Occurs despite baseline opioid control and needs rapid-acting analgesia.
Breakthrough pain
Priority action for suspected allergic reaction / anaphylaxis?
Assess and maintain airway
Low WBC count during chemotherapy treatment requires this intervention.
Neutropenic precautions
Most accurate indicator of fluid balance
A patient in DKA is receiving insulin therapy. The nurse must monitor potassium closely for this reason.
What is potassium shifting into the cells causing hypokalemia?
A needlestick injury involving a needle used on an unknown patient requires this urgent step.
HIV post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) must be initiated within this timeframe for maximum effectiveness.
What is initiating post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP)?
What is 72 hours?
First assessment when a patient on epidural morphine has not voided for 10 hours.
Assess for bladder distention
Next step after a patient reports a positive rapid HIV test result
Confirmatory antibody/antigen testing
Minimum distance for visitors of internal radiation implants
6 feet
Diuretic phase
Clean urethral area with provided towelette
Void a small amount into the toilet, then void into the specimen container.
A newly diagnosed HIV patient asks if they still need precautions if they “feel healthy.” The correct teaching point is this.
What is HIV can still be transmitted even when asymptomatic?
Most critical assessment for patients receiving PCA opioids.
Respiratory rate and depth
PPE required for contact precautions
Gloves and Gown
Prevention of chemotherapy-induced nausea
Administer anti-emetics
Priority for electrical burns
S/S of electrolyte imbalance post thyroidectomy
S/S of hypocalcemia
Early findings:
Circumoral numbness (tingling around mouth)
Paresthesias of fingers and toes
Muscle cramps
Fatigue
Anxiety
Unpleasant tingling of hands and around mouth
Life-threatening findings:
Carpopedal spasm (hand/foot spasms)
Laryngospasm (can cause airway obstruction)
Tetany (severe muscle spasms)
Seizures
The MOST important method for preventing spread of infection in healthcare.
What is hand hygiene?
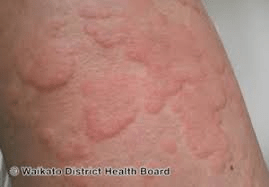
You assess the above image on your patient while in the Operating room. What is your priority action?
Notify the anesthesia provider.
Strategies to support ART adherence in HIV+ patient
Create a daily medication schedule
Reminders
support groups
assess barriers to care
Regular follow up
Simplify regimen as much as possible
Key principle: Adherence interventions must be patient-centered, individualized, and sustained over time. Technical solutions (pill organizers) combined with behavioral approaches (motivational interviewing, education) and ongoing support yield the best outcomes.
The hallmark visible sign of superior vena cava syndrome.
What is facial or periorbital edema
First 8 hour volume to be administered for a total of 30000mL using the Parkland formula._______mL
Set the pump at _____mL/hr for the 8 hrs.
15,000 mL
S/S of Compartment Syndrome
5 P's
A diabetic patient with foot ulcers is at highest risk for this type of infection requiring IV antibiotics.
What is osteomyelitis?
A patient in the pre-operative area tells the nurse that they are afraid of dying. What's the nurse's best action?
Therapeutic communication techniques. Open ended questions.
Neutropenic Precautions
Hand hygiene (#1)
Low bacteria diet
private room
no fresh flowers, standing soil/water
visitor restrictionsA patient receiving external radiation has skin irritation. The nurse should recommend this skin-care measure.
Use mild soap, avoid lotion/heat/ice, and keep the area dry and protected
A patient with SIADH will have urine with this characteristic.
What is high specific gravity and concentrated urine?
Laboratory test that evaluates long-term glucose control
Hemoglobin A1C
HIV targets this immune cell, leading to immune suppression.
What are CD4 T lymphocytes?
A patient post-op begins shivering violently in PACU. The priority action is this.
What is apply warm blankets or warming device?
A patient with a fever and chills begins IV antibiotics. The nurse should draw these labs BEFORE the first dose.
What are blood cultures?
Primary intervention for preventing kidney injury in Tumor Lysis Syndrome.
Most life-threatening electrolyte balance associated with Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Aggressive IV hydration.
Hyperkalemia
A patient with fluid overload will have this lung assessment finding.
What are crackles?
DI = Low SpG and dilute urine
A burn patient with a hoarse voice after house fire may be experiencing this.
What is inhalation injury?
What are other s/s of inhalation injury?