Industries where animals are raised in small confined spaces and treated for fast growth and high output.
What are Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations (CAFOs)?
The three most important human staple crops.
What are corn, wheat, and rice?
Areas deficient of accessible and nutritious foods.
What are food deserts?
DAILY DOUBLE: Explain the difference between K-selected and R-selected species. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each? Give an example of each.
K-selected species tend to live longer lives, giving birth to fewer offspring, caring for them for longer periods of time, and reaching sexual maturity relatively later.
Advantages: longer parental care increases safety and likelihood of offspring to reach adulthood. K-selected organisms tend to be larger and live longer.
Disadvantages: tend to be near carrying capacity, so over competition is a risk.
Examples can include whales, elephants, bears, and humans.
R-selected species live shorter lives and give birth to large sets of offspring. Parenting is often limited or completely absent after offspring have emerged. Species reaches sexual maturity earlier. Examples include mice, rabbits, insects, and invertebrates.
Advantages: Opportunistic and able to reproduce quickly in order for genes to withstand disturbances or unstable habitats.
Disadvantages: Shorter life span, generally smaller body size
Name the 4 stages of demographic transition, what their characteristic age-structure pyramids look like, and what changes cause the shapes to shift.
Preindustrial, Transitioning, Industrial, Post-industrial 
Give 2 pros and 2 cons of aquaculture
Pro:
Reduces pressure on wild populations
Reduces bycatch
Lowers cost of product
Provides more accurate estimates for MSY
Reduces loss due to unexpected disasters
Cons:
Increases cultural eutrophication
More likely to spread disease due to lack of genetic diversity and close quarters
Less humane
Increased use of corn, chum, and unnatural feed (such as animal byproduct from livestock)
Need for more artificial coloring to meet market demands
The type of fertilizer that Ca(NO3)2 would be classified as.
What is inorganic fertilizer?
The condition known as "the sickness that comes after the younger child is born"-- what is the diagnostic symptom and cause?
What is kwashiorkor -- the gut becomes distended due to excess fluid retained by a protein deficiency.
Explain how carrying capacity works by using the terms "overshoot" and "dieback". Give an example of a documented crash (case study) in carrying capacity and name 3 factors that can change the carrying capacity over time
Carrying capacity is the maximum population of a givens species that a particular habitat can sustain indefinitely. The growth rate of a population may "overshoot" and exceed capacity if resources are plentiful and the population is not controlled by predation or diseases. After exceeding capacity, there is a decrease or a "dieback" as resources are depleted. Over time, the population typically stabilizes at or near the carrying capacity.
Name 2 of the 3 trends observed in urban areas around the world.
1. More and more people around the world are living in urban areas
2. The numbers and sizes of urban areas are increasing
3. Poverty is becoming increasingly urbanized, mostly in LDCs.
In the United States, it is illegal to use _______________ when raising chickens.
What are growth hormones?
Produce that is certified as "organic" must be grown under what conditions?
Must use only organic fertilizer and first generation pesticide, cannot be GMO.
DAILY DOUBLE!
Give an example each of organic-allowed pesticide and fertilizer. Also give an example each of the non-organic alternatives.
The three types of calorically-significant macronutrients and their importance in the human body.
What are carbohydrates (energy), proteins (structure and formation), and lipids (energy storage, immune system, insulation)
Edge habitats have allowed deer to flourish despite human encroachment on their habitat. Name 3 of the strategies that humans are using to try to reduce or discourage the deer population.
Applying IPM practices such as: Changes in hunting regulations, hiring licensed archers, using predator scents and rotting deer meat to scare them away, using high frequency sounds, trapping and moving, contraceptive darts, sterilization in captivity
What are 3 of the issues that women in preindustrial and transitioning countries face
Poverty, lack of decisions on body, lack of education, lack of healthcare, male-preference, traditional/cultural/societal pressures
The three aspects that are the basis for The Green Revolution?
What are the switch from subsistence agriculture to commercially-profitable monoculture, the introduction of GMOs, and increased use of irrigation techniques, pesticides, and fertilizers?
DAILY DOUBLE!
Synthesize an explanation which links together malnutrition, noncommunicable diseases such as cardiovascular disease or diabetes, and poverty or low-socioeconomic backgrounds. (more details = more points)
In areas of low-socioeconomic populations, access to nutritious food may be price-prohibitive, forcing people to resort to low-quality foods such as fast food or heavily processed foods, which are affordable and provide sufficient calories, but are not nutritious. As a result, malnourished people are more likely to develop preventable health risks such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes.
LIGHTNING ROUND! You will have 3 seconds to respond "True" or "False" to a set of questions. Each question you get correct increases your point value multiplier, but each wrong answer will deduct the same amount.
1.High range of tolerance allows individuals of the same species to have varying physical or chemical tolerances. TRUE
2.Birth, death, immigration, and mutation govern changes in population size. FALSE (emigration, not mutation)
3.Too much or too little of even one necessary life factor can limit or prevent the growth of a population. TRUE
4.The age structure of a population can affect how it rapidly grows or declines in the future. TRUE
5.The three habitat dispersion patterns are clumped, uniform, and vertical. FALSE (random, not vertical).
Lightning Round! Give the key term that matches the definition. You have 3 seconds.
1.The average number of children that couples in a population must bear to replace themselves.
REPLACEMENT-LEVEL FERTILITY RATE
2.The average number of children born to the women in a population during their reproductive years. TOTAL FERTILITY RATE
3. The equation for doubling time.
THE RULE OF 70 or 70/r
4.The movement of people out of a geographic area.
EMIGRATION
5.The policy enacted by China, although intrusive, strict, and expensive to enforce, was an example of this.
FAMILY PLANNING
Explain how e-coli contamination occurs in beef and how it can be prevented or reversed.
Cows fed a corn-based diet may develop acidosis, which acidifies the rumen and blood, promoting the growth of acid-resistant e-coli bacteria. After the cow is slaughtered, the beef product may by ground-up and combined with beef from other sources, which causes widespread contamination. Cows switched to an all-grass diet show 80% reduction in e-coli have just 5 days.
This strategy strives to use pesticides as a last result by doing what instead? (Give 2 examples)
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) may include the use of biological controls such as natural or introduced predators, pathogens, parasites, pheromones, or physical control factors such as crop rotation, prescribed burns, or removal by hand.
Synthesize an explanation which links famine, undernutrition, violence, and one of the demographic transition phases. (More details = more points)
Hungry populations suffering from undernutrition, or a lack of calories needed for basic survival, are more likely to demonstrate civil unrest in response to famine. Pre-industrial and transitional societies, such as those in Africa and the Middle East, are a greater risk for violence due to a lack of food accessibility for their quickly growing populations.
Explain the significance of this graph and provide an example for each type.
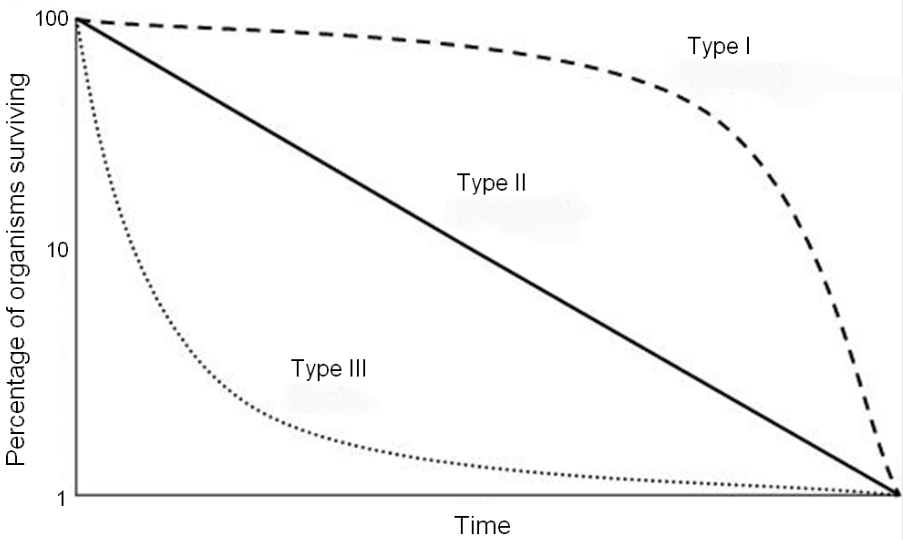
A survivorship curve is a graph showing the number or proportion of individuals surviving to each age for a given species or group.
There are three generalized types of survivorship curves:
Type I or convex curves are characterized by high age-specific survival probability in early and middle life, followed by a rapid decline in survival in later life.
- They are typical of species that produce few offspring but care for them well, including humans and many other large mammals. (K-selected species)
Type II or diagonal curves are an intermediate between Types I and III, where roughly constant mortality rate/survival probability is experienced regardless of age.
- Some birds and some lizards follow this pattern.
Type III or concave curves have the greatest mortality (lowest age-specific survival) early in life, with relatively low rates of death (high probability of survival) for those surviving this bottleneck. This type of curve is characteristic of species that produce a large number of offspring.
- This includes most marine invertebrates. For example, oysters produce millions of eggs, but most larvae die from predation or other causes; those that survive long enough to produce a hard shell live relatively long. (r-selected species)
At the end of the Hundred Years War, the population of the Northern Water Tribe had a crude birth rate of 20 births per 1000 women and a crude death rate of 40 per 1000. Immigration was 2 per 1000 and emigration 12 per 1000. Calculate the growth rate. What is the likely age structure pyramid type for the Water Tribe as time goes on if the rate does not change?
-3%. Inverted triangle.