What are amino acids?
Amino acids are the building blocks of protein. Proteins are long chains of amino
acids.
Describe the process of polymerization.
Monomers bond together to form polymers during a chemical reaction called polymerization
What is an enzyme?
* use and define the words catalyze and activation energy in your answer :)
Enzymes are proteins that (catalyze) speed up chemical reactions in the body by lowering activation energy?
Involves sharing of electrons between two or more atoms
Covalent bonding
What are the levels of protein folding?
primary, secondary, teritiary, quaternary
How many amino acids are there, or are needed for your body?
Your body needs 20 different kinds of amino acids to function correctly.
These 20 amino acids combine in different ways to make proteins in your body
Give an example of a monomer and polymer.
monomer - polymer
Amino Acid - Protein
Monosaccharide—Carbohydrate
Nucleotide - Nucleic Acids
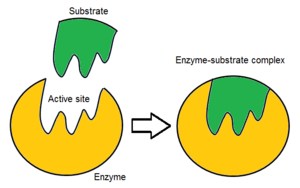
This is the term for the specific region on an enzyme where the substrate binds to initiate a chemical reaction.
Active site
Involves transfering of electrons between two or more atoms
Ionic Bonding
What type of bond holds amino acids together in a protein?
Peptide Bonds
What amino acids (the umbrella name) are classified as essential when you are sick or stressed?
Some nonessential amino acids are classified as conditional. This means they’re only
considered essential when you’re ill or stressed
What is Hydrolysis?
Breaking down large molecules (polymers) to form smaller molecules (monomer) with the addition of water
This process occurs when an enzyme's active site undergoes a slight change in shape to better fit the substrate.
Induced fit
a covalent bond that links amino acids together to form a protein
Peptide bond
What two common shapes are formed in the secondary structure of a protein?
Alpha helix and beta-pleated sheet
How many amino acids can the body produce? What is the umbrella name for these amino acids?
Your body produces 11 amino acids. They are called nonessential amino acids.
What is Dehydration synthesis?
Building large molecules by removing water from smaller molecules (monomers) to form bonds between them
Order the steps of the enzymatic reaction:
- The enzyme binds to a specific molecule, called a substrate, at its active site.
- The enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate complex.
- The enzyme weakens chemical bonds in the substrate, causing them to link together.
- The product is released from the active site, and the enzyme returns to its original state.
- The reaction produces a new molecule, called the product.
- An enzyme binds to a specific molecule, called a substrate, at its active site
- The enzyme and substrate form an enzyme-substrate complex
- The enzyme weakens chemical bonds in the substrate, causing them to link together
- The reaction produces a new molecule, called the product
- The product is released from the active site, and the enzyme returns to its original state
a weak attraction between molecules where a hydrogen atom, which is slightly positive because it's bonded to a very electronegative atom
hydrogen bond
What makes a protein have quaternary structure instead of just tertiary structure?
It consists of two or more polypeptide chains bonded together
Our body needs all the amino acids. But can only produce some.
How many amino acids is the body UNABLE to make? What is an umbrella name for these amino acids, and where does the body get them from?
Your body makes hundreds of amino
acids, but it can’t make nine of the
amino acids you need.
These are called essential amino
acids. You must get them from the food
you eat
What is condensation reaction and how does it relate to dehydration synthesis?
In a condensation reaction, two molecules form a larger molecule and release a small molecule.
"condensation reaction" is a broader term that often includes dehydration reactions when water is the small molecule released; essentially, a dehydration reaction is a type of condensation reaction where water is the molecule lost.
get up and draw ;)
Draw the active site of an enzyme and a substrate.
Label each part of the image and name the product (or complex) that is made when the substrate binds to the active site.
the weakest type of bonds between covalent molecules, such as in gases, liquids, and polymers. These bonds are responsible for holding molecules together loosely
van der waals interaction
Why is the correct folding of a protein essential for its function?
Misfolding can cause diseases.
Structure = function