What muscle is commonly injured in soccer players and attaches to the AIIS
Rectus Femoris
Name the 3 conditions of the unhappy triad
Tear of
MCL
Medial Meniscus
ACL
What is the innervation of the short head of the biceps femoris muscle?
Peroneal component of the sciatic nerve
A 70 year old male has a slow, shuffling gait with reduced arm swing and forward-leaning posture
What part of the basal ganglia is most likely affected ?
Substantia Nigra
A T12 ASIA C patient would like to perform wheelies in his wheelchair. Would you recommend the wheels be placed more anteriorly or posteriorly to facilitate his goal
Anterior
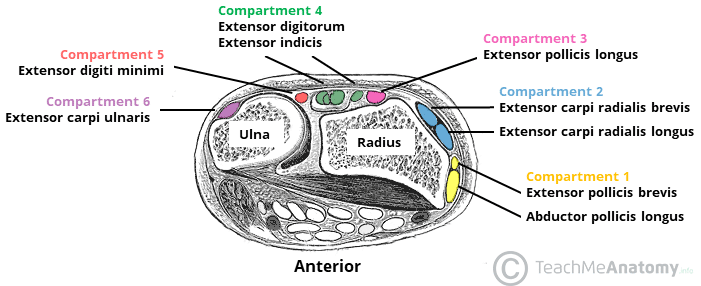
What muscle is in the 3rd extensor compartment of the wrist
Extensor Pollicis Longus
- Patient: A 13-year-old boy, a basketball player.
- History: Complains of a dull, aching pain in the front of his right knee for several weeks, which has recently become worse. He denies any specific injury but notes the pain increases significantly after basketball practice and games, especially after jumping or sprinting. He sometimes limps after sports.
- Physical Exam: Tenderness and mild swelling over the tibial tubercle (bump below the kneecap) on the right knee. Resisted knee extension (straightening the knee) or direct pressure on the tubercle increases pain.
- DIAGNOSIS
Osgood Schlatter
Name the muscles that are innervated by the ulnar nerve in the forearm?
-Felxor carpi ulnaris
-Medial half of flexor digitourm profundus
An elderly female complains that her legs "twitch". Symptoms occur only during the night.
What class of medication is most often used to treat her condition.
Dopaminergic agents
Name this phase of gait
Point in time when foot comes in contact with the ground.
Initial Contact
Name the 4 principal muscles of shoulder abduction
A female soccer player complains of a snapping sensation in her right hip, which worsens with play.
The snapping worsens with internal rotation.
What muscle is most likely involved?
Iliopsoas
Describe the nerves and muscles involved in medial and lateral scapular winging
-medial Serratus Anterior (Long Thoracic Nerve)
-lateral trapezius (CN 11)
A medical student is evaluating plantar flexion tone. When assessing spasticity at the foot he notes that it is more difficult to range when the knee is straight. When the knee is bent it becomes easier to range the foot.
Which muscle would you be more likely to inject botox?
Gastrocnemius
How many degrees must a Tilt and space wheelchair rotate posteriorly
At least 45 degrees
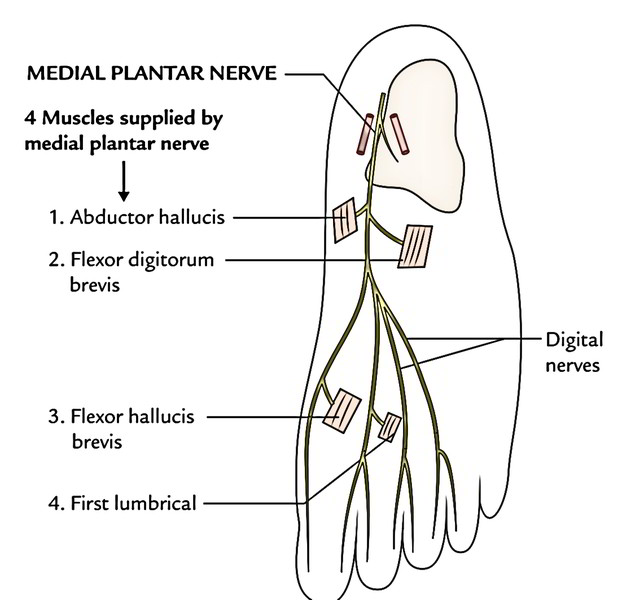
Name 3 muscles innervated by the medial plantar nerve of the foot
Name 2 equipment modifications that could be made to treat tennis elbow in a tennis player
Decrease string tension
Increase grip size
Name the 2 muscles that lateral femoral cutaneous nerve sits
-Sartorious
-Tensor Fascia Latae
In deep brain stimulation for treatment of parkinsons where would the electrodes be placed?
Name 2 structures
Globus Pallidus Internus
Subthalamic Nucleus
The proper height of the walker is determined by having the patient stand upright with the shoulders relaxed and the elbows flexed to ____ degrees.
20 degrees.
Name the 3 muscle tendons that make up the pes anserine and give their respective nerve innervations
Sartorious, Gracilis, Semitendinosous
Femoral, Obturator, Tibial
SGT FOT
Which graft choice is most commonly used in modern UCL reconstruction? Tommy John Surgery
Palmaris longus autograft
Explain what nerve is commonly affected by rapid weight loss and give the proposed mechanism
depleting the protective fat pad around the peroneal nerve at the fibular head, making it vulnerable to compression (entrapment) and damage (neuropathy).
Explain this manuever.
The Hoover maneuver helps tell whether leg weakness is organic (real neurologic) or non-organic (functional). Normally, when a person lifts one leg, the other leg automatically pushes down. If downward pressure is felt from the “weak” leg when the opposite leg is lifted, the weakness is organic. If no downward pressure is felt, the weakness is likely non-organic.
patellar tendon
medial tibial flare
anterior compartment
lateral tibial shaft
popliteal area
