You are treating an agitated adult patient with severe psychosis. Per ICEMA, you may give Midazolam. What is the maximum IM dose you can administer?
Answer: 5 mg IM/IN
Midazolam, 5 mg IM/IN. May repeat in 10 minutes. Max 3 doses
Burn patients with respiratory compromise or potential for such, will be transported to…
- The closest receiving hospital for airway stabilization
Name this rhythm

3rd degree
What does Para and Gravida mean?
Gravida indicates the number of times the mother has been pregnant.
Para indicates the number of viable (>20 wks) births.
Which I.O. insertion site requires Base Hospital Contact?
Distal femur
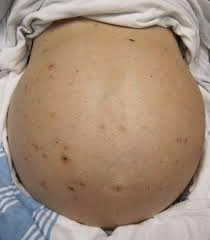
What is this and what might be some causes?
Ascites
- condition that happens when fluid collects in spaces in your belly (abdomen).
Most common cause is cirrhosis of the liver (Heavy Drinking). Some types of cancer, like ovarian or bladder cancer, can also cause it.
What dose DOPE stand for and when is it used?
Displacement
Obstruction
Pneumothorax
Equipment Failure
During your pupil assessment of a patient found down, you observe...
Why am I confused?
Constricted pupils from opioid use.
A 90 kg adult patient is complaining of 10/10 pain from a fractured femur. You initially are unable to get an IV. What is the maximum total dose of Fentanyl (in mcg) you can administer and how frequently?
Answer: 200 mcg IM
Fentanyl, 100 mcg IM/IN. May repeat 50 mcg every 10 minutes titrated to pain, not to exceed 200 mcg.
T OR F Patients on a 5150 hold with no medical complaints or conditions, may be released to law enforcement for transport directly to a behavioral health facility
TRUE
Where is the STEMI?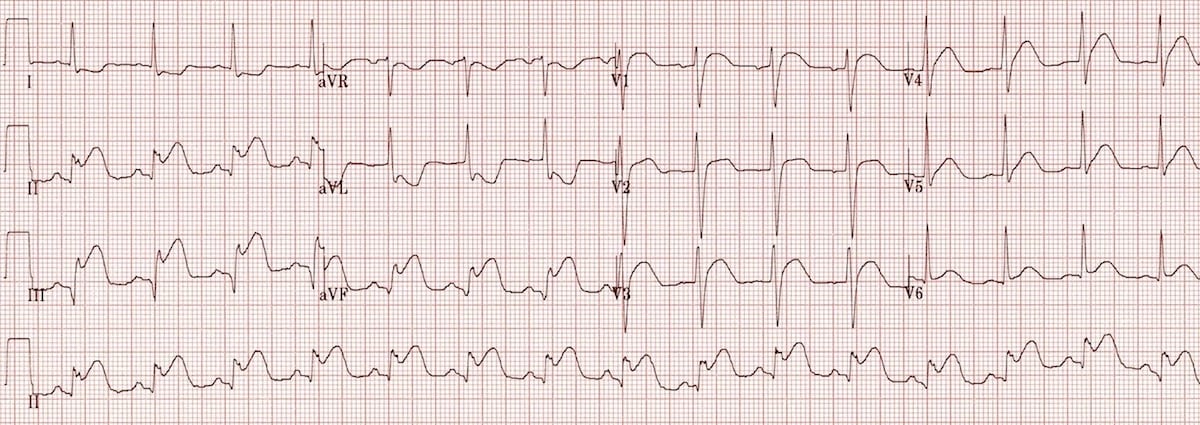
Inferior MI
Elevation in leads II, III, AVF
What is the compression to ventilation ratio for a newborn?
compressions with ventilations at a 3:1 ratio
During the later stages of pregnancy, a midaxillary needle thoracostomy should be placed at the…
- 3rd intercostal space
What organs are in the RUQ (right upper quadrant) of the abdomen?
- Liver: The liver is a large organ located primarily in the RUQ.
- Gallbladder: This small organ stores bile and is located beneath the liver.
- Pancreas: A portion of the pancreas extends into the RUQ.
- Intestines: Parts of the small and large intestines (colon) are also found in this area.
- Diaphragm: The right portion of the diaphragm, a muscle crucial for breathing, is located in the RUQ
Name the Lung Sound
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Wheeze
You arrive on scene to find a 69 yo female in her home with her daughter. The daughter states the patient has been acting strangely every evening but acts herself the rest of the day. The patient has been wandering out of the house for the past week. All vitals are stable. A&Ox4 but has difficulty following conversation. What is most likely the cause?
Sundowners due to Alzheimers or Dementia
A 4-year-old child is unresponsive with a blood glucose of 38 mg/dL. You are giving Dextrose 10%. How many mL will you administer?
Answer: 85ml
Explanation: 5 mL/kg = 5 × 17kg = 85ml
Name at least 2 things that must be transported to the hospital with a VAD patient
- VAD emergency bag
- Power module
- Power base unit
- Batteries
- Charger
- Backup controller
What are the three natural pacemakers of the heart and what are their intrinsic rates?
SA Node- 60-100
AV Node 40-60
Perkinje Fibers 20-40
What does APGAR stand for?
- Activity (muscle tone). 2 points = active
- Pulse. 2 points = over 100 bpm
- Grimace (reflex irritability). 2 points = prompt response to stimulation
- Appearance (skin color). 2 points = pink
- Respiration. 2 points = vigorous cry
For suspected spinal injuries, “NSAID” criteria stands for…
- Neuro deficits
- Spinal tenderness
- Altered mental status
- Intoxication
- Distracting injury
How do you perform and abdominal assessment and in what order?
1. Inspection:.Observe the abdomen for shape, size, distention, scars, lesions, and skin conditions.
2. Auscultation:.Listen for bowel sounds, bruits, and rubs in all four quadrants of the abdomen.
You arrive on scene to find a 5y/o sitting in a tripod stance in severe respiratory distress. Per parent the patient spike a fever and suddenly had difficulty breathing with heavy drooling. What is your differential diagnosis and how can you treat it?
Epiglottitis,
Treatment: keep the patient in an upright position, provide humidified oxygen stress reduction and transport.
You arrive on scene to a 88 y/o female with urinary incontinence, HTN and dementia, patient that has been increasingly confuses for the last two days, denies fever, sob and mLAPSS negative.
Why am I confused?
UTI
Inflammation and Cognitive Function:
UTIs trigger inflammation, which can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, leading to confusion.
Worsening of Pre-existing Conditions: UTI can exacerbate cognitive decline, causing a temporary worsening of symptoms.
Dehydration: UTIs can also lead to dehydration, which can further contribute to confusion and cognitive impairment
You have an 8-year-old male with a severe asthma attack. You have given an initial duo neb treatment and repeated the albuterol without relief. You now would like to give Mag, what is your dose?
8y/o = 27kg, 27kg x 50mg = 1350mg = 2.7ml in a 100ml bag over 20min
(base hospital order only): Magnesium Sulfate, 50 mg/kg slow IV drip over 20 minutes. Do not exceed the adult dosage of 2 gm total. Do not repeat.
Name 5 out of the 8 Determination Of Death Criteria
- Decomposition
- Obvious signs of rigor mortis such as rigidity or stiffening of muscular tissues and joints in the body, which occurs any time after death and usually appears in the head, face and neck muscles first
- Obvious signs of venous pooling in dependent body parts, lividity such as mottled bluish tinged discoloration of the skin, often accompanied by cold extremities
- Decapitation
- Incineration of the torso and/or head
- Massive crush injury
- Penetrating injury with evisceration of the heart, and/or brain
- Gross dismemberment of the trunk
What syndrome is defined as a congenital condition involving abnormal conductive cardiac tissue between the atria and the ventricles that provides a pathway for a reentrant tachycardia circuit.
Wolf-Parkinson white
Your providing care to a 36 week pregnant patient that is having seizures. What are you concerned about and medication can be provided?
Eclampsia
Magnesium Sulfate, 4 gm IV/IO slow IV push over three (3) to four (4) minutes.
Magnesium Sulfate, 10 mg/min IV/IO drip to prevent continued seizures.
Name 2 of the 3 relative contraindications for Vagal Maneuvers
- Hypertension
- Suspected acute MI
- Suspected head/brain injury
During your assessment, of an 80 y/o female you notice these. What are they and why would the patient need them?
Nephrostomy tube
flexible tube inserted through the skin into the kidney to drain urine when the normal flow is blocked. This blockage can be caused by various factors, including kidney stones, infection, or congenital abnormalities
What type of heart problem can give you this lung sound?
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
.
Crackles
Left sided heart failure
During your assessment you observe this.
Why am I confused?
High Ammonia:
Elevated levels of ammonia in the blood, resulting from the liver's inability to convert it into urea for excretion.
You’ve just delivered the first shock to a patient in refractory VF. You’re preparing to administer lidocaine to a 145lb female. What is the first dose (in mg) per protocol, and how many mL will you draw? What is the second dose if unresolved?
145/2.2=66kg – 66kg x 1.5mg = 99mg = 4.95ml=5ml
Dose 2 = 2.5ml
Initial Dose: Lidocaine, 1.5 mg/kg IV/IO For refractory VT (pulseless)/VF, may administer an additional 0.75 mg/kg IV/IO, repeat one (1) time in five (5) to 10 minutes; maximum total dose of 3 mg/kg.
What 4 things must be on a DNR in order to make it valid?
- Patient’s name
- Signature of the patient or a legally recognized decision maker if the patient is unable to make or communicate informed healthcare decisions
- Signature of patients’ physician, affirming that the patient/legal representative has given informed consent to the DNR instruction
- All signatures must be dated
Why is MAP important? How do you obtain it?
it reflects the average pressure in a person's arteries during a single cardiac cycle, indicating how well blood is flowing to vital organs
MAP = SBP + 2(DSP) / 3
exp. 120 +2(80) /3=93
Provide 4 treatment options for a patient experiencing Postpartum Hemorrhage.
Massage fundus to control bleeding.
Encourage immediate breast feeding.
Place in trendelenburg position.
Administer fluid challenge of 500 ml, if signs of inadequate tissue perfusion persist may repeat fluid bolus.
Maintain IV rate at 150 ml per hour.
Establish second large bore IV en route
Administer TXA with a SBP less than 90 mm or Significant hemorrhage with heart rate greater than or equal to 120.
Name 3 of the 6 contraindications for I.O. insertion…
- Fracture of target bone
- Previous IO attempt and marrow entry at target site
- Infection at target site
- Severe burn to the extremity
- Crush injuries
- Known bone disease
What does the Dr. Germ acronym assess?
DISTENTION
RIGIDITY
GUARDING
EVISCERATION
REBOUND TENDERNESS
MASSES
You arrive on scene to find a 50 yo male involved in a TC. Pt was not wearing his seatbelt and there is steering wheel deformity. Anterior neck has significant swelling. Massive swelling to the neck, upper chest, and face with a "rice crispy" feel to the skin. What is the patient most likely suffering from?
Tracheobronchial Rupture
You are called out to a 28y/o patient with c/c of N/V, abdominal pain, fatigue and lethargy, during your assessment you place the pt on monitor and see this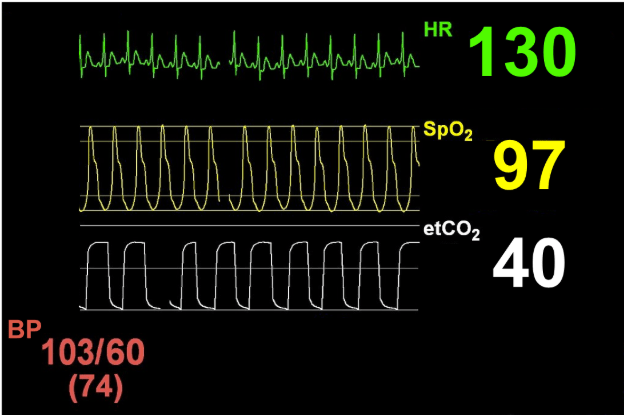
Why am I confused?
DKA with Kussmaul respirations