This describes how far an object moves regardless of direction.
What is distance?
This is the SI unit for mass.
What is the kilogram (kg)?
The formula for momentum.
What is mv?
This type of energy is stored due to an object's position or condition, such as a stretched spring or an object at height.
What is potential energy?
In a simple series circuit, this quantity is the same through all components.
What is current?
A flat line on a velocity versus time graph means this.
What is the object is not accelerating or the velocity is constant?
This variable represents displacement.
What is ∆x or x?
The unit of momentum.
What is kg•m/s?
The energy of motion that depends on mass and velocity.
What is kinetic energy?
The equivalent resistance of three resistors of 2 Ω, 4 Ω, and 6 Ω connected in series?
What is 12 Ω?
This is the shape of a velocity versus time graph for constant acceleration.
What is a (straight) diagonal line?
The standard unit for force.
What is the newton (N)?
This law says total momentum stays the same in a closed system.
What is the law of conservation of momentum?
The unit of energy used in physics, equivalent to 1 kg·m²/s².
What is a joule?
This circuit has the same potential difference (V) in all branches.
What is a parallel circuit?
This is the area under a velocity versus time graph.
What is displacement?
The variable p stands for this.
What is momentum?
A collision where objects stick together is this type.
What is an inelastic collision?
The rate at which work is done or energy is transferred over time is called this.
What is power?
The equivalent resistance of two resistors of 3 Ω and 6 Ω connected in parallel.
What is 2 Ω?
When an object's velocity and acceleration have opposite signs, the object is doing this.
What is slowing down?
This unit, named after an English scientist, is used to measure power.
What is the watt (W)?
A force applied over time causes this.
What is impulse?
This law states that the total energy remains constant if no external forces act on a system.
What is the Law of the Conservation of Energy?
A wire placed here will cause all three bulbs to be lit.
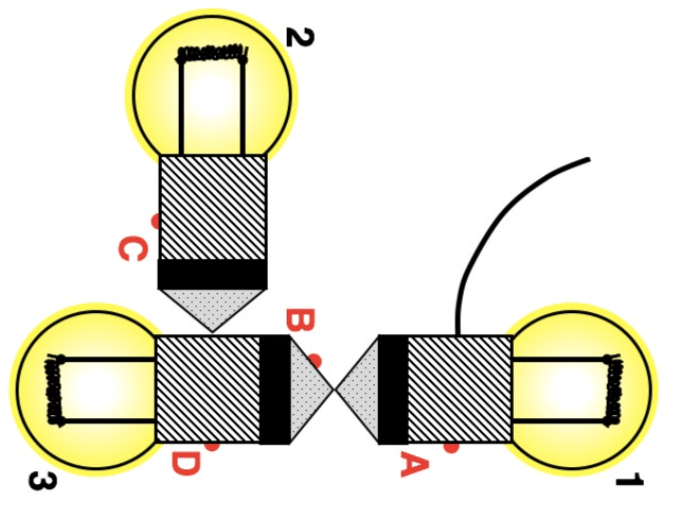
What is position C?