Define "dead load" in the context of building structures.
Dead load refers to the permanent static weight of the structure itself and any fixed components.
State one of Newton's Laws of Motions.
- A body remains at rest, or in motion at a constant speed in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by a force.
- At any instant of time, the net force on a body is equal to the body's acceleration multiplied by its mass or, equivalently, the rate at which the body's momentum is changing with time.
- If two bodies exert forces on each other, these forces have the same magnitude but opposite directions.
What is a zero-force member in a truss?
A member that carries no force under specific loading conditions, often used for stability.
What is a tributary area?
The area contributing load to a structural element, used to calculate distributed load.
Define tensile stress.
Stress caused by forces that attempt to stretch a material.
What is the centroid of a shape?
The geometric center or average location of the area of a shape.
Name two types of loads commonly applied to beams.
Point loads and distributed loads.
List three basic functional requirements of a structure.
Stability, Equilibrium, Strength, Stiffness, Continuity, Redundancy. (Others include Economy, Functionality, Aesthetics, but not covered in this class.)
What is a free-body diagram, and why is it important?
A diagram showing all external forces acting on a body; essential for solving statics problems.
Name the two methods used to analyze plane trusses.
Method of Joints and Method of Sections.
Explain the concept of load path in structural systems.
The route through which loads travel from the point of application to the ground.
What is the modulus of elasticity?
A measure of a material’s stiffness, defined as stress divided by strain.
Define moment of inertia in structural analysis.
A measure of an object's resistance to bending or rotation.
What does a shear diagram represent?
It shows how shear force varies along the length of a beam.
Determine the X and Y components of the force F if theta (θ) = 32°, and F1 = 250 kN.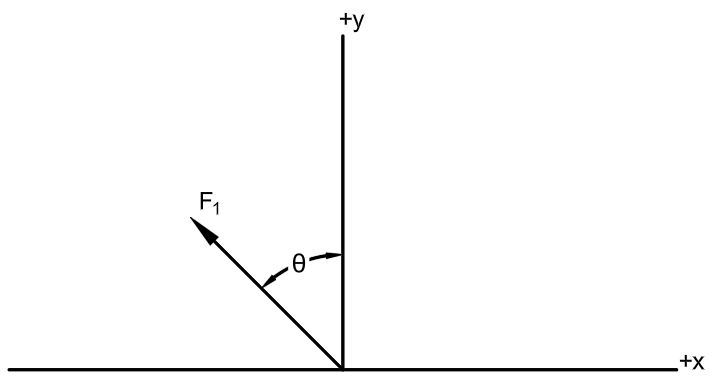
Fx = -132.48 kN
Fy = 212.01 kN
Calculate the moment of a 50-lb force acting 6-ft from a pivot point.
Moment = Force x Perpendicular distance = 50 lb x 6 ft = 300 lb-ft.
Explain how diagonal tension counters work in trusses.
They resist tensile forces and stabilize the truss under varying loads.
Calculate the tributary area for a column supporting a 20 ft x 20 ft floor with columns spaced 10 ft apart.
Tributary area = 10 ft x 10 ft = 100 ft2.
Calculate the tensile stress in a rod with force 500 lb and cross-sectional area 2 in².
Stress = Force / Area = 500 lb / 2 in² = 250 psi.
Calculate the moment of inertia of a rectangle (b=4 in, h=6 in) about its centroid.
I = (b × h³) / 12 = (4 × 216) / 12 = 72 in⁴.
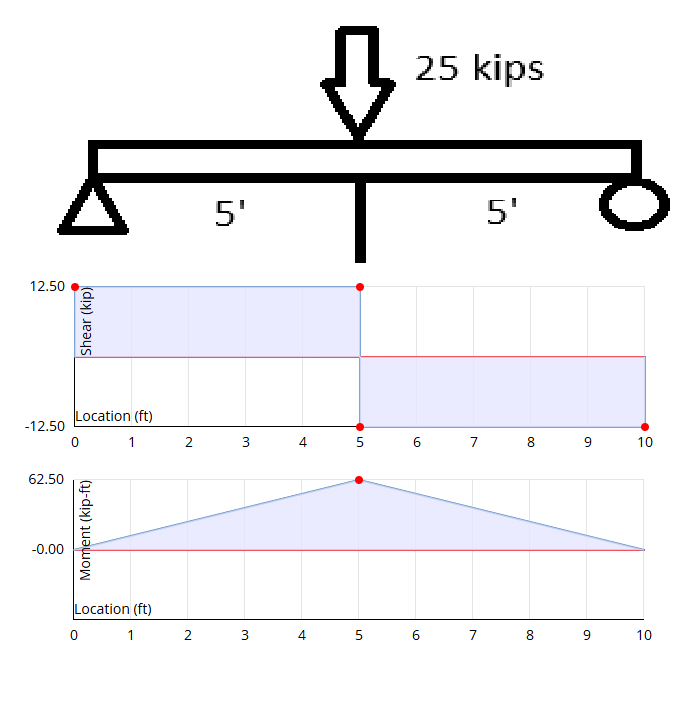
Draw the shear and moment diagram for the beam shown.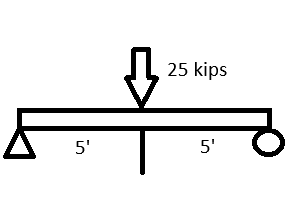
Vmax = 12.5 kips, jump down at mid-span
Mmax = 62.5 k-ft
Determine the X and Y components of the force if F1 = 425 kN.
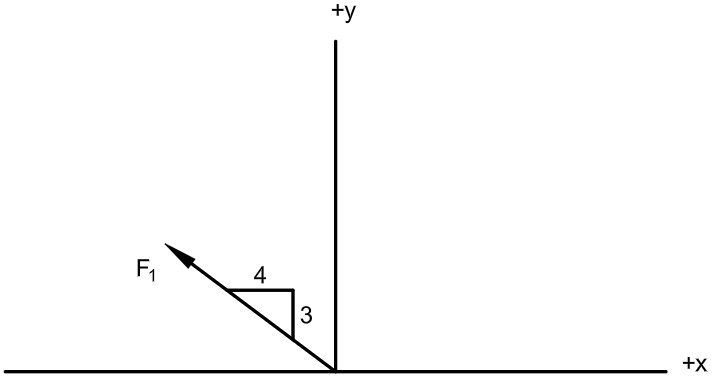
Fx = 340 kN
Fy = 255 kN
What does it mean if a structure (or beam) is statically determinant?
Internal forces and reactions can be found using equilibrium equations alone.
For the following beam, state the number of equations of equilibrium, the number of unknown support reactions, and then classify it as statically determinate, unstable, or statically indeterminate. If indeterminate, state to what degree.
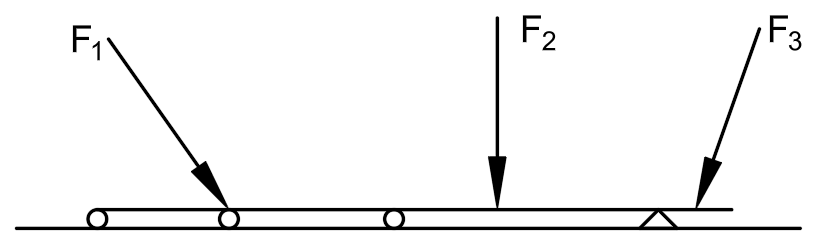
Number of Equations of Equilibrium: 3
Unknown Support Rxns: 5
Classification: Statically indeterminate to the 2nd degree
In a three-story building, each floor is 12 ft high. What is the tributary height for the 2nd floor?
The tributary height for the 2nd floor is 12 ft.
Compare brittle and ductile materials in terms of deformation.
Brittle materials fracture with little deformation; ductile materials deform significantly before breaking.
Find the radius of gyration for a section with I = 200 in⁴ and A = 50 in².
r = √(I/A) = √(200/50) = √4 = 2 in.
What degree curve will exist in the moment diagram if two point loads are present on the load diagram with nothing between them?
1st degree curve
Name the five different kinds of loads that structures experience. Identify one static and one dynamic.
Static: Dead loads, live loads, snow loads.
Dynamic: Wind loads, earthquake load.
A beam is supported at both ends and has a point load of 100 lb at its center. Calculate the reactions at the support.
Each support carries half the load: 100 lb / 2 = 50 lb at each support.
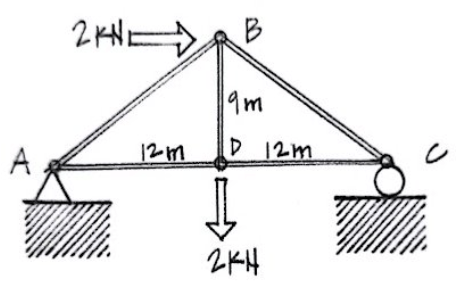 Using the method of sections, determine the force in member AD of the truss shown.
Using the method of sections, determine the force in member AD of the truss shown.
Hint: Ax = 2 kN, Ay = 0.25 kN, Cy = 1.75 kN
A two-story building has columns spaced at 15 ft in one direction and 20 ft in the other. The roof carries a uniform snow load of 40 psf. Calculate the load carried by an exterior column and an interior column, assuming tributary areas are based on column spacing.
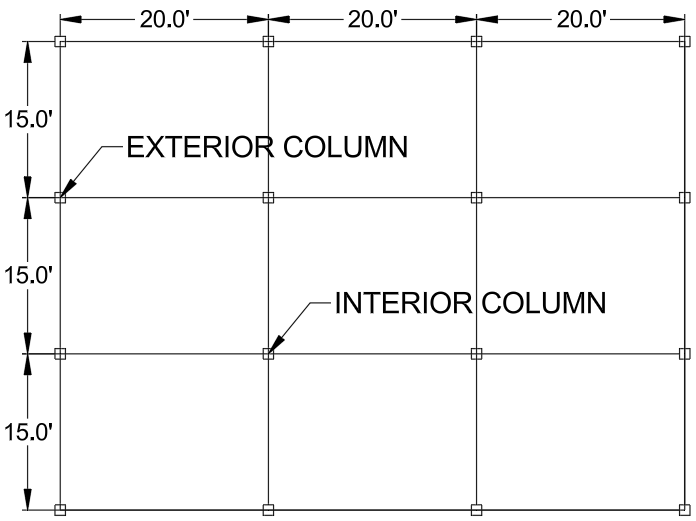
Exterior column: Tributary area = (15 ft / 2) × (20 ft / 2) = 7.5 ft × 10 ft = 75 ft² → Load = 75 ft² × 40 psf = 3,000 lb.
Interior column: Tributary area = 15 ft × 20 ft = 300 ft² → Load = 300 ft² × 40 psf = 12,000 lb.
A steel bar elongates 0.1 in under a load of 1,000 lb. If its original length is 10 in and area is 2 in², find the modulus of elasticity.
E = (PL/Aδ); P = 1,000 lb, L = 10 in, A = 2 in2, δ = 0.1 in
E = (1000*10)/(2*0.1) = 50,000 psi
Calculate the moment of inertia for the following shape. A = 3 ft, B = 12 ft.
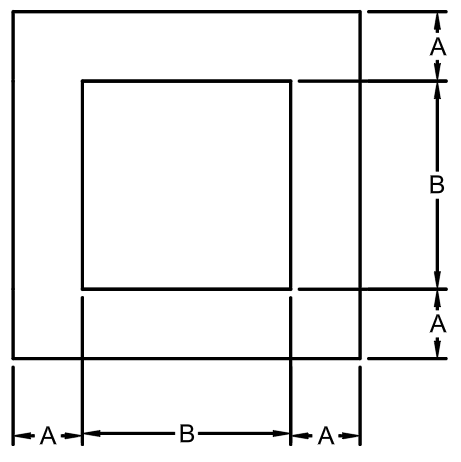
Ix = 7020 ft4
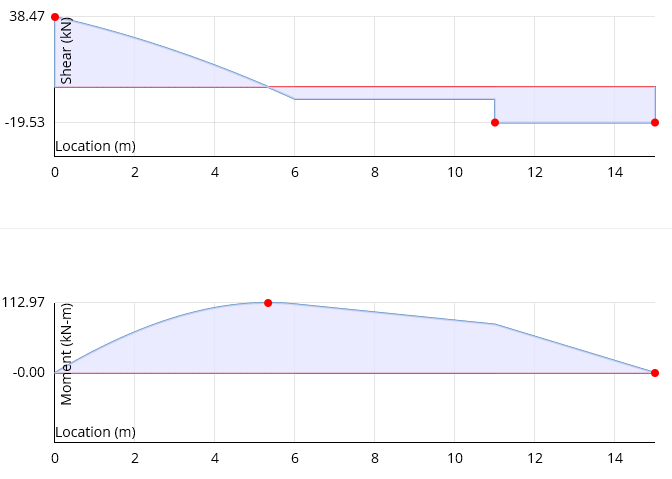
Find Mmax for the following beam. Hint: the left support is 38.47 kN and the right support is 19.53 kN, both upwards.
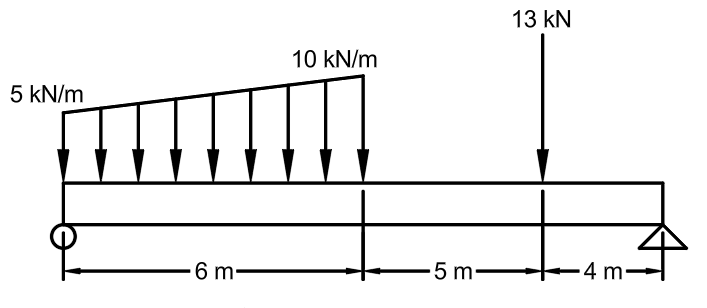
Mmax = 112.975 kN-m