The splitting of a heavy nucleus into smaller nuclei.
What is nuclear fission?
The time it takes for half of a radioactive substance to decay.
What is a half-life?
Name a type of energy transformation that occurs in a light bulb.
Electrical energy to light energy.
The transfer of thermal energy through direct contact.
What is conduction?
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 degree Celsius.
What is specific heat?
The combining of light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus.
What is nuclear fusion?
True or False: Radioactive decay can be predicted exactly.
False
What type of energy transformation occurs in a car engine?
Chemical energy to mechanical energy.
The transfer of thermal energy through the movement of fluids.
What is convection?
What is water a good coolant?
Because it has a high specific heat capacity.
Describe how the nucleus changes during nuclear fusion.
During nuclear fusion, light nuclei combine to form a heavier nucleus, releasing energy in the process
Radioactive decay is the process by which a substance loses its radioactivity over time, and half-life is the time it takes for half of the substance to decay.
How does radioactive decay relate to half-life?
Describe the energy transformation in photosynthesis.
Light energy to chemical energy.
The transfer of energy through electromagnetic waves.
What is radiation?
Justify the use of copper in cooking vessels.
Copper has a high thermal conductivity, allowing for even heat distribution.
Neutrons and energy.
What particles are typically released during nuclear fission?
Calculate the remaining amount of a substance after two half-lives if you start with 100 grams.
25 grams.
What type of energy is involved in nuclear reactions?
Nuclear energy.
How does molecular motion relate to thermal energy?
Increased molecular motion increases thermal energy.
Analyze a heating curve to explain phase changes. 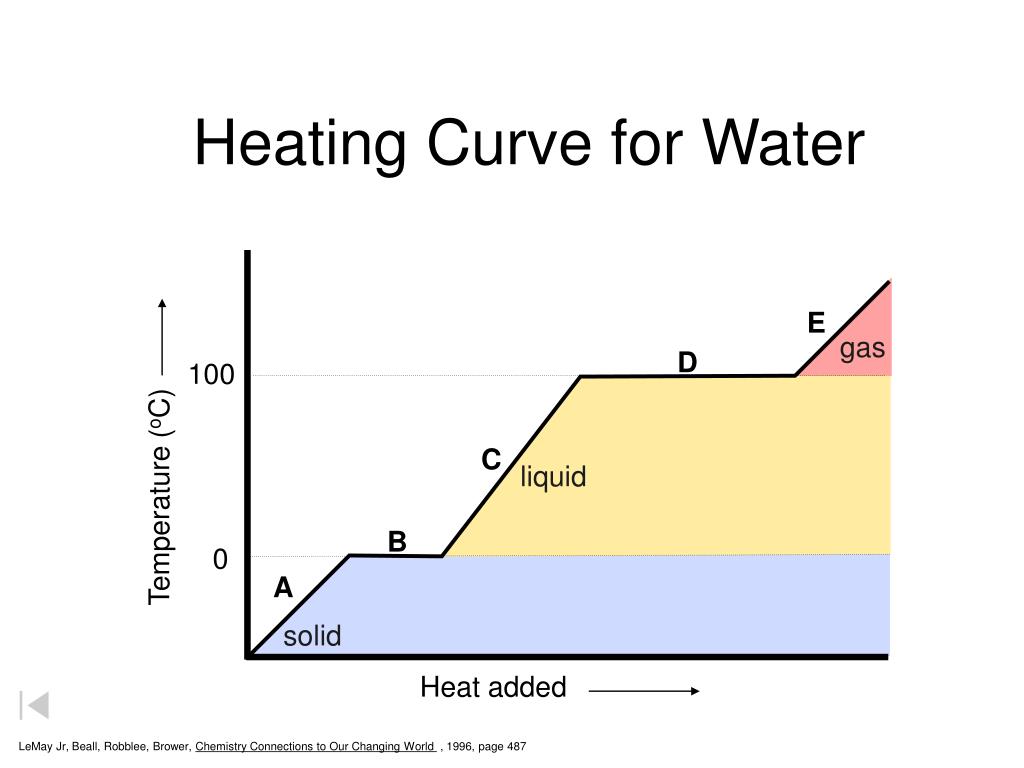
During phase changes, energy is absorbed or released without changing temperature, as seen in the flat portions of the heating curve.
Explain the difference between fission and fusion.
Fission splits a heavy nucleus into smaller nuclei, while fusion combines light nuclei to form a heavier nucleus.
Alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay.
What are the three main types of radioactive decay?
Explain how energy is conserved during transformations.
Energy is neither created nor destroyed; it only changes forms.
Describe how thermal energy is transferred in a pot of boiling water.
Thermal energy is transferred through conduction from the stove to the pot, and through convection within the water.
Explain the selection of materials for insulation based on specific heat data.
Materials with low specific heat are good insulators because they do not absorb much heat, keeping the temperature stable.