What are the three main opioid receptors?
Mu
Kappa
Delta
(4th receptor nociception/orphonin FQ receptor activated by F/OFQ peptide)
In addition to full mu-opioid receptor agonist activity, this opioid also has NMDA antagonist effects.
Methadone
The phenothiazine class of sedatives mediates its sedative effects primarily through blockade of these receptors.
Primarily: Dopamine (D2) receptors
Blockade of central α1-adrenergic, muscarinic, and histaminic (H1) receptors may also play a role in sedation
Describe the mechanism of action through which α2-adrenergic receptor agonists lead to sedation.
Locus coeruleus in pons (major noradrenergic nucleus of the brain; contains dense populations of α2-adrenergic receptors) --> Activation of presynaptic α2-adrenergic receptors --> Inhibition of norepinephrine release and reduced activity in ascending noradrenergic pathways --> Hypnosis and sedation
Barbiturates
Activation of GABAA receptors which increases transmembrane chloride conduction, resulting in hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell membrane:
- Reduce rate of dissociation of GABA
- At increasing concentration, acts as a GABA agonist, directly activating chloride channels
Maropitant, a potent antiemetic drug, antagonizes this receptor to reduce binding of what neuropeptide neurotransmitter?
Neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor
Substance P
Opioids are primarily this form of solubility, allowing for rapid and extensive absorption after SC/IM administration, and allowing them to move easily across cell membranes and distribute to the CNS where they elicit there analgesic effects.
Lipophilic
List the opioids that are considered only full mu agonists.
- Morphine
- Hydromorphone
- Oxymorphone
- Fentanyl
- Remifentanil
- Sufentanil
- Meperidine
- Carfentanil, thorphine, alfentanils, thiafentanil
- Hydrocodone, oxycodone, codeine
This sedative's cardiovascular effects include hypotension through vasodilation and decreased stroke volume and cardiac output though antagonism of what receptors?
Acepromazine
α 1-adrenergic receptor antagonism
Which α2-adrenergic antagonist has the most specific α2-adrenergic receptor antagonist specificity?
Atipamezole: α2:α1 binding ratio of over 8500:1; no significant effects at dopaminergic, serotonergic, histaminergic, or cholinergic receptors
Etomidate
GABAA agonist activity: Activation of GABAA receptors which increases transmembrane chloride conduction, resulting in hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell membrane
- Increases affinity of GABA, potentiating effect of GABA
Omeprazole and pantoprazole are proton pump inhibitors, which act on the proton pump located at the luminal surface of these gastric cells?
Parietal cells
Systemic analgesic opioid doses are more effective at decreasing pain transmitted by these types of nociceptors.
C-fiber nociceptors = slow conducting unmyelinated nerves associated with dull aching pain
(A-gamma fiber nociceptors = fast conducting, myelinated nerves associated with sharp pain)
Name the receptors and effect (agonist/antagonist) at those receptors that buprenorphine, butrophanol, and nalbuphine bind to.
Buprenorphine: partial mu-opioid agonist
Butorphanol: antagonist to partial agonist at mu-opioid receptor, kappa-opioid agonist
Nalbuphine: mu-opioid antagonist, kappa-opioid agonist
State of sedation and analgesia induced by the combined administration of a tranquilizer and an opioid.
Neuroleptanalgesia
In addition to adrenergic receptors, α2-adrenergic receptor agonists may secondarily activate this receptor.
Imidazoline receptors (I1, I2, I3)
Alfaxalone
Activation of GABAA receptors which increases transmembrane chloride conduction, resulting in hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell membrane
- Low concentrations, modulates ion currents through GABAA receptor
- At increasing concentration, acts as a GABA agonist, directly activating chloride channels
Doxapram has the ability to increase minute ventilation through an increase in both respiratory rate and tidal volume through what mechanism?
Stimulation of respiratory brainstem neurons
Oral administration of standard opioid doses in animals are typically rendered ineffective by this "form" of metabolism in this organ.
Extensive first-pass metabolism
Liver
What are the three main opioid antagonist agents used as opioid reversals and what receptors do they antagonize?
Naloxone: Primarily full u-opioid antagonist, minimal kappa and delta antagonism
Naltrexone: Antagonist at mu-, kappa-, and delta-opioid receptors
Methylnaltrexone: Selective peripherally-acting mu-opioid receptor antagonist, minimal kappa-opoid binding, does not bind with delta-opioid receptors
This drug is a competitive antagonist with a high affinity for the benzodiazepine recognition site on the GABAA receptor but no appreciable agonist or inverse agonist activity at the site.
Flumazenil
As the drug is specific to the benzodiazepine-binding site on the receptor, it does not antagonize the CNS effects of other anesthetic agents interacting with the GABAA receptor such as propofol, alfaxalone, etomidate, and barbiturates.
Through what mechanisms do α2-adrenergic receptor agonists produce diuresis?
1. Reduced production/release of ADH from the pituitary gland
2. Inhibition of ADH activity on renal collecting tubules
3. Enhanced sodium excretion
4. Inhibition of RAAS system - directly through activation of renal α2-adrenergic receptors and indirectly through α2-adrenergic receptor agonist-induced hypertension
Propofol
Primarily: Activation of GABAA receptors which increases transmembrane chloride conduction, resulting in hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell membrane
- Reduce rate of dissociation of GABA from its receptor, potentiate effect of GABA
Secondary: Inhibition of NMDA receptors
Desmopressin (DDAVP), a synthetic analog of vasopressin, is used for perioperative management of patients with what disease? (Be specific)
Type I and Type II Von Willebrand's Disease
Opioids can lead to bradycardia and occasionally hypotension through what mechanisms?
Vagally mediated via increase in parasympathetic tone and inhibition of sympathtic tone.
Binding of opioids to their respective receptors causes a reduction in release of these excitatory neurotransmitters, resulting in analgesia.
Glutamate
Substance P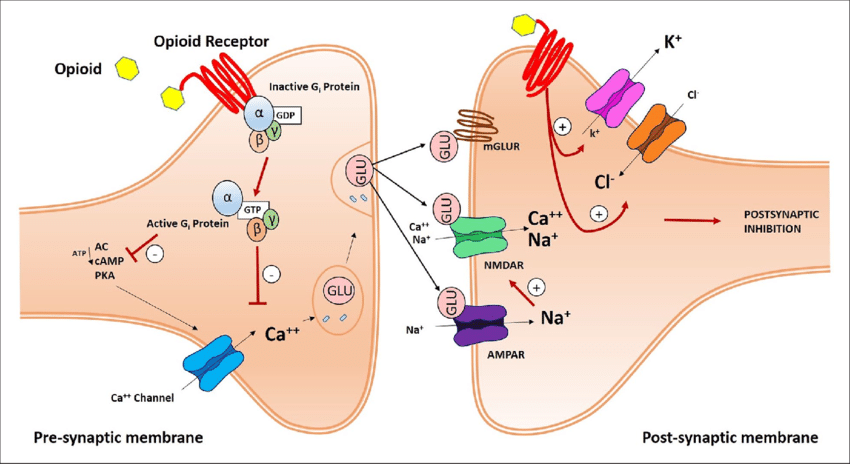
What is the mechanism through which benzodiazepines exert their sedative, anxiolytic, anticonvulsive, and muscle relaxation effects?
Bind to the benzodiazepine recognition site on the GABAA receptor and augment GABA-mediated inhibitory transmission at all levels of the CNS, resulting in increased chloride conductance and hyperpolarization of postsynaptic cell membranes.
- Enhance GABAA receptor’s affinity for GABA
- Lack direct agonist activity
Through what mechanisms do α2-adrenergic receptor agonists produce bradycardia and hypotension?
Activation of postsynaptic α1-and α2-adrenergic receptors → peripheral vasoconstriction → ↑ SVR & arterial BP → baroreceptor-mediated reflex bradycardia → ↓ CO
Activation of central presynaptic α2-adrenergic receptors → ↓ norepinephrine release & sympathetic outflow → bradycardia, ↓ CO
Net result: Bradycardia and hypotension
Dissociative anesthetics: ketamine and tiletamine
NMDA: Non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonists, preventing glutamate from binding, resulting in depression of the thalamocortical, limbic, and reticular activating systems
Opioid receptors (μ, δ, & κ): Analgesic effect
Monoaminergic receptor: Analgesic effect
Possible muscarinic receptor antagonism
The primary analgesic effect of tramadol is due to metaboliism to this active metabolite, which acts as a full mu agonist.
O-desmethyltramadol (M1)