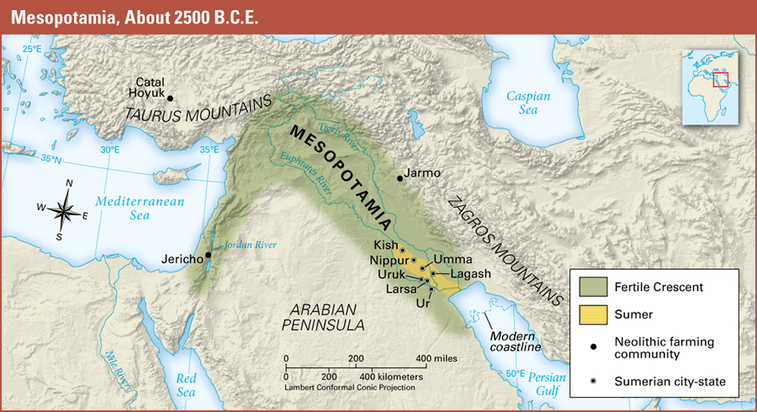
What does the word Mesopotamia mean in Greek?
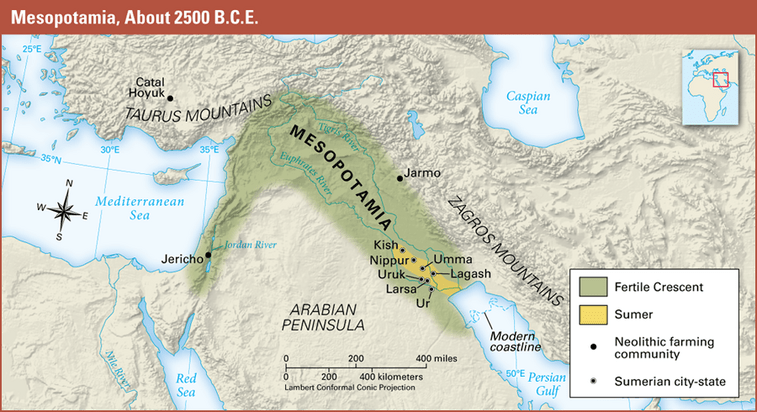
Land between the rivers
What problem did farmers face in the Zagros foothills?
Food shortages due to an increase in population and a lack of farmland
What material did Sumerians use to build city walls?
Sunbaked mud bricks
What was the main job of most Sumerians?
Farming
What is a city-state?
An independent city with its own ruler and farmland
What are the two main rivers of Mesopotamia?
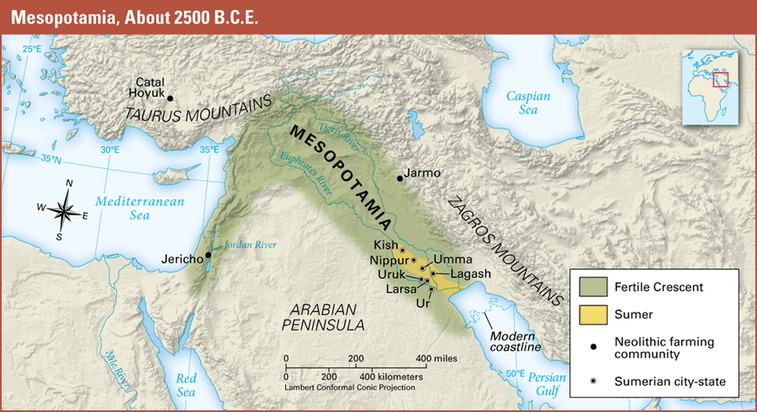
The Tigris and Euphrates Rivers
What was the Sumerians’ solution to food shortages in the hills?
They moved down to the river valley (Sumer)
What did Sumerians dig outside their city walls for protection?
Moats
What did levees help prevent?
Flooding of crops and farmland
Why did Sumerians build walls and moats around their cities?
To protect themselves from attacks by other communities
What modern-day country is Mesopotamia located in?
Iraq
What problem did farmers face in the river valley?
Uncontrolled water supply—too much or too little water
Why did people move inside city walls during attacks?
For protection from enemies
Why did Sumerians dig canals?
To carry water from rivers to their fields
What caused city-states to fight with each other?
Disputes over water and land
Why was southern Mesopotamia harder to live in than the north?
It was hot, dry, and had little rain or natural resources
How did Sumerians control the water supply?
They built levees, dams, and irrigation canals
What did cooperation among villages lead to?
The growth of larger communities and city-states
What happened when canals became clogged with silt?
Water couldn’t flow and crops could die
How did solving geographic problems lead to the rise of city-states?
Each solution brought people together and created organized cities
Why was Mesopotamia part of the “Fertile Crescent”?
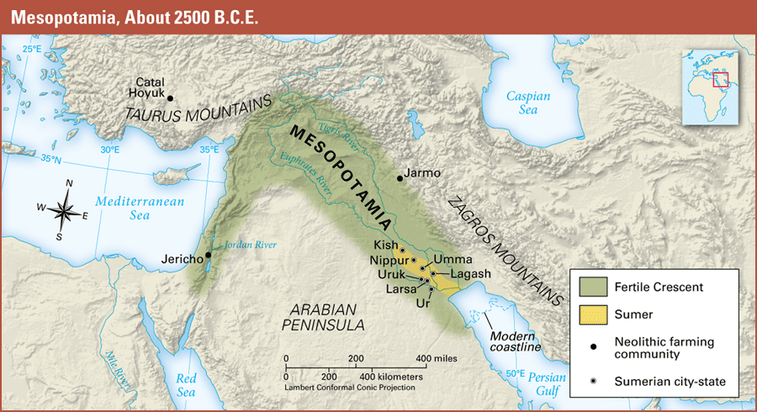
Because the land between the rivers had rich soil good for farming
What problem came from irrigation systems crossing village boundaries?
They had to cooperate and work together to maintain the system and clear away the silt
Around what year did most Sumerians live in walled city-states?
By about 3000 B.C.E.
Why did Sumerians have to depend on each other for irrigation?
The system connected many villages and needed teamwork to maintain
What was the final result of the Sumerians’ problem-solving?
Small villages became large, walled city-states in Sumer
Name three Sumerian City-States
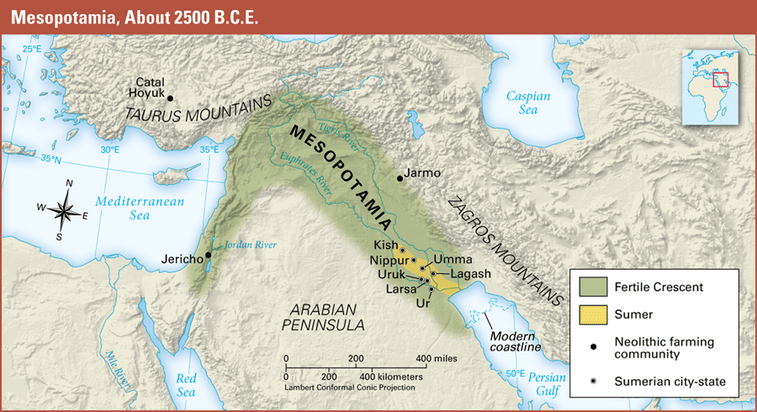
Ur
Uruk
Lagash
Umma
Eridu
Kish
Nippur
Larsa
Isin
Adab
Babylon