A biconvex, lens-shaped hyperdensity on a non-contrast CT that does not cross cranial sutures is the hallmark of:
Epidural Hematoma
Usually arterial (Middle Meningeal Artery); the blood is contained by the suture lines where the dura is tightly adhered to the skull.
NOT: Subdural Hematoma: Crescent-shaped; can cross suture lines because it is in the potential space between the dura and arachnoid. Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage: Occurs within the brain tissue. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage: Fills the CSF spaces/cisterns.
What mode of imaging is required for the diagnosis of MS?
None
The McDonald criteria of at least two lesions disseminated in space and time. A diagnoses can be made on clinical evidence alone.
Many pts will not meet clinical criteria early in the disease course and MRI, CSF analysis, and visual evoked potentials are helpful in meeting the Dx criteria.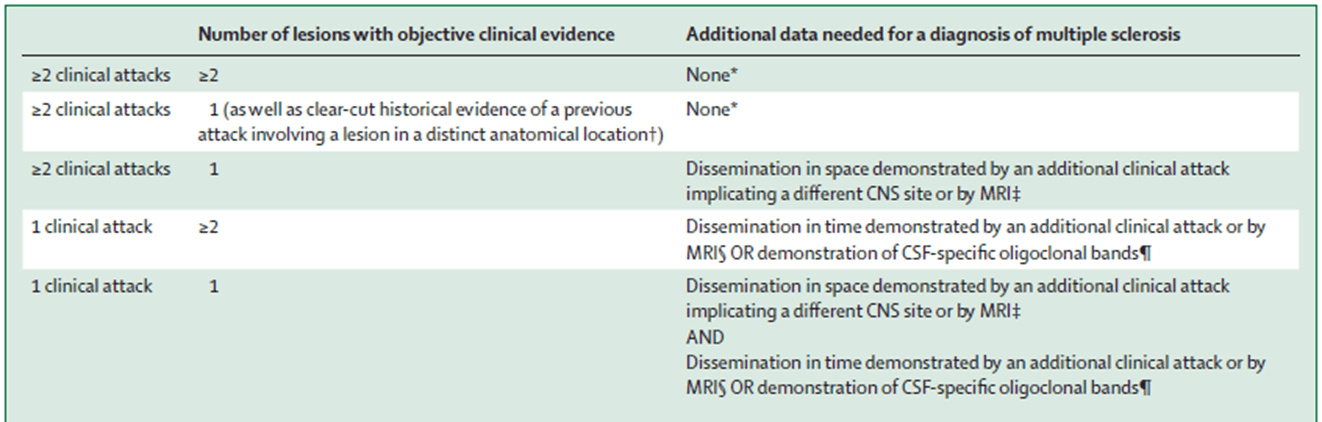
This simple, crucial maneuver must be performed on any pregnant patient in cardiac arrest to relieve aortocaval compression.
manual left uterine displacement
As of 2023, this is the name to replace Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease
This type of edema does not restrict diffusion, preserves the gray-white junction, and is not directly consistent with ischemia.
vasogenic edema
(cytotoxic edema blurs the gray-white junction, restricts diffusion, and is consistent with ischemia.
Antidote for suspected Magnesium toxicity in maternal arrest:
Calcium Gluconate
The terminology used to refer to brightness on CT and MRI
CT - density (hypo, iso, hyper)
MR - intensity (hypo, iso, hyper)
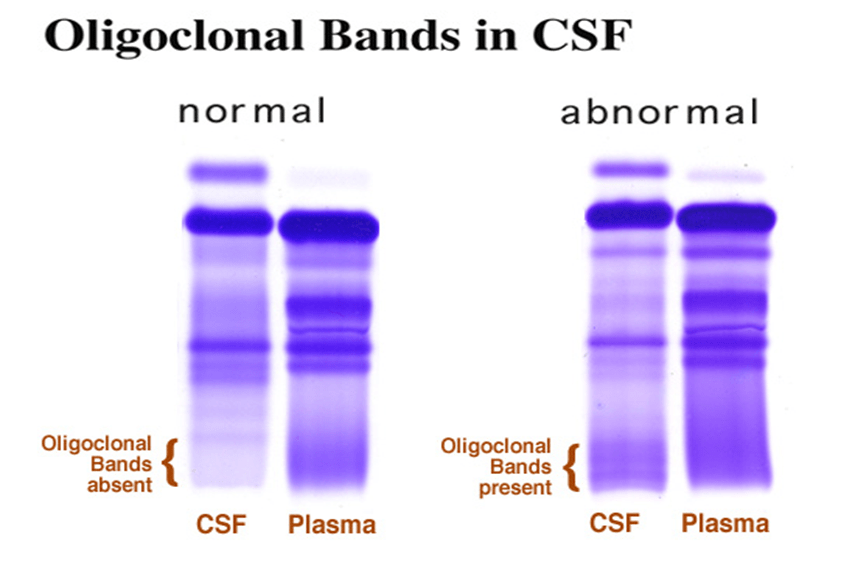
The presence of immunoglobulins in CSF that are visible on gel electrophoresis are referred to as this, as seen in MS.
oligoclonal bands
This catastrophic event, a unique cause of cardiac arrest in pregnancy, involves fetal material entering the maternal circulation.
amniotic fluid embolism
Patients with MASH and F3 fibrosis die most commonly from this
CVD
Vasogenic or cytotoxic edema?
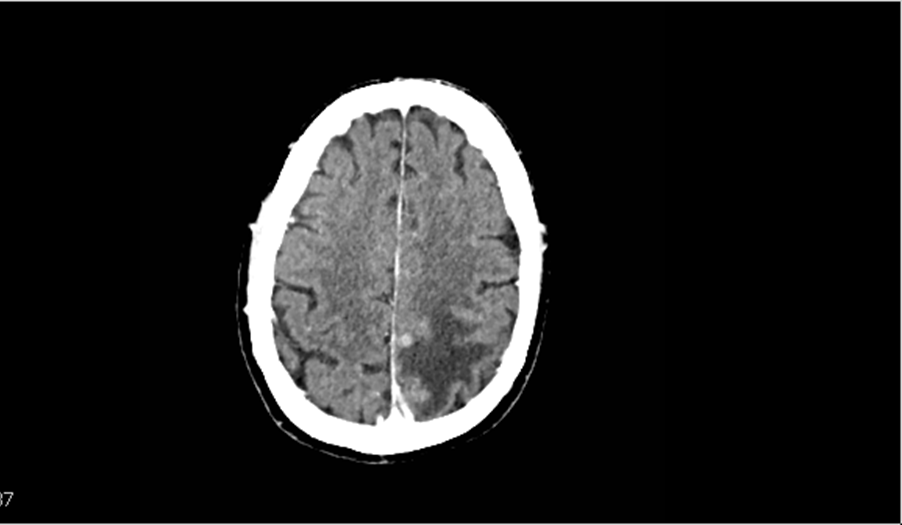
Vasogenic edema
preserves the gray-white junction
Which niCM has a 'Cherry on top' apical sparing pattern?
Cardiac Amyloidosis
Myocardial strain imaging shows preserved contraction at the apex and impaired contraction at the base.
A hyperdense vessel sign on non-contrasted CT suggests this
intraluminal thrombus
one of the earliest indicators of an acute ischemic stroke
electrical pain with neck flexion is known as this eponymous sign
Lhermitte sign
This is the recommended time frame from the start of maternal arrest to delivering the baby via perimortem cesarean section if there is no return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC).
5 minutes
Perimortem Cesarean Delivery (PMCD) should be considered if ROSC is not achieved within: 4 minutes. Goal is delivery by 5 minutes to improve maternal hemodynamics and fetal survival.
guidelines from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology (AACE) suggest this diabetic medication for off-label use in patients with MASH
pioglitazone
While some newer agents like GLP-1 receptor agonists may show greater reductions in liver fat, pioglitazone remains a valuable option due to its affordability and accessibility. (proposed anti-inflammatory, improved insulin sensitivity, lipids in SQ instead of liver)
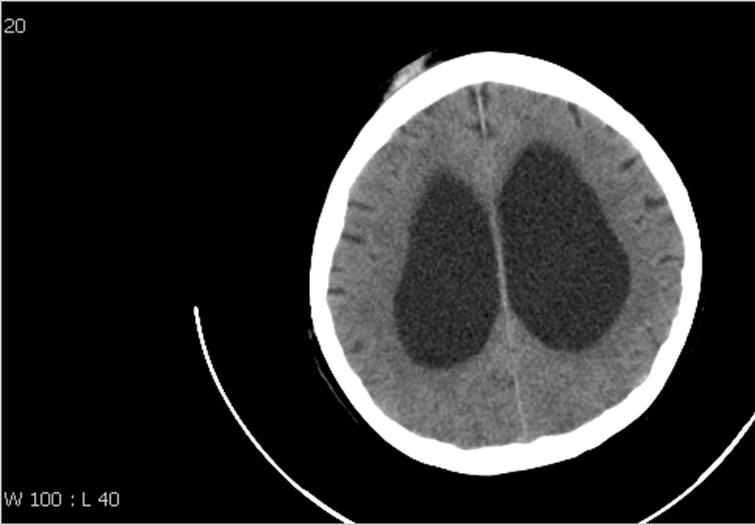
Exvacuo or normal pressure hydrocephalus?
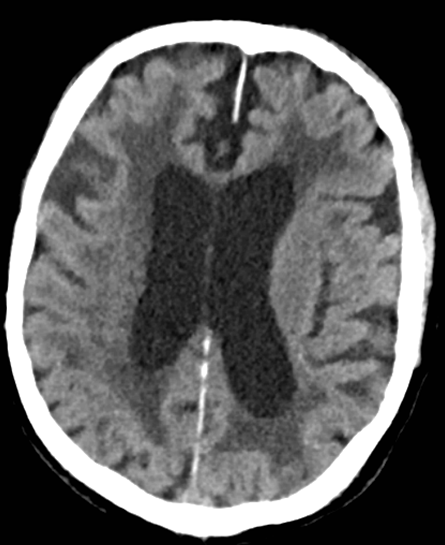
Ex-vacuo hydrocephalus with diffuse cortical atrophy.
Absence of cortical atrophy below
Three phases of Loeffler's endocarditis.
necrotic
thrombotic
firbotic
On MR imaging, this is color of CSF on T1, T2, and FLAIR- weighted images
T1 - dark
T2 - bright
FLAIR - dark
temporary worsening of neurological symptoms in people with multiple sclerosis (MS) and other demyelinating diseases when their body temperature rises
Uthoff phenomenon, sign or syndrome
In addition to the code team, these two specialized teams should be summoned immediately for a maternal cardiac arrest.
Neonatal and Obstetrics
These are three of the components of FIB-4 score
Age, AST, ALT, and Platelets
DWI is hyperintense in the same location that ADC is hypointense. Dx and timeframe?
Acute infarction < 1 week
Cardiac myosin inhibitor for obstructive HCM
Mavacamten
EXPLORER-HCM Trial
The sensitivity of DWI to detect ischemic lesions (+/- 3%)
92%
identify 2 different mechanism of action of highly effective medications for the treatment of MS.
oral: Nrf2 modulators (dimethylfumarate, diroximel fumarate, monomethyl fumarate) Activates Nrf2 anti-inflammatory pathway-leads to alteration of dendritic cell activation and Th cell differentiation
S1PR modulators Binds to sphingosine 1-P receptors on lymphocytes causing peripheral sequestration: Gilenya* (S1PR 1,3,4,5), Mayzent* (S1PR 1,5), Zeposia* (S1PR 1,5)
Nucleotide synthesis inhibitors - blocks proliferation of activated T cells (teriflunomide)
IV: anti CD20 (ocrelizumab, rituximab)
integrin inhibitors - blocks integrin VLA-4,(natalizumab)
antiCD52 - alemtuzumab - depletes B-/T-cells, monocytes, macrophages, NK cells, granulocytes
Recommended energy dose for defibrillation in a pregnant patient. (biphasic and monophasic)
biphasic 200J (120 - 200J)
monophasic 360J
Which recently FDA-approved medication is the first targeted treatment for MASH with F2-F3 fibrosis?
Resmetirom (Resduffra) THR-Beta agonist (localized to liver)
subacute infarction (T2 shine through) > 1-2 weeks
(double bright --> 2 weeks)
Identify the niCM with Epsilon Wave and fibro-fatty RV replacement:
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
Caused by desmosomal mutations.
Dx and time frame: DWI hyperintense and same location on FLAIR is hypointense.
hyperactue Infarction < 4.5 - 6h
DWI-FLAIR mismatch (tissue clock)
DWI hyperintensity (bright spot) and a corresponding FLAIR hypointensity (dark spot) in the same location is highly suggestive of a hyperacute ischemic stroke, typically within the first 4.5 to 6 hours of onset.
MS drug requiring JC Virus (JCV) antibody monitoring:
Natalizumab
High risk of PML if JCV antibody is positive and treatment exceeds 2 years.
Which ACLS medication must be avoided in a pregnant patient during cardiac arrest?
None
ACLS drugs/doses are used because maternal survival is the priority for fetal survival.
This non-invasive imaging modality is the most accurate method for identifying advanced fibrosis (F3-F4).
Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE)
Useful MR modality for for identifying microhemorrhages 2/2 diffuse axonal injury (DAI) or amyloid angiopathy
susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI)
amyloid angiopathy
16kDa fragment of this hormone implicated in post-patum cardiomyopathy
prolactin
Region of the brain not well visualized by CT
posterior fossa
First-line treatment and dose for acute MS relapse
Typically 1000mg Methylprednisolone daily for 3-5 days.
(AAN Practice Guidelines: Corticosteroids in MS.)
Hormone responsible for increasing airway edema in pregnancy, affecting airway management.
Estrogen causes increased airway edema
also important: a gravid uterus elevates the diaphragm, reducing Functional Residual Capacity
What is the FIB4 value below which you can exclude advanced fibrosis in a patient 65 or older?
< 2.0 (according to new threshold)
< 1.3 in ages 36-64
MRI lesions oriented perpendicularly to the lateral ventricles seen in MS
Dawson's Fingers
Represents demyelination along periventricular venules
PYP scan Grade 2/3 is diagnostic for:
Transthyretin Amyloid (ATTR)
PYP was initially used for bone scintigraphy, bone tracers bind to TTR fibrils, not typically to AL fibrils.
technetium-99m pyrophosphate (Tc-99m PYP)