It is the term that describes how fast or slow a reaction occurs over time.
What is a reaction rate
When the reactant -------- increases, then the reaction shifts to the right.
What is the concentration.
In a rate expression, k is referred to as this.
What is the rate constant
The order of a reaction show this.
What is the relationship between the participating species and the rate of a reaction.
These graphs are two ways to plot this type of reaction: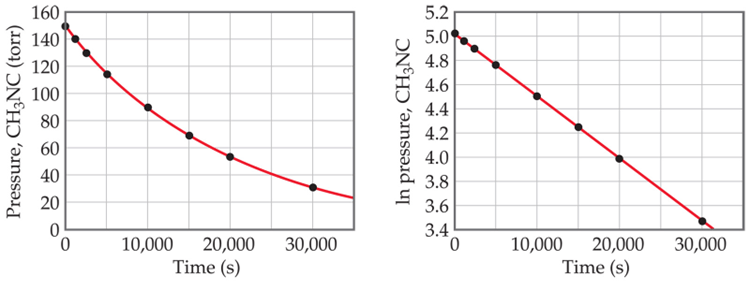
What are the first order reactions.
A reaction occurs when particles collide with sufficient energy and proper orientation.
What is according to collision theory.
This is an environmental factor which contributes to the increase in the rate of a reaction.
What is the temperature?
The rate of a reaction at a point where a tangent touches the reaction rate curve.
What is instantaneous rate?
The overall order of the reaction shown below:
Rate = k[KI]2[Pb(NO3)2]1
What is 3.
The photocatalysis of hydrogen gas and chlorine gas produces hydrogen chloride gas which can be plotted to produce a graph which follows --------------order reaction: 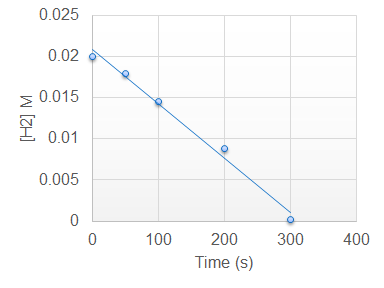
What is zero order.
The minimum energy required for a reaction to occur
What is the Activation Energy Ea.
Oh! This is not consumed during a reaction, or is recreated at the end of the reaction.
What is a catalyst?
The reaction does not respond to the concentration of the reactants at any time during the reaction.
What is a zero order reaction?
The Order of a reaction as determined by taking the ratio of rates for two initial concentration is:
Rate2 /Rate 1 = k(0.0060) Ms-1/k(0.0015) Ms-1
What is two.
Predict the amount of reactant or product present after a period of time.
What are integrated rate laws.
The energy required to remove an electron from an atom or an ion.
What is an Ionization energy.
This is an important factor, determining how fast or slow the reaction may proceed.
What is the nature of reacting atoms and molecules; What is their electronic configuration?
Integrated rate laws.
What is the relationship between the reactant concentration and time.
True or false: Reaction order can be deduced from the balanced chemical equation of the overall reaction.
False
Reactions that exhibit larger rate constants and correspondingly shorter half-lives when fast; smaller rate constants with longer half-lives when slow.
What are first order reactions.
This is how the crystal structure is determined
What is the X-ray diffraction technique.
A finely divided piece of Magnesium reacts more violently with HCl than a large nugget of Magnesium.
What is due to larger available surface area?
In a rate law, this is typically used to determine the units of the rate constant, k.
What is the method of initial rates?
The expression Rate = k[A]0 informs us about an important relationship.
What is the rate is independent of the initial reactant concentration.
The rate constant cannot be calculated directly from the half life of this type of reactions.
What are second order reactions
The minimum amount of energy needed by a chemical reaction to occur in addition to the proper orientation of the molecules.
What is the energy of activation.
The reaction proceeds along this path on the reaction coordinate.
What is the lowest energy path.
This picture explains the rate of reaction.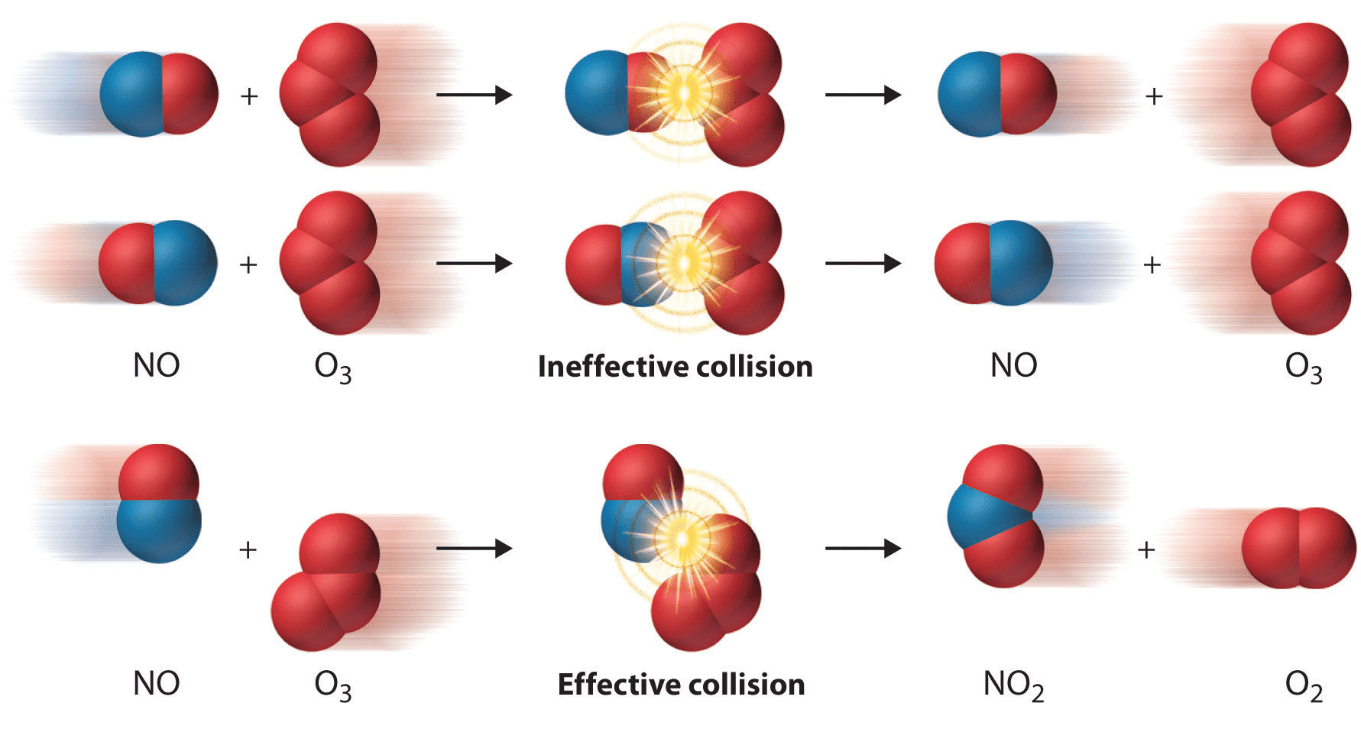
What is the collision theory.
Radiocarbondating is based on the fact that C14 decay follows a certain kinetics order.
What is the first order kinetics.
For this type of reactions, as the concentration of reactants decreases, the half-life increases.
What are the second order reactions.