Another unit for this is Coulombs/Volt
q\vec v\times \vecB
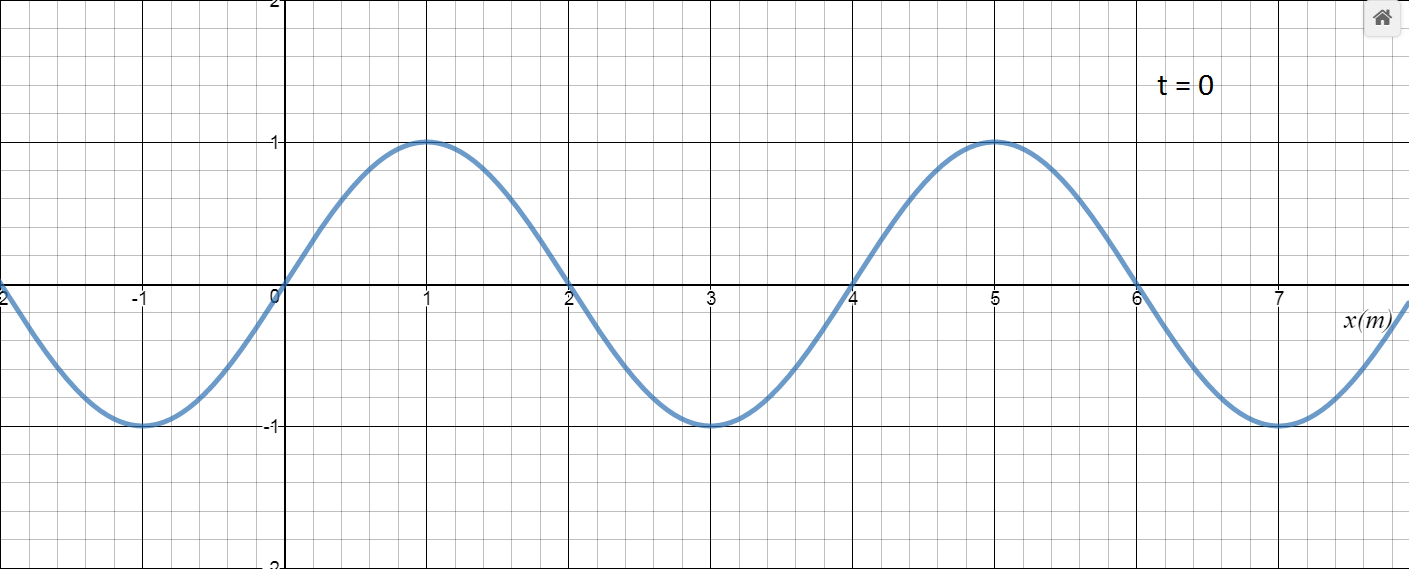
With this wave number k (in multiples of pi), we get this plot for a snapshot of a wave.
{2pi}/4 = pi/2
Another unit for this is Joule/Coulomb
\vec \mu \times \vec B
This is the minimum number of charges to fill the space with electric field.
This is the major difference between a capacitor and a battery.
What is the voltage drops as the capacitor looses charges while the battery's voltage is constant?
I\vec A?
This is the speed of this wave travelling in the +x direction.

This is the property of electric field that when ignored, you will get the wrong net electric field by adding the magnitudes from a set of given charges.
What is a "vector"?
The capacitance for a parallel plate capacitor
What is
C=epsilon_0A/d
\mu_0 I_{enclosed}
\oint \vec B\cdotd\vec l?
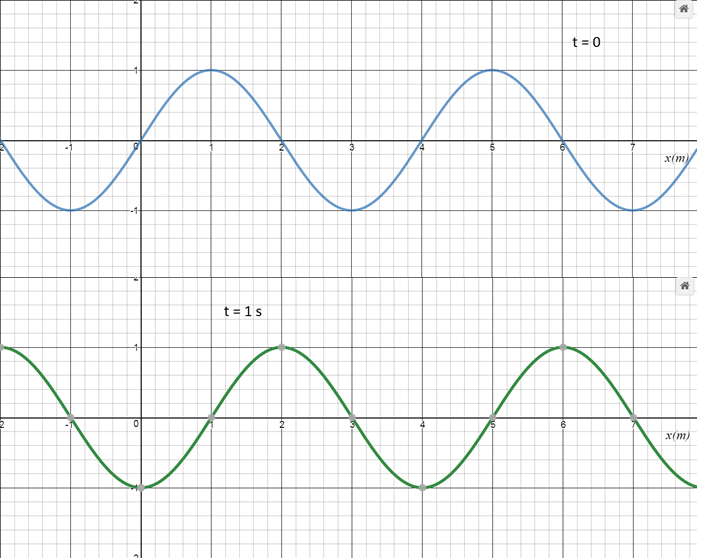
What is the speed of this wave if it were travelling in the -x direction?
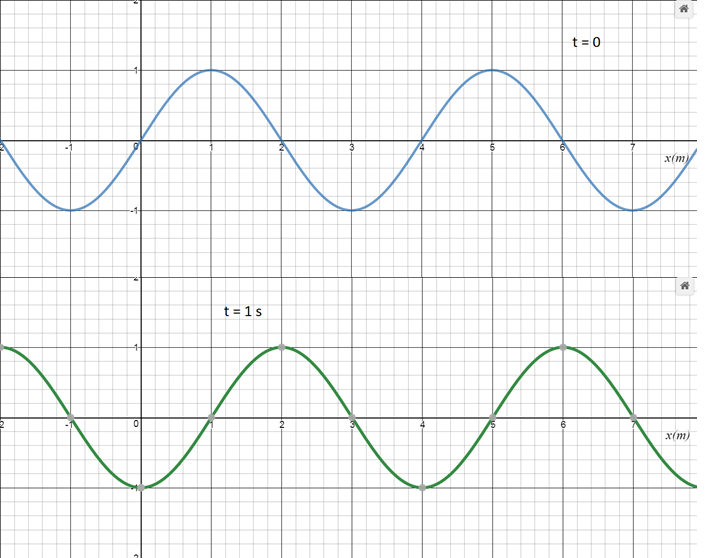
The answer is
-int_a^b \vecE\cdotd\vecr
What is the potential gained going from point a to b in an electric field?
Another unit for this is Ohms*Farad
What is seconds?
What is
\vec B \cdot \vec A
where A is the area of the current loop.
v_f =v_i +at
x_f =x_i +vt+1/2at^2