This type of vowel has an unchanging quality.
What is a monophthong?
This consonant is made when air is obstructed and then suddenly released.
What is a stop or plosive?
This anatomical structure creates harmonics.
This is the power source for speech.
What is respiration or the lungs?
This type of vowel does change in quality.
This consonant is created when airflow is blocked in the mouth and flows through the nasal cavity.
What is a nasal?
This group of anatomical structures creats formants.
What is the vocal tract?
This is the term used to say that the vocal folds are vibrating or creating a voiced sound.
What is phonation?
When the the vocal tract is lengthened, this happens to the frequency of the formants.
What is lowered?
This is the name of the place when a consonant is made using the teeth and the lips.
What is labiodental?
This anatomical structure/space determines the first formant frequency.
What is the pharynx?
This term describes the movement of structures to produce sounds.
What is articulation?
All vowels in American English are this (Hint: vibrations).
What is voiced?
This consonant is created when articulators are close together, but there is no frication and the tongue moves from one point in the oral cavity to another.
What is a glide?
This anatomical structure/space determines the second formant frequency.
What is the oral cavity?
This term is used to the describe the maximal vibration of an object.
What is resonance?
These four things are used to classify vowels.
What is tongue height, tongue tension, tongue position, and lip position?
Consonants are classified using these three methods.
This spectrogram is showing what speech sound? 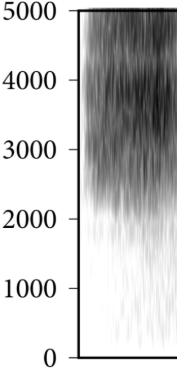
What is a fricative?
This happens when two articulators move at the same time for different phonemes and they overlap.
What is coarticulation?