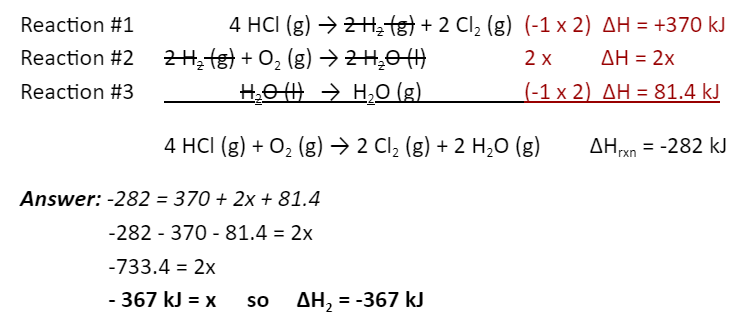This physical property of a material refers to the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 g of that material by 1 oC
What is specific heat capacity?
This would be the part of the graph where a gas is condensing.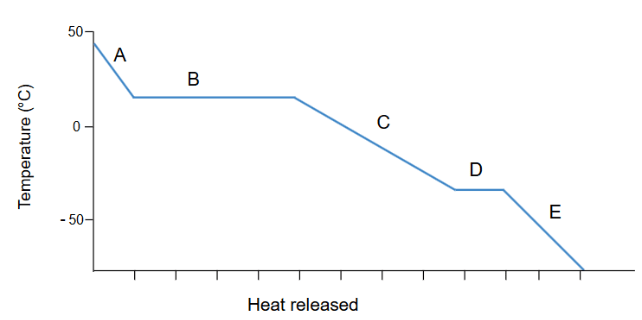
What is section B?
*Bonus 100: Which is a greater value for this substance: enthalpy of fusion or enthalpy of vaporization?
This type of enthalpy change would result in the surroundings getting colder.
What is endothermic.
(if wrong answer given, the steal is for the sign of the energy change of the system in question)
This “law” stating that energy is not created or destroyed, only transferred, is particularly important when performing a calorimetry experiment. (give only one name for the law)
Answer: reasonable response
Bonus 100: What is another name for this law?
This would be the ΔH_rxn for:
NO (g) + ½ O2 (g) → NO2 (g)
Rxn 1: ½ N2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → NO (g) ΔH = 91.3 kJ
Rxn 2: ½ N2 (g) + O2 (g) → NO2 (g) ΔH = 33.2 kJ
What is - 58.1 kJ?
This would be the type of energy change that occurs when a block of ice cools down.
What is kinetic energy?
This would be the number of moles of water that must freeze in order to release 30 kJ of heat.
What is 5.0 moles?
This is the name given to the enthalpy change when a solute dissolves in a solvent.
This would be one assumption that COULD be important when using a simple calorimeter.
Answer: Any reasonable response
Bonus 100 for each additional assumption that applies to calorimetry experiments.
This would be the ΔHrxn for:
4 FeO (s) + O2 (g) → 2 Fe2O3 (s) ?
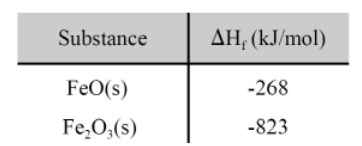
What is -571.6 kJ?
This would be the temperature in degrees kelvin at which water boils.
What is 373.15 k?
These types of forces are overcome when a substance changes state.
What are intermolecular forces?
This would be the molar enthalpy of combustion based on the potential energy diagram provided.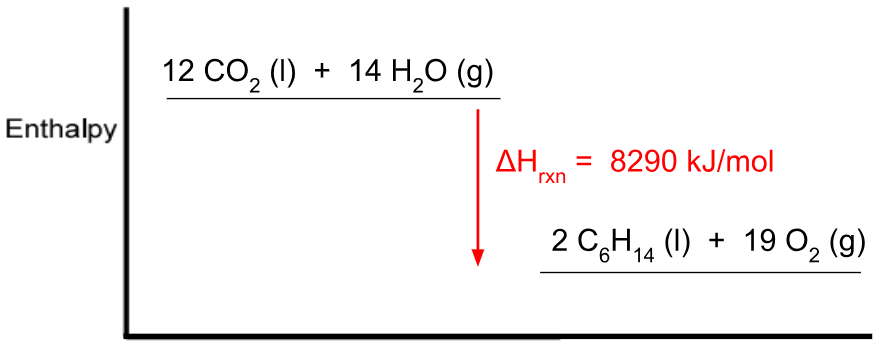
What is -4145 kJ?
A 45.0 g piece of unknown metal is heated to 98.0 °C and then quickly transferred into a coffee-cup calorimeter and the final temperature of the water and metal is 25.8 °C. If the calorimeter absorbs 83.6 J of energy, this would be the specific heat capacity of the unknown metal.
What is 0.489 J/goC?
This would be an approximate ΔHrxn calculated using bond energies for the reaction:
C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) → 3 CO2 (g)
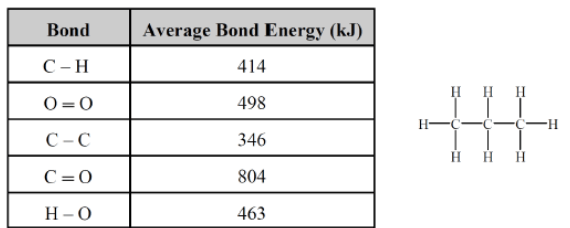
What is -2034 kJ?
This would be the mass (with correct significant figures) of a piece of copper that absorbs 2.25 kJ of heat and goes from -3.5oC to 12.7oC. (cCu = 0.385 J/goC)
What is 3.6 x 102 g?
This would be the total heat involved in taking 10.0 g of naphthalene (C10H8) and cooling it from 100.00oC to 0.00oC.
-3.32 kJ
This would be the mass of water produced if 85.0 kJ of energy is released in the reaction below:
O2 (g) + 2 H2 (g) → 2 H2O (g) + 241.8 kJ
What is 12.7 g?
A student has a calorimeter with 100.0 g of water at 21.0 oC. Before performing the experiment, they calculated a theoretical temperature change of +8.3 oC. This would be the percent error of the experiment if the final temperature of the calorimeter is found to be 24.3oC.
What is 60.2 %?
This would be the energy required to break the C-H bond based on the information below.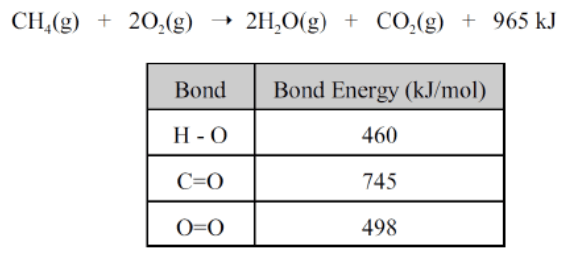
What is 342 kJ/mol?
This block would have the highestheat capacity, C.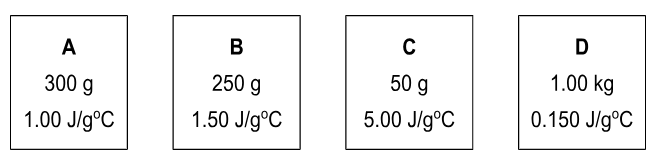
What is block B?
ALL PLAY: You drop a red hot ball of iron at 1500 oC into a block of SOLID dodecanoic acid containing 15.0 g (which is 0.0749 mol). The iron transfers 10.85 kJ of heat to the block of dodecanoic acid, which starts at 20oC. This will be the % of acid that vaporizes as a result of this energy transfer.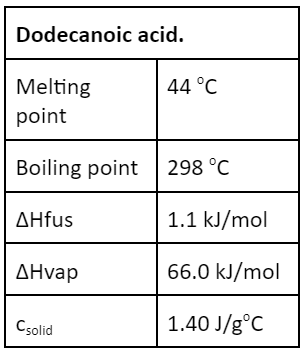
What is 20%?
When 15.0 g of iron reacts with excess oxygen to form Fe2O3(s), the reaction releases 112 kJ of energy. The balanced chemical reaction is shown below.
4 Fe (s) + 3 O2 (g) → 2 Fe2O3 (s)
This would be a thermochemical equation representing the molar enthalpy of iron.
What is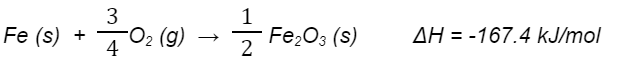
ALL PLAY: This would be the expected temperature change in a calorimeter if the following experiment was performed by dissolving KCl: (closest answer wins, you need to remember the ΔH sol of KCl!)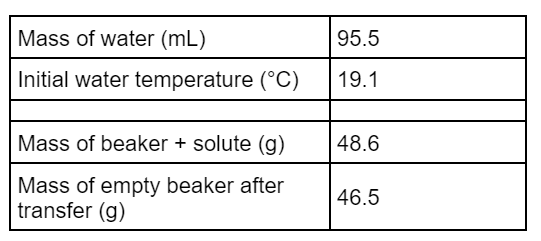
What is -1.2 oC?
ALL PLAY: This would be the ΔH for reaction #2:
Target reaction: 4 HCl (g) +O2 (g) → 2 Cl2 (g) + 2 H2O (g) ΔHrxn = -282 kJ
Reaction #1 H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2 HCl (g) ΔH = -185 kJ
Reaction #2 H2 (g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (l) ΔH = __?____
Reaction #3 H2O (g) → H2O (l) ΔH = ______
What is -367 kJ?