What is the difference between an observation and an inference in a scientific investigation?
Observation: something you notice using your senses or tools (e.g. “The water is boiling”). Inference: a conclusion or explanation based on observations (e.g. “The water is boiling because it’s at 100°C”).
Which heavenly body is at the centre of our Solar System?
The Sun.
Define force in scientific terms.
A push or pull on an object that can change its motion, shape, or direction.
Name the two poles of a magnet.
Attraction and Repulsion
List the five kingdoms commonly used to classify living things.
Animals, Plants, Fungi, Protists, Monera (Bacteria).
Name one advantage of repeating trials in an experiment.
Improves reliability by showing consistent results and reducing the effect of random errors.
Why do we see different constellations at different times of the year?
Because Earth orbits the Sun, changing our view of the night sky.
Give one example of when forces are balanced, and another when forces are unbalanced.
Balanced: a book resting on a table. Unbalanced: a ball being kicked and speeding up.
What are the two terms starting with "A" and "R" that describe magentic force?
Attraction and Repulsion
What key features are similar between frogs and fish, and what is the key difference?
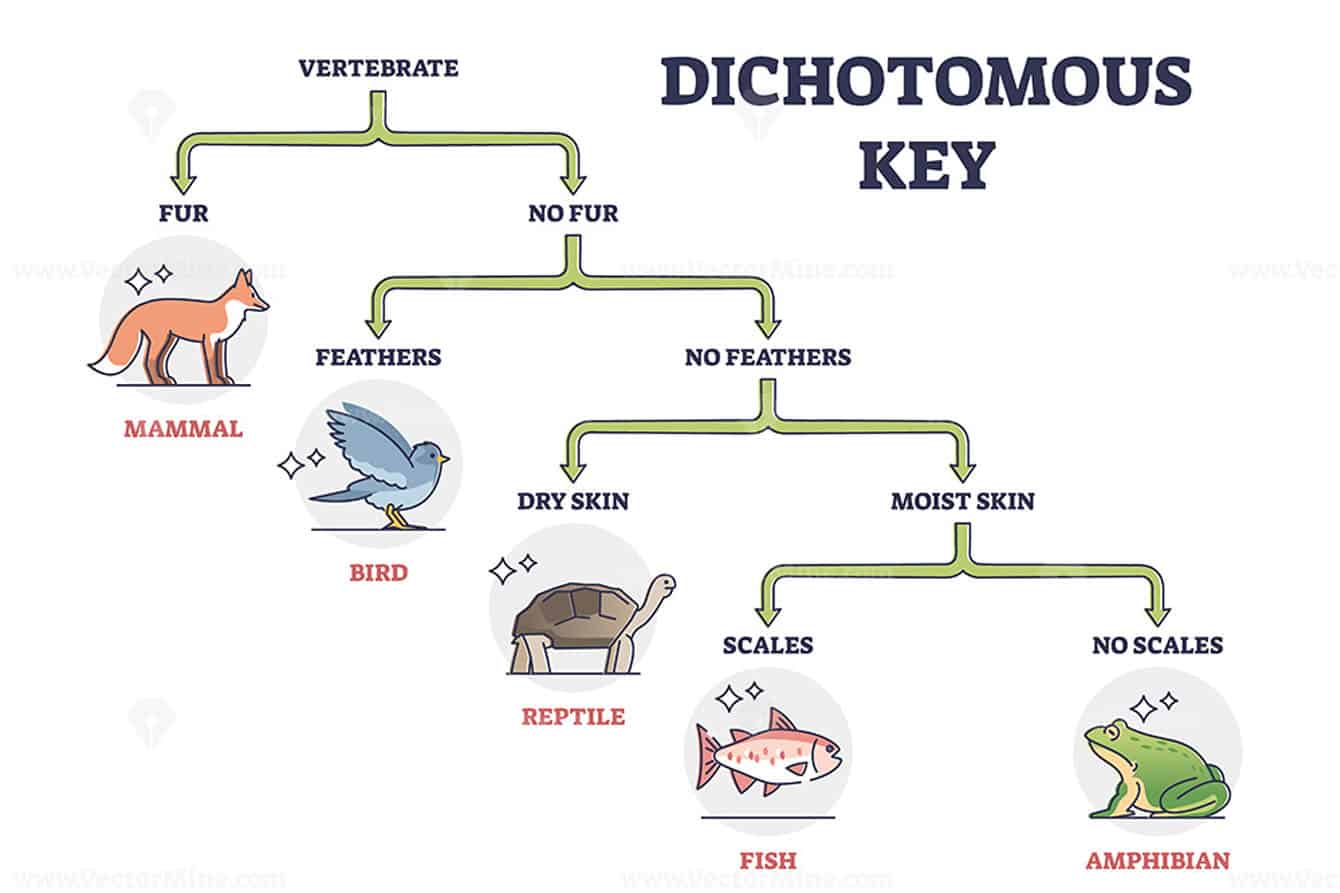
They both have no fur, no feathers and moist skin, however, a fish has scales and a frog does not
Identify the independent and dependent variables in this example: A student tests whether sunlight affects plant growth.
Independent: amount of sunlight. Dependent: plant growth (height or mass)
How does the tilt of Earth’s axis cause the seasons?
The tilt makes parts of Earth receive more direct sunlight at different times of the year, changing temperature and daylight hours.
Name four different types of forces and describe what each one does.

Explain how a pulley makes lifting a load easier.
It changes the direction of the force and can reduce the effort needed by spreading the load over more rope lengths.
Name two organelles found in plant fungi and animal cells.
Nucleus and mitochondria
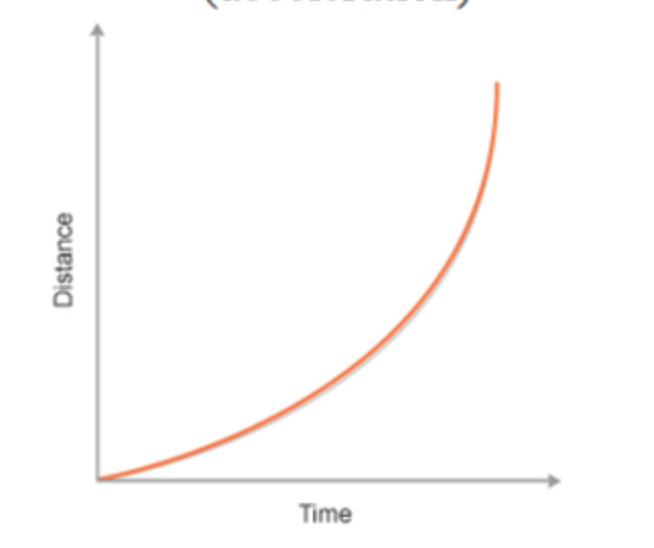 Describe the trend of this graph - As "___" increases "______" (increases/decreases)
Describe the trend of this graph - As "___" increases "______" (increases/decreases)
As time increases, distance increases
What are the TWO hemispheres on Earth called, and how are they significant in terms of seasonal change
The northern and southern hemispheres.
Due to the Earth's tilt, at certain times of the year, more direct sunlight hits that hemisphere, causing summer.
For example, in December, the Southern Hemisphere is tilted towards the sun; therefore, more direct sunlight is hitting the Southern Hemisphere. This causes summer.
On the other hand, during December, the Northern hemisphere is tilted away from the sun, with less direct sunlight, causing winter.
Explain what happens to the motion of an object when an unbalanced force acts on it.
It will accelerate, decelerate, or change direction depending on the direction of the force.
The woomera is a traditional Aboriginal tool. What kind of simple machine is it, and how does this increase mechanical advantage.

Lever - It allows you to throw a spear further and faster with less work
What organelles are ONLY found in plant and fungi cells
(Bonus 100 points to identify an organelle ONLY found in plant cells not fungi or bacteria)
Cell wall, vacuole
Bonus - Chloroplast
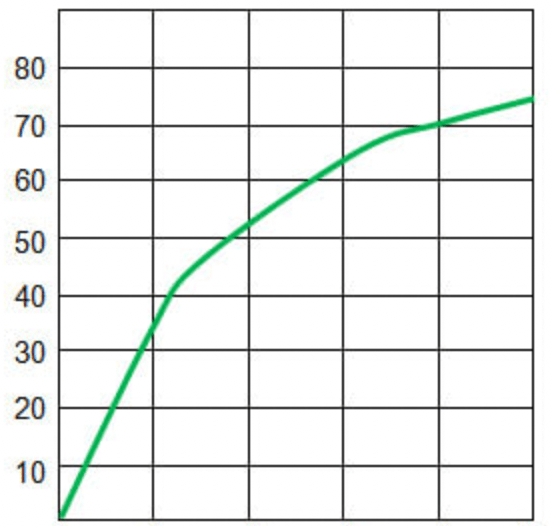
Identify 4 things missing from this graph
title
axis heading for independent and dependent variable
scale on x axis
What is the difference between a solar and lunar eclipse?
In a solar eclipse - The Moon moves between the Earth and the Sun, blocking sunlight from reaching Earth
In a lunar eclipse - The Earth moves between the Sun and the Moon, casting a shadow on the Moon
What direction is this car moving in?
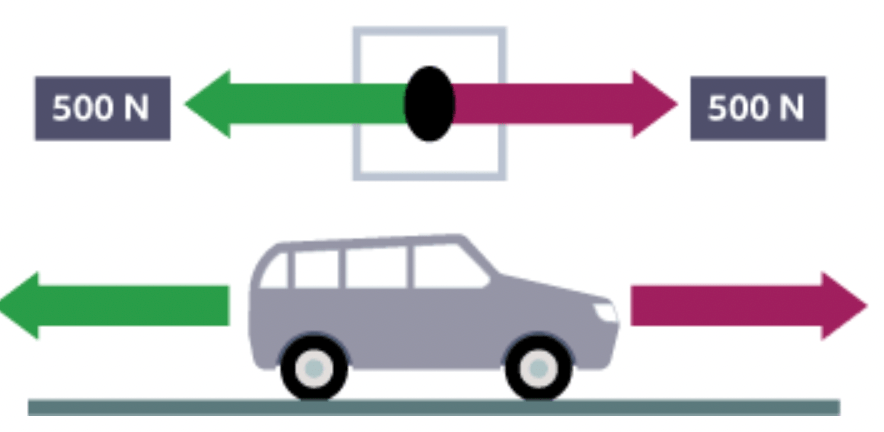
The car is stationary
Identify what type of simple machine this is, what each term is AND what they mean
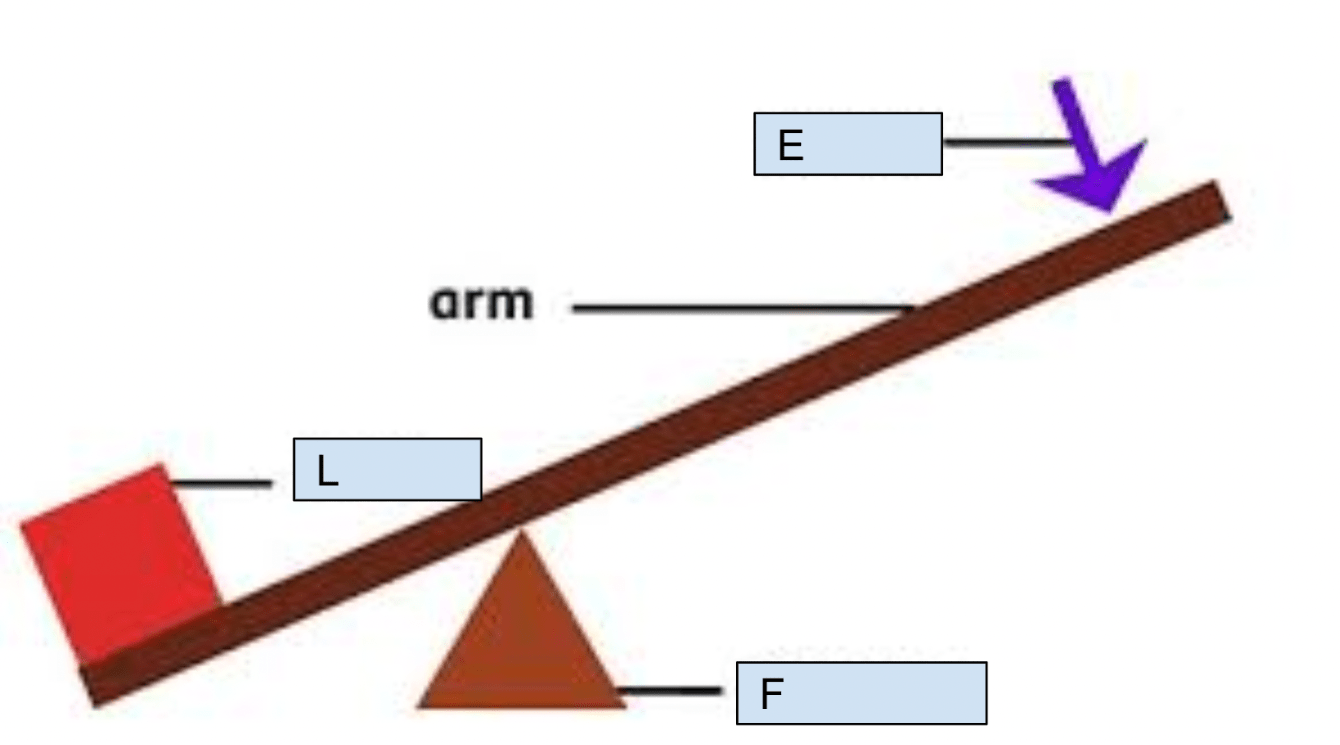
Seesaw is a lever
Load - The object you are trying to lift
Effort - is the amount of work you apply to the machine
Fulcrum - is the pivot point that allows the work to be easier
Name the organelles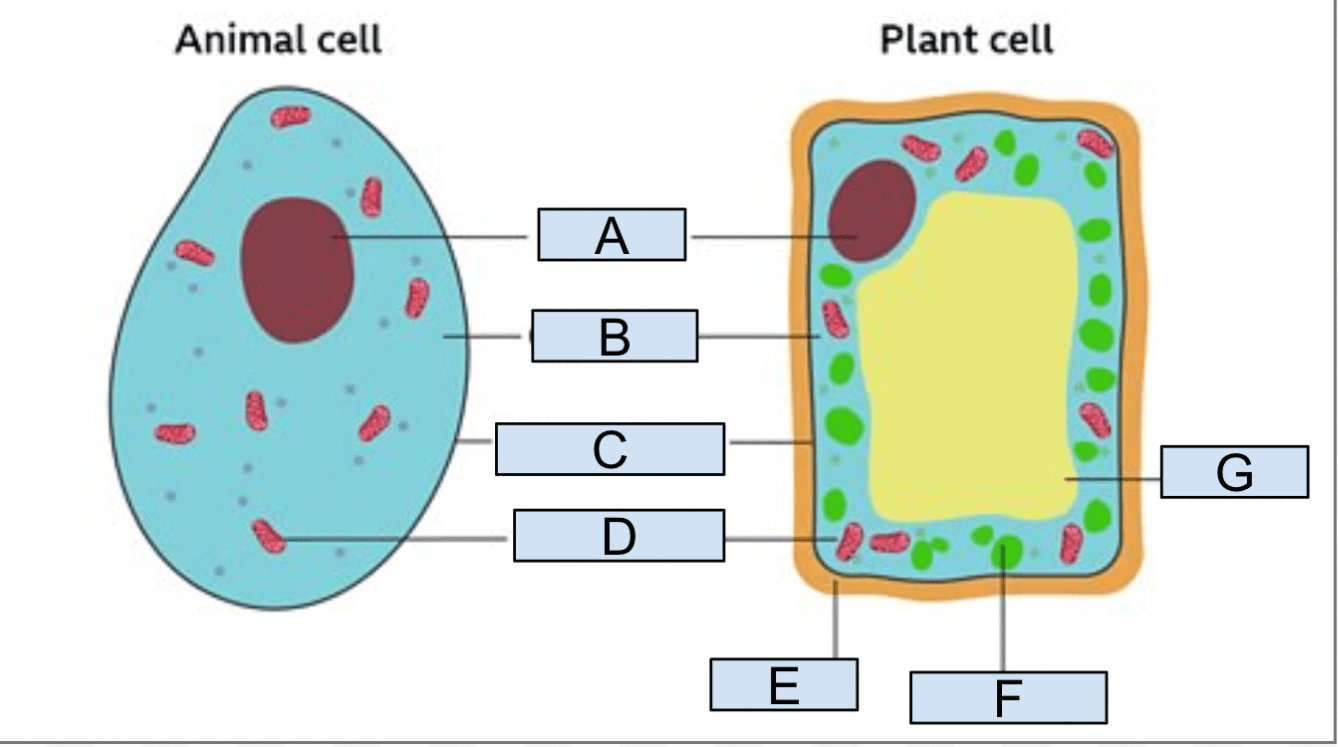
A - Nucleus
B- Cytoplasm
C - Cell membrane
D - Mitochondria
E - Cell Wall
F - Chloroplast
G - Vacuole