you are comparing the IV to.
What are the monomers for:
Carbs
Lipids
Proteins
Nucleic Acids
Carb= monosaccharide
lipid= triglyceride
protein= amino acid
Nucleic Acid= nucleotide
Label the parts of the following diagram illustrating the catalytic cycle of an enzyme. (skip E)

a=enzyme
b=active site
c= substrate
d= enzyme substrate complex
f= products
Name 2 types of cells that have a cell wall
prokaryote and plant cell
Expelling large molecules from the cell occurs through this process
EXOCYTOSIS
Where did the leaf Chad get the CO2 from in our experiment?
baking soda
Why can cows digest cellulose but we can't?
cows have microorganisms that break down (HYDROLYZE) the bonds in cellulose and they can use the glucose for energy
How do you write a CER?
C= answer the question asked
E= data (quantitative and qualitative) with units
R= C+E+ scientific concept involved.
Which of the 4 organic molecules would you say polysaccharides are?
carbohydrates
what is anabolism and catabolism?
anabolism= put molecules together
catabolism= take molecules apart
correctly matchthe product to the location of the cell during the milk secretion process
milk protein?
milk sugar?
milk Fat?
protein= ribosome
fat= Smooth ER
sugar = gogi apparatus
define dynamic equilibrium.
dynamic equilibrium is when there is an equal percentage of solutes and solvents on both sides of the membrane
what are the chemical equations for cell respiration and photosynthesis?
6H20+ 6CO2 + sunlight energy-> C6H12O6+ 6O2
C6H12O6+ 6O2->6H20+ 6CO2+36 ATP
What is the difference between these two enzyme regulators: Allosteric inhibitors and Allosteric activators/enhancers ?
allosteric inhibitors have a molecule that binds with the allosteric site shutting down the availability of the active site.
allosteric activators have a molecule that binds with the allosteric site allowing the availability of the active site.
On a graph where does the IV and DV go?
IV= x axis
DV= y axis
describe dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis
dehydration synthesis= put two molecules together by taking out water
hydrolysis= put in water to separate molecules
name these organelles: A-N (skip I and L)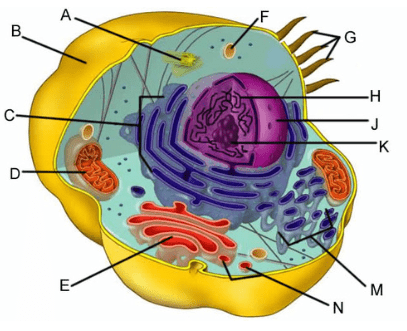
A-centriole
B-cell membrane
C-Rough ER
D- Mitochondria
E- Golgi
F- Lysosome
G-Cilia
H- DNA- chromatin
I-skip
J-nuclear membrane
K-Nucleus
L-skip
M-smooth ER
N- vescile
What is the diffusion of water called?
osmosis
How does Lactic Acid form?
When there is a lack of oxygen- the cell undergoes glycolysis creating pyruvic acid which then turns into Lactic Acid.
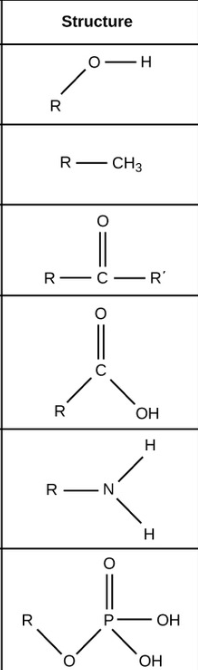
hydroxyl
methyl
ketone (carbonyl)
carboxyl
amine
phosphate