Which state of matter has the highest potential energy?
Gas
What are the units of specific heat capacity?
J/g°C
Is heat of vaporization associated with melting or boiling?
Boiling
What phase change is happening at Segment D?

Condensation/Vaporization
Convert 55°C to Kelvin
328 K
Would a plastic toy float or sink if placed in oil?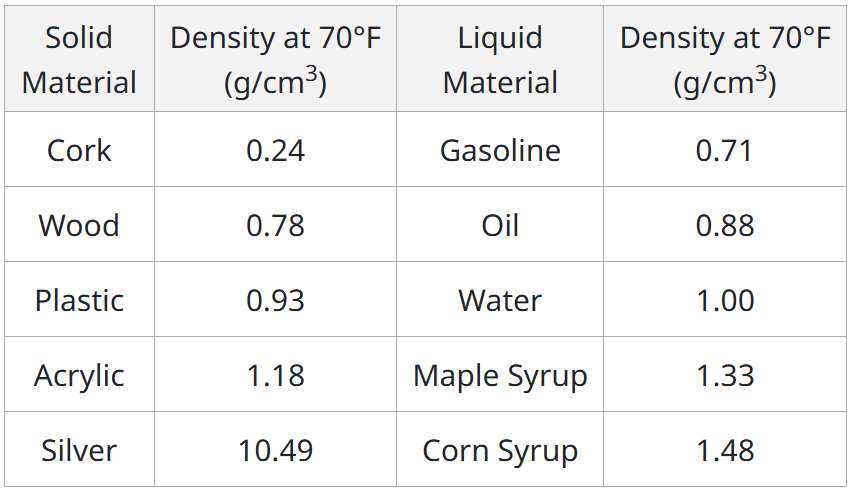
Sink
A 2 kg block of metal is heated by 10 °C. If the metal’s specific heat is 400 J/(kg·°C), how much energy is absorbed?
8000 J
Why does ice absorb heat without changing temperature as it melts?
Energy it absorbs is used to break the attraction between particles rather than to increase their kinetic energy.
Which segment, A or D, does the substance have a higher kinetic energy?

D
A basketball deflates overnight. Which conditions changed?
Temperature and volume
Explain why gases can be compressed but solids cannot.
Gases have lots of empty space → can be compressed; solids have almost no empty space → cannot be compressed.
A metal block absorbs 3600 J of heat and its temperature rises by 12 °C. If the mass is 0.3 kg, what is the metal’s specific heat?
1,000J/(kg °C)
How much energy is needed to melt 80 grams of NH3?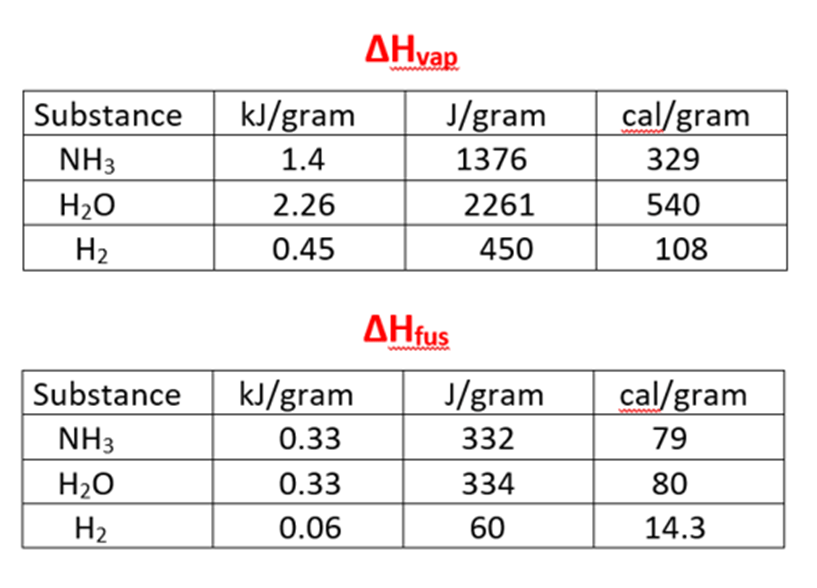
110,080 J
Why are substances more likely to be solids at high pressures?
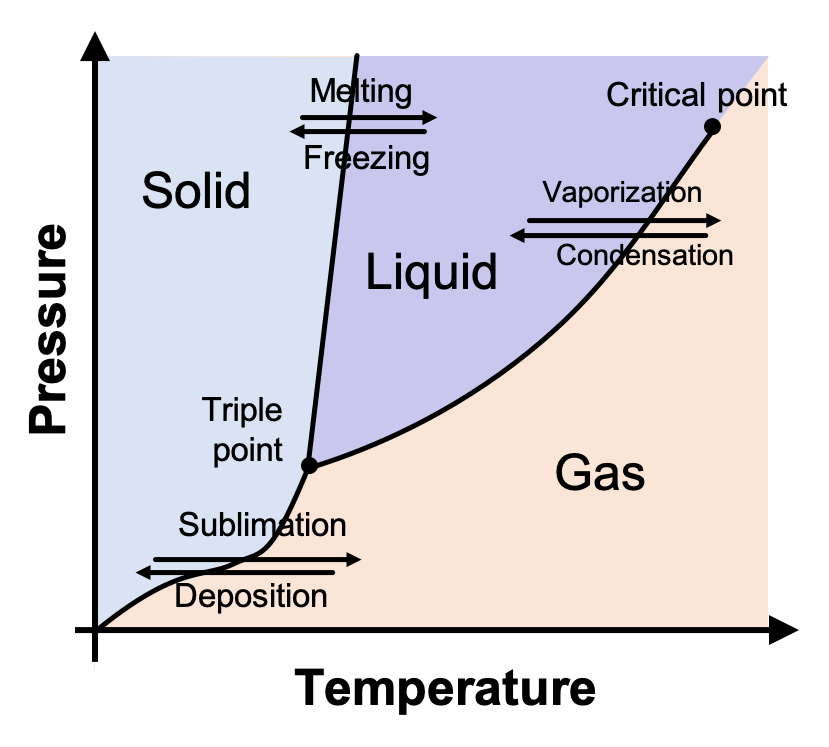
High pressure reduces the space between particles, making it harder for them to move freely.
Is the relationship between pressure and volume direct or inverse?
Inverse
What is the density of the substance based on the following graph?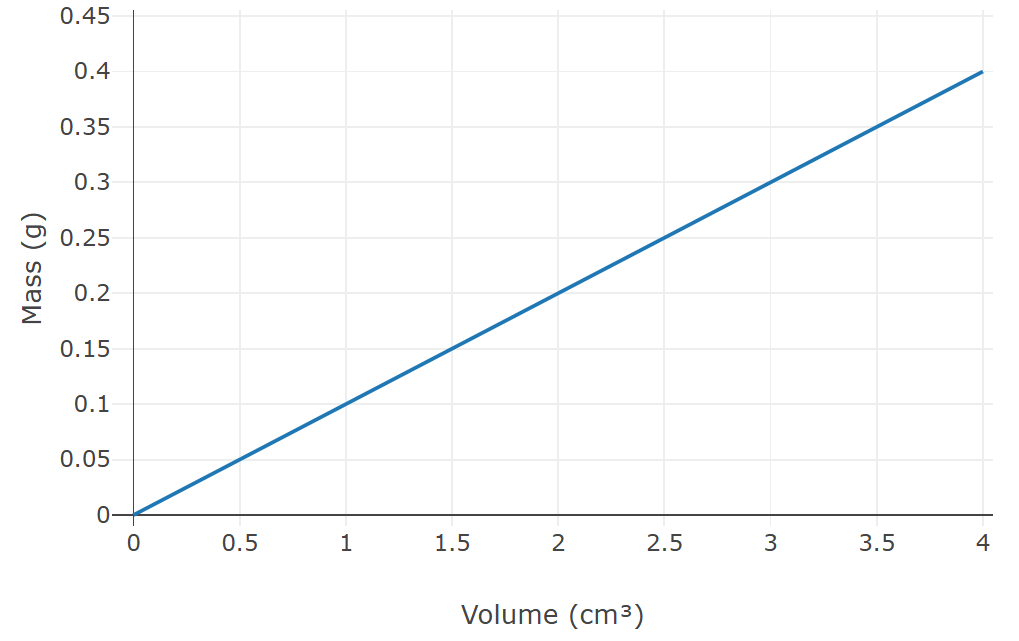
0.1 g/cm3
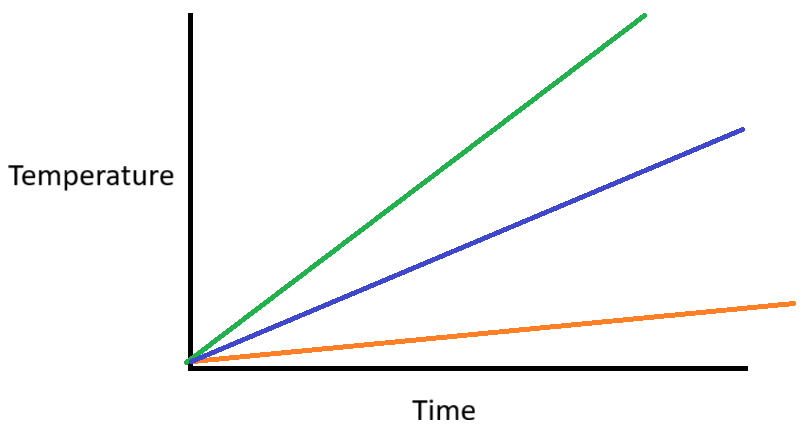
Based on the table below, which substance corresponds to the Orange line?
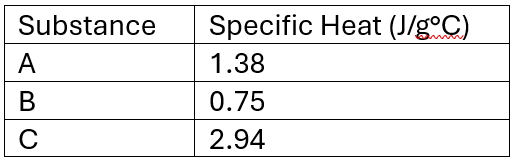
Substance B
It takes 550,000 J of energy to completely vaporize 16 grams of a substance. What is the heat of vaporization?
34,375 J/g
What is the state of matter at a pressure of 50 atm and a temperature of 35°C?
liquid
A gas at 2 atm and 300 K is heated to 600 K. What is the new pressure?
4 atm
Rank Liquid A, Liquid B, and the solid sample in order of increasing density.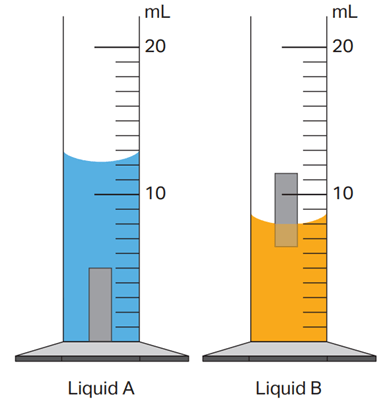
Liquid A, Solid Sample, Liquid B
You calculated the energy needed to raise the temperature of a substance and found it to be q. If the change in temperature tripled and the mass was halved, how does q change?
3/2 q
Explain why sweating cools the body.
Sweat is mostly water, which absorbs heat from your skin as it evaporates. The heat energy from your body is used to break the attractive forces between water particles so the liquid can turn into a gas.
If the temperature decreases from 300K to 250K at a constant pressure of 1atm, what change of state happens? 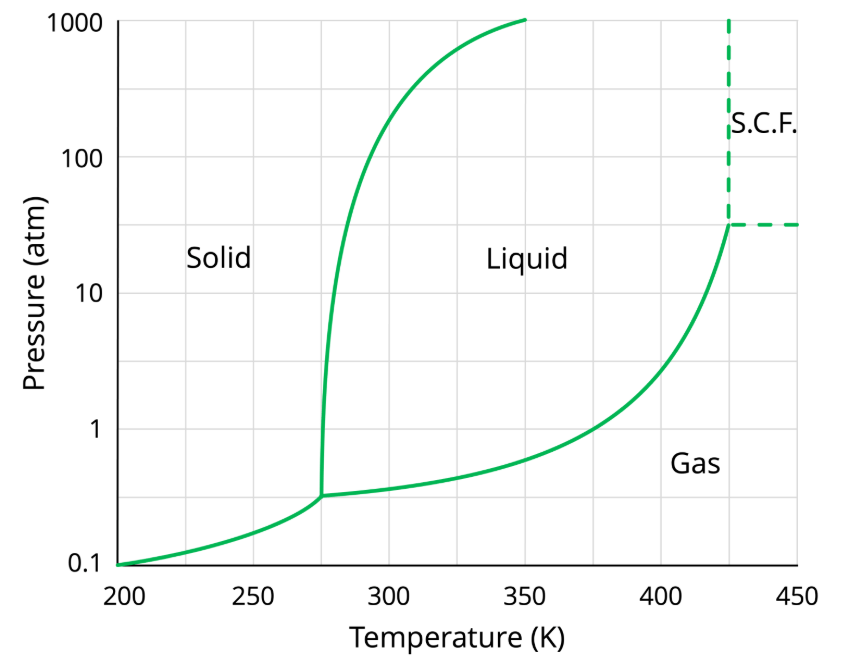
Freezing
Name a condition under which real gases behave ideally.
Real gases behave most ideally at high temperatures and low pressures.