Explain the carbon sources that form coal, oil, and natural gas.
Coal and oil are both derived from the undecomposed and compressed remains of ancient organisms. Coal is formed on land, where the remains can be dried into a solid, whereas oil is formed underwater, where it is pressurized but remains liquid. Natural gas may form over oil deposits as a byproduct of the same process.
Which form of renewable energy is most common in the United States? How does it compare in cost to coal?
Hydropower is the most common in the US -- it is similar in cost to coal, almost 1:1.
Look at the graph below:
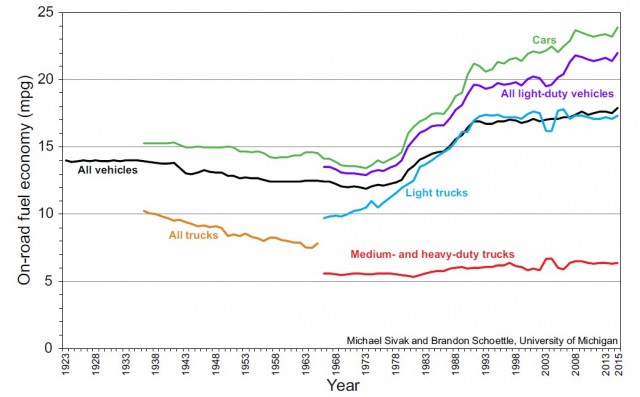
In the grand context of this data, summarize fuel-efficiency in the US for the last 30 years.
In the last 30 years, it has remained fairly stable over time, with small increases in MPG over the three decades.
Give 2 environmental impacts of mountaintop removal.
* Decreased biodiversity
* Increased soil erosion
* Contamination of waterways with heavy metals
* Decreased groundwater recharge
Give 2 examples of sustainable forestry practices
Selective cutting of mature trees
Using controlled burns to maintain ecosystem health
Planting native tree species to restore habitats
Identify and describe one law or treaty that helps regulate the international trade of endangered species.
The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species (CITES) is an international agreement that regulates the trade of endangered and threatened species to prevent overexploitation. It classifies species into different protection levels based on their conservation status and restricts or bans trade accordingly.
If involving the United States, the Endangered Species Act legislates similarly.
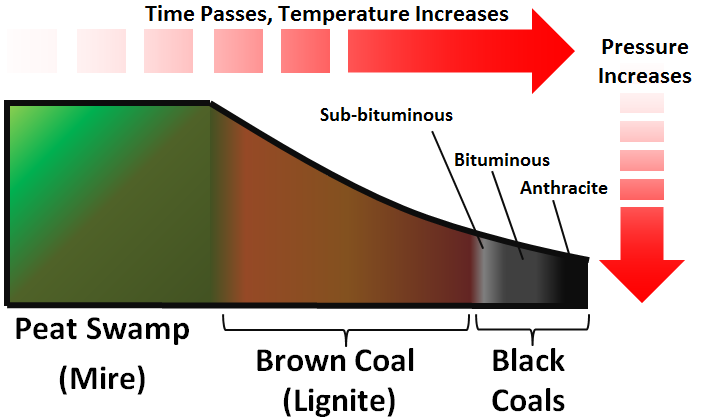
Name the 4 stages of coal formation. Which is combusted for energy production?

Why can't all forms of renewable power be used in all parts of the world? Give 2 examples of renewables and where they make the most sense in the United States.
Based on the natural climate, hydro, wind, solar, and geothermal power sources will vary in intensity and therefore efficiency.
Hydro- areas of significant elevation and river courses; largely west and east coast.
Wind - areas with frequent strong winds; midwest
Solar/photovoltaic - areas low in cloud cover; southwest
Geothermal - areas high in volcanic activity; western United States
The world's leading renewable energy source and how does it work?
What is hydropower. Potential energy (water behind the dam) is converted to kinetic energy (moving water), water then flows through a turbine which is connected to a generator.
DAILY DOUBLE: Name 3 other forms of energy production (renewable or nonrenewable) that share a similar process/pathway.
Ores are placed in a furnace and heated until the metal melts into a liquid and is collected. This process is called smelting.
Give 2 ecosystem services provided by forests
Decreased risk of floods
Nutrient cycling
Habitats for other organisms / higher biodiversity
Increased carbon sequestration
Decreased soil erosion
Wind/storm damage protection
Increased precipitation
Climate regulation (via shade and evapotranspiration)
Increased O2
Explain how the Endangered Species Act (ESA) provides protections for species in the United States.
The Endangered Species Act (ESA) protects species listed as endangered or threatened by prohibiting their capture, killing, or trade and by designating critical habitats for conservation efforts. It also requires recovery plans for species at risk.
What is the process of extracting natural gas called?
Fracking
Daily Double: describe how it is done and 2 of its negative byproducts.
What does it mean to be "carbon neutral"?
The amount of carbon that is released is equal to the amount of carbon that was initially consumed. An example of this is with biofuels, where plants are used to create hydrocarbons, rather than relying on fossil fuel hydrocarbons. Since plants photosynthesize and take in CO2 from the atmosphere, the source of carbon is already in the air, rather than being converted from the source underground.
Give three examples of programs that are designed to improve energy efficiency in municipal areas across the board.
1. Energy Star Appliances - trade in older units that use more energy
2. Innovation of common household items, like lightbulbs
3. Innovation of vehicle fuel efficiency (MPG) to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease per capita fuel cost.
Related to efficiency and having more to do with promotion of renewables:
1. Distributional surcharges
2. Renewable portfolio at state or federal level
3. Green pricing
Aside from mountaintop removal, which mining method is the most destructive to terrestrial ecosystems?
Open-pit mining (subsurface is the least destructive)
What is agroforestry?
A sustainable growth strategy that integrates trees and crops for both environmental and economic benefits.
Describe one challenge in enforcing laws aimed at protecting endangered species.
illegal poaching, black-market trade -- high economic incentives drive illegal trafficking despite regulations
limited funding and resources for enforcement agencies make monitoring difficult
Give 2 advantages and 2 disadvantages of nuclear power
Advantages
- emits only steam
- generates significantly more power than coal per kg
- less use of fuel overall (transport, building, running, etc.)
Disadvantages
- accidents have larger consequences
- if there is an accident, effects are much more long lasting
- requires highly educated workforce
- more expensive to start and maintain
- spent fuel rods are radioactive and must be disposed of far from municipal areas without contaminating soil or water
Give an example of an active solar heating system and a passive solar heating system

The average laptop draws 60 W while plugged in. You spend 4 hours working on an essay for school. If the current cost per kWh is $0.15, how much did the energy cost?
= $0.036
Which law would most likely regulate the environmental cleanup after coal mining in the United States?
CERCLA/superfund
Resource Conservation and Recovery Act
Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act
How do buffer zones help promote sustainable forestry?
The protect waterways by reducing erosion and runoff from logging operations.
Explain how the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) differs from the Clean Water Act in terms of its focus.
The Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) differs from the CWA in that it focuses on the quality and safety of drinking water. It establishes standards for contaminants in public water systems to ensure safe drinking water for human consumption.
The Clean Water Act (CWA) regulates water pollution by setting water quality standards and controlling the discharge of pollutants into surface waters (rivers, lakes, and wetlands).
Explain what the present-day countries with the greatest coal deposits had in common during the Carboniferous Era?
North America, Northern Europe, and Asia line up with the largest carboniferous swamps, where large quantities of biotic material was buried.
3 advantages of hydrokinetic power
-close to 1:1 cost to coal
-renewable
-no emissions
-recreation
-tourism
Daily Double!
3 disadvantages of hydrokinetic
-disruption of ecosystems on both sides of dam
-disruption of migration
-flooding upstream
-loss of nutrients downstream
-loss of homes in flooded area and/or near floodplain
Noticing the sink full of dishes, you place them in the dishwasher and let it run for an hour and a half (including the drying cycle). The dishwasher uses 2000 watts per hour. How many kWh have been used?
1.5 hr x (2000 W / hr) x (1 kW / 1000) = 3 kWh
What is a major consequence of acid mine drainage? How can it be remediated?
Nearby waterways, groundwater and soils will experience a decrease in pH (become more acidic) and become contaminated with heavy metals
Remediation mostly focuses on neutralizing the acid content of the mine tailings by applying alkaline reagents such as limestone, planting sulfur-consuming plants (phytoremediation), or sealing the mine using impermeable covers to prevent rainwater from seeping in.
Explain one way deforestation can contribute to climate change
Deforestation contributes to climate change primarily by reducing carbon sequestration. Trees absorb carbon dioxide (CO₂) from the atmosphere during photosynthesis, helping to regulate global temperatures. When forests are cleared or burned, the stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere as CO₂, increasing greenhouse gas concentrations and contributing to global warming.
Describe the main goal of the Kyoto Protocol and explain one reason why it has been criticized
The main goal of the Kyoto Protocol was to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from industrialized nations to combat climate change. It set legally binding targets for developed countries to lower their emissions of CO₂ and other greenhouse gases.
One major criticism of the Kyoto Protocol is that it did not require developing nations, including large emitters like China and India, to reduce their emissions at the same level as developed countries. This created concerns about economic fairness and effectiveness, as some of the world’s largest greenhouse gas emitters were not held to the same reduction targets.
Additionally, some countries, including the United States, withdrew or never ratified the treaty, limiting its global impact.