200 points:
Do all fractures need to be Reduced?
Do all fractures need to be Immobilized?
Reduced = no
Immobilized = yes.
How many bones are in your Axial Skeleton?
80
What kind of joint are freely movable?
Synovial joints.
Why does your knee joint have to be the strongest joint in your body?
It supports about 90% of the total body weight
What part of the body grows the fastest once you are born?
Arms and legs
How are Bone fractures treated?
With Reduction and Immobilization
How many bones are in your Appendicular Skeleton?
126
What are the four major joint dislocations you should immediately treat?
Hip, shoulder, knee, and elbow.
What is unique about the knee joint?
Most complex synovial joint of the body.
What is the largest part of your body when you are bone?
The head
Describe this bone fracture:
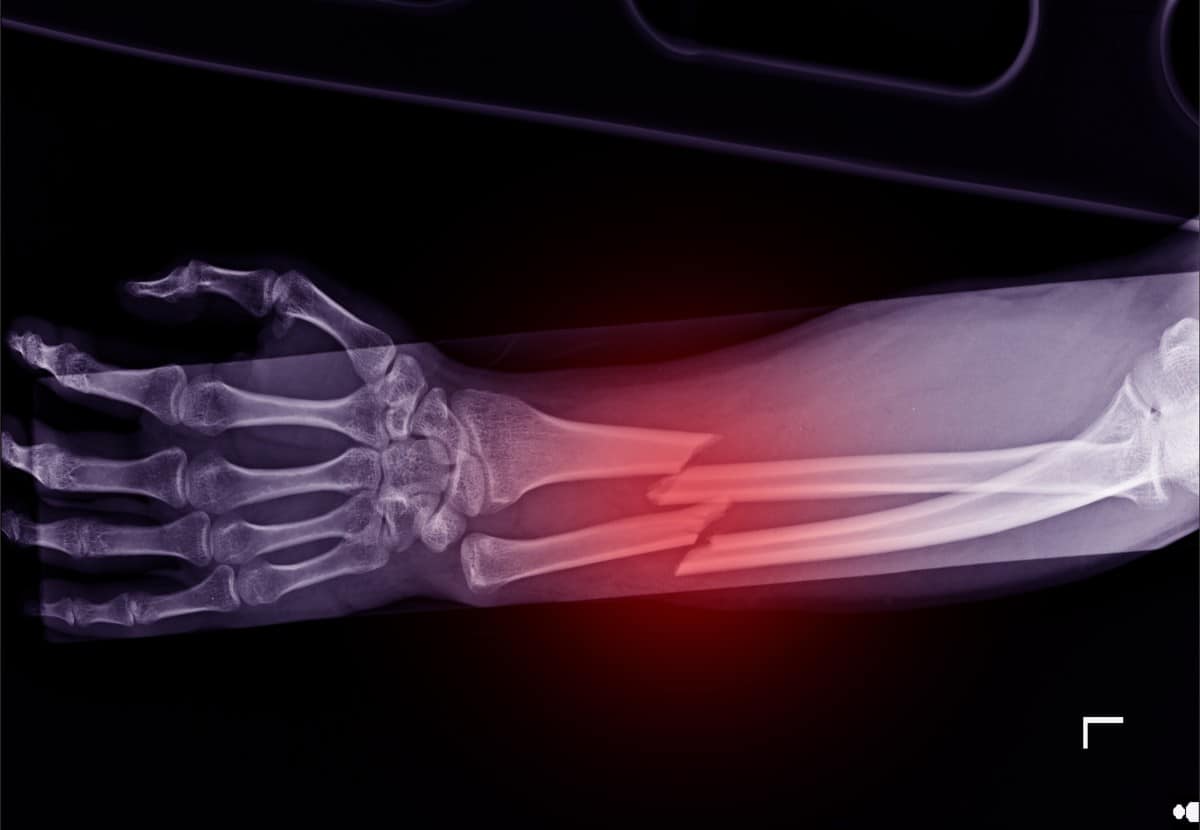
Complete, Displaced and closed
What is unique about the Hyoid Bone?
Only bone that does not interact with another bone.
What are the three factors that determine joint stability? List and them and put them in order from least important to most important.
1. Shape
2. Ligament number and location
3. Muscle tone
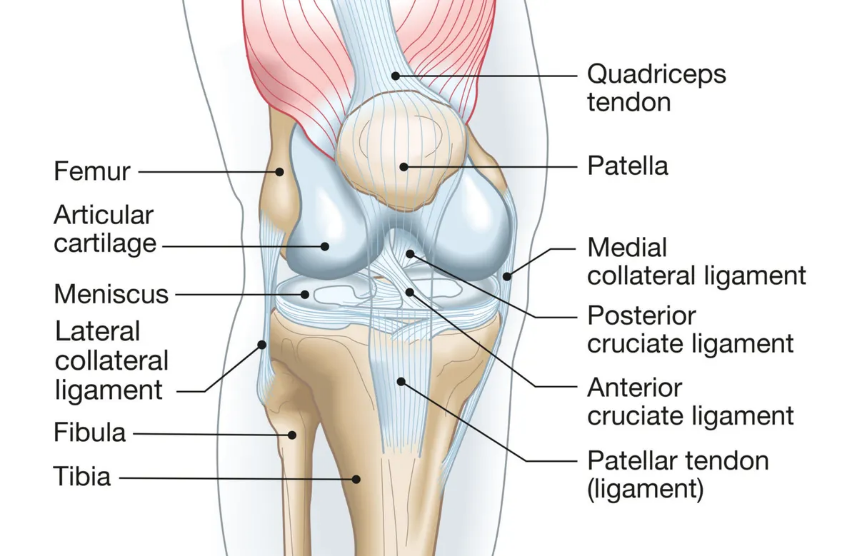
Come draw a knee joint and label the Medial Meniscus, Lateral Meniscus, Anterior Cruciate Ligament, Posterior Cruciate Ligament, Lateral Collateral Ligament, and Medial Collateral Ligament.
What is unique about an infant's skull compared to an adult skull?
They have more bones than an adult and the bones are not yet fused together.
Put the four steps to Bone Fracture Repair in order 1-4:
Bony Callus Formation
Bone Remodeling
Hematoma Formation
Fibrocartilage callus formation
1. Hematoma Formation
2. Fibrocartilage callus formation
3. Bony callus formation
4. Bone remodeling
What is the difference between female and male pelvic girdles?
Females are wider, shallower, lighter, and rounder since they have to give birth.
List 5 synovial joints.
Shoulder, elbow, wrist, fingers, hip, knee, toes, temporomandibular, atlantoaxial, zygapophyseal.
What are all 6 structural supports of the knee?
Medial Meniscus, Lateral Meniscus, Anterior Cruciate Ligament, Posterior Cruciate Ligament, Lateral Collateral Ligament, and Medial Collateral Ligament.
What commonly causes knee injuries?
Horizontal forces/blows
What are the five forces that can cause bone breaks? Come up to the board and label the bones with arrows and list the forces?
Compression, Tension, Torsion/rotation,shear Bending,
What is the Brace Position and its goal?
Put your hands over your occipital bone and arms over your temporal bones.
Goal is to protect your brain stem, cerebellum, and temporal lobes.
What are the three types of joints?
Fibrous, Cartilaginous, and Synovial
What are 4 of the six general features all synovial joints have?
Articular cartilage, joint cavity, articular capsule, synovial fluid, reinforcing ligament, nerves and blood vessels.
What are the three grades of sprains? Describe each one.
Grade 1: Stretched but not torn
Grade 2: Ligament is partly torn
Grade 3: Ligament is completely torn