Gram for gram does lipids provide cells with more energy? TRUE OR FALSE
TRUE
Which of the following is a function of a carbohydrate?
A. Insulation
B. Forms the cell wall
C. Regulates enzymes
D. Gene expression
B. Forms the cell wall
Which macromolecule helps animals conserve heat and acts as a insulation?
Lipids (fat)
How does diffusion benefit the cells?
A. Cells decrease and increase concentration of certain molecule
B. Cells achieve balance with their environment
C. A&B
D. None
C. A&B
Which of the following is a function of nucleic acid?
A. Increases the rate of chemical reaction
B. Stimulates metabolism in all body cells
C. Activates secretion of the body's hormones
D. Stores genetic information and helps to make proteins
D. Stores genetic information and helps to make proteins
Which are not a characteristic of enzymes?
A. they act as a catalyst
b. they are proteins
c. they are unaffected by change in temperature
d. they react with a specific substrate
c. they are unaffected by change in the temperature.
Lipases are enzymes that speed up the digestion, which biomolecule do they belong to?
Lipid
Which two macromolecules store energy?
Carbohydrate, Lipids
Water moves freely across a cell membrane by?
A. Exocytosis
B. Endocytosis
C. Osmosis
D. Meiosis
C. Osmosis
Proteases are enzymes that hydrolyze peptide bonds, which biomolecule do they belong to?
Protein
Based on this image
A. Enzymes work most effectively at low temperatures
B. Enzymes are not affected by temperatures
C. Enzyme function decreases after a certain favorable temperature
D. Raising temperature always makes an enzyme work better
C. Enzyme function decreases after a certain favorable temperature
 Active transport occurs through which biomolecule?
Active transport occurs through which biomolecule?
Protein
Why are proteins essential to all life?
A. They provide genetic information
B. They are used for energy storage
C. They form cellular membranes
D. They build structure and carry out metabolism
D. They build structure and carry out metabolism
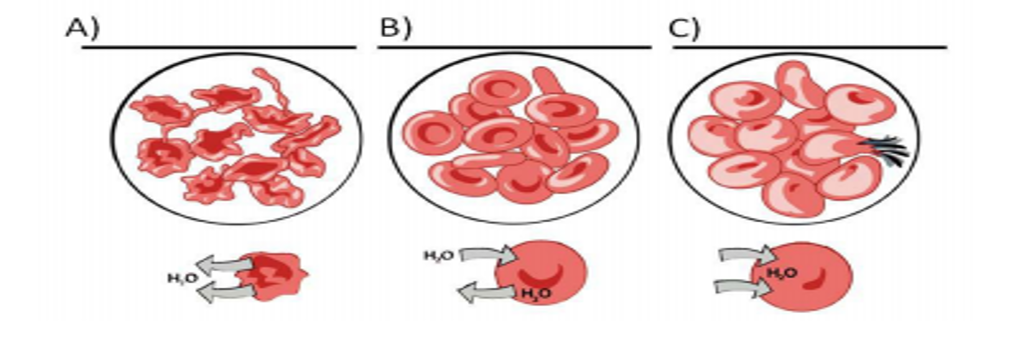
Osmosis is the intake of water molecules, when a cell swells and bursts it is?
Hypotonic
Four different nucleotides are used as building blocks for DNA? How can you tell one from another?
A. The shape of the deoxyribose sugar
B. The nitrogenous base
C. The length of the phosphate group
D. The type of fatty acid
B. The nitrogenous base
Bonus(Name the 4 nucleotides)
Name: A,B,C,D
A:Enzyme
B:Substrate
C:Enzyme/Substrate Complex
D:Product
Which cellular process takes place in the ribosomes?
A. The conversion of radiant energy to glucose
B. They synthesis of new proteins
C. The breakdown of waste materials
D. The replication of nucleic acids
B. They synthesis of new proteins
FREE
When molecules are transported into a cell with a protein present and there is no energy being used, what type of passive transport is this?
Facilitated Diffusion
What element is found in amino acids, but not in carbs?
A. Carbon
B. Phosphorous
C. Hydrogen
D. Nitrogen
D. Nitrogen
Name the 4 elements of the biomolecules
Carbohydrate- CHO
Lipids-CHO
Protein- CHON
Nucleic acid-CHONP
FREE
How do cells maintain homeostasis without using energy?
A. Membrane proteins breakdown molecules to move other molecules from low concentration to high concentration
B. Membrane proteins use the negative charge inside of the cell to increase the concentration of a chemical inside of the cell
C. Maintaining osmotic balance by taking in or releasing water to match the water concentration of the extracellular environment
D. Form the cell membrane around food to create a vacuole that is kept separate from the rest of the cytoplasm while enzymes break down the food
C. Maintaining osmotic balance by taking in or releasing water to match the water concentration of the extracellular environment
What are the 3 types of passive transport?
Diffusion
Facilitated Diffusion
Osmosis
Name the three
Hypertonic, Isotonic, Hypotonic