What is this rhythm?
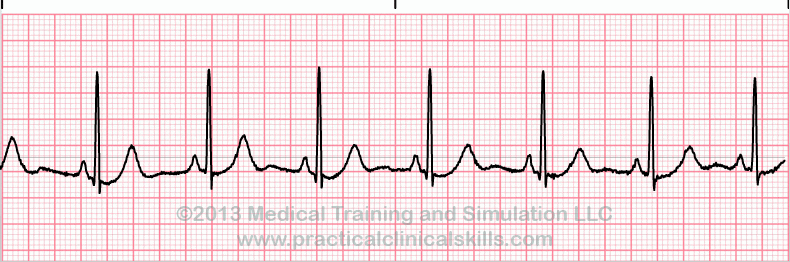
Normal sinus rhythm
What is a "normal" heart rate range?
60-100
Below what number for HGB do we transfuse a patient with blood?
<7
Which procedure takes the longest: X-ray, CT, or MRI?
MRI
What medication do we give to many patients in the hospital to help prevent blood clots?
Heparin
What is this rhythm?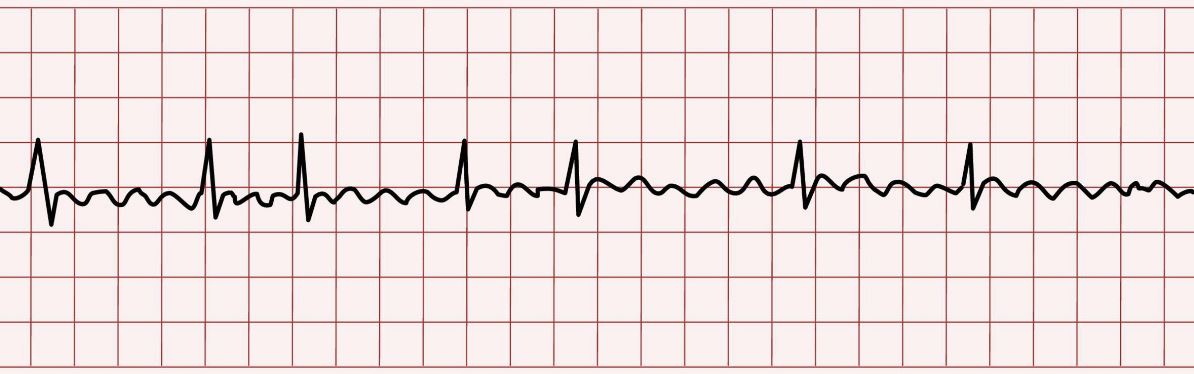
Atrial fibrilation
What does MAP stand for, and what is the MAP goal for patients here in the hospital?
Mean arterial pressure. >65
Why do we never want to push IV K?
Risk for cardiac arrest
What do we always want to be mindful of when entering the MRI suite?
NO magnetic material
Is Insulin Humalog fast-acting, intermediate-acting, or long-acting?
Fast-acting
What is the name of this ectopic beat, and what are three causative factors?
-Premature ventricular complex (PVC)
-Electrolyte abnormalities, nicotine, caffeine, alcohol, heart failure, MI, certain medications (such as antihistamines)
88%
A patient's VBG is as follows:
pH 7.22, CO2 68, O2 44, HCO3 30.
Acidosis or alkalosis? Respiratory or metabolically driven? Compensated or not compensated?
Uncompensated respiratory acidosis
What does a TTE stand for, and what does it tell us?
Transthoracic echocardiogram. Provides ultrasound picture of heart, can assess heart function as well as help diagnose heart failure
What is a PPI and what do we give it for?
-Proton pump inhibitor
-Gastric ulcer prophylaxis, treatment/prevention of GERD
The patient is pulseless with this rhythm. What is it called, and how do we treat?
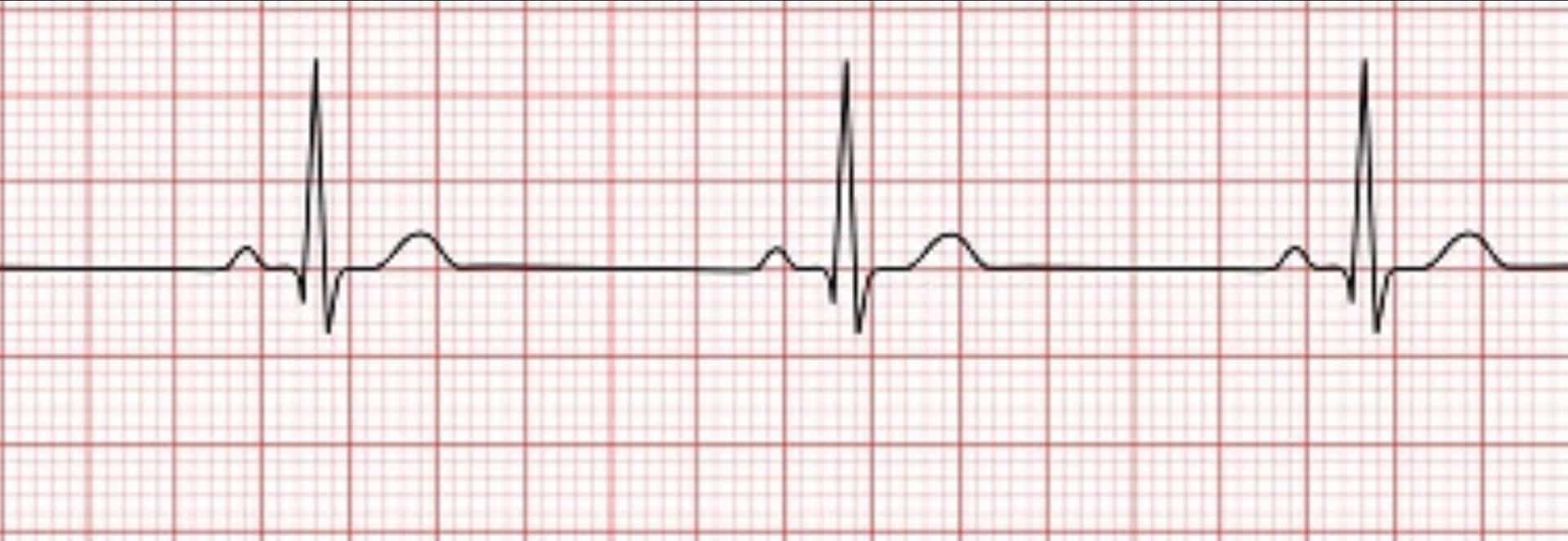
Pulseless electrical activity. NOT a shockable rhythm. CPR and IV Epinephrine are the treatment.
A patient has a FSBG of 52. They are alert and oriented. What is the treatment for the hypoglycemia?
Juice and oral glucose BEFORE IM glucagon or IV Dextrose
What is lactic acid (lactate), and what does an elevated lactate indicate?
-By-product of anaerobic glycolysis (cells converting glucose to energy)
-Indicates poor perfusion/oxygenation. i.e. Low blood pressure --> muscle tissues not receiving enough blood with oxygen --> anaerobic glycolysis--> increased lactate
What are the two invasive procedures to assess for GI-bleeding?
-Colonoscopy and EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy)
What is the suffix for beta-blockers, and what do beta-blockers do?
-"lol" i.e. metoprolol, labetalol, carvedilol
-Decrease HR, decrease BP
What is this segment called? When elevated, what are we worried about?
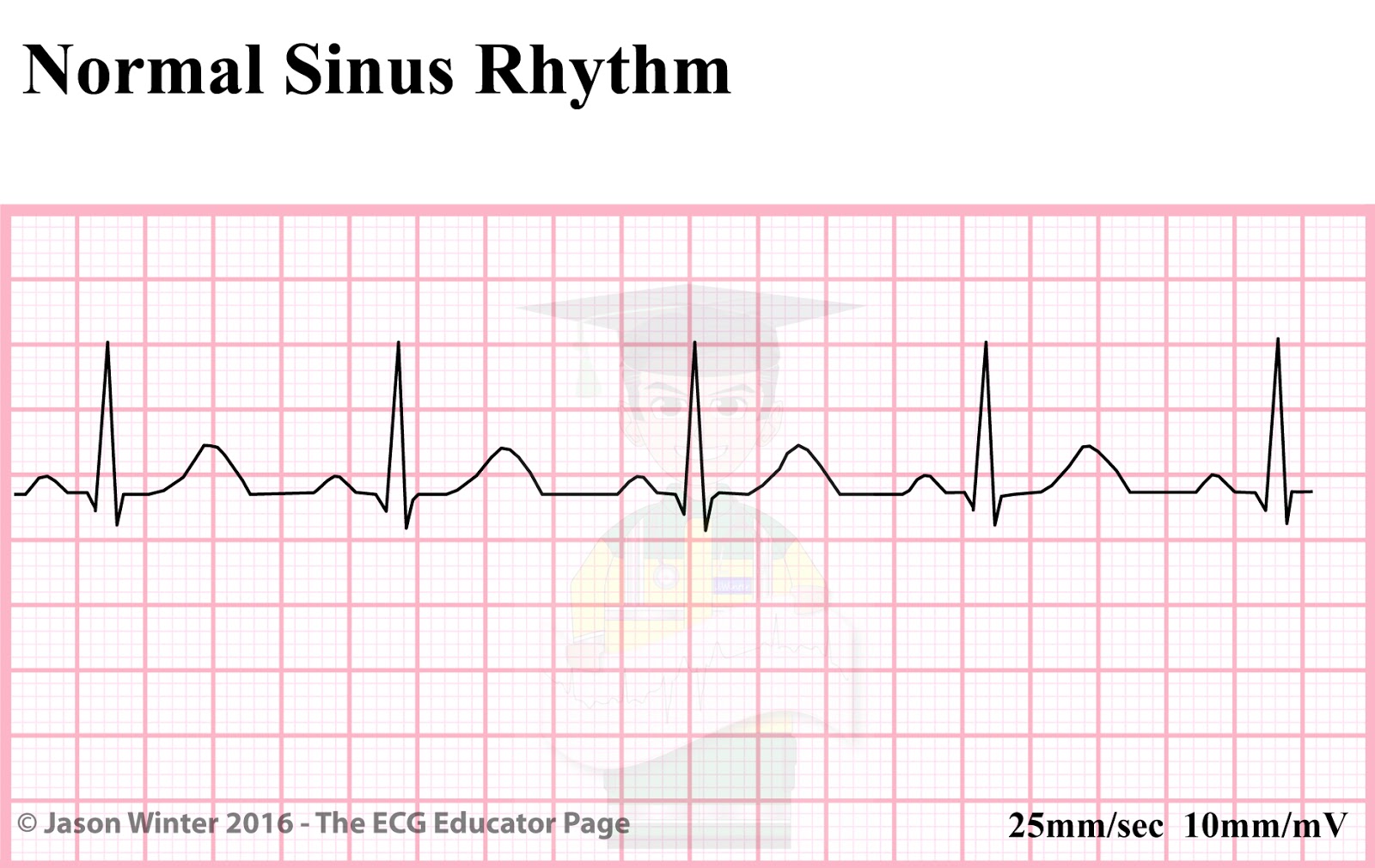
ST segment. ST elevation raises concern for STEMI (st-elevated myocardial infarction)
A patient is tachycardic to 130, hypotensive to 80/40, and febrile to 102.3. What type of shocked are we concerned for?
Septic shock
Elevated troponin levels are indicative of what?
Heart muscle death, likely MI
What does NPO stand for? (hint: Latin)
Nil per os
What is the goal of medication therapy for patients with A-fib?
-Anticoagulation (i.e. Eliquis, heparin)
-Rate control (i.e. beta-blocker)