The type of analysis of motion that describes how the human body "looks" on visual observation as it performs a skill or athletic movement.
What is the qualitative analysis?
The magnitude of the resultant velocity.
What is speed?
The type of acceleration when the athlete is speeding up while moving towards the ground (T to I) and slowing down while moving up (I to T).
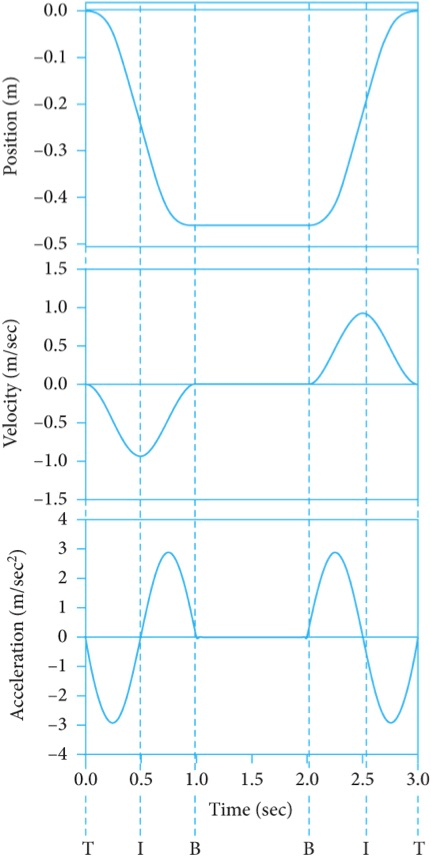
What is negative acceleration?
Resistance of an object to having its state of angular motion changed.
What is the rotational inertia?
This law states that an object at rest or in motion at a constant velocity will remain in this state unless acted on by an external force.
What is the Law of Inertia (Newton's First Law)?
The description of this FMS movement that the "torso is parallel with tibia and the shoulders are elevated during the squat" is an example this approach of qualitative analysis?

What is the composite approach?
This rule governs the direction of an axis perpendicular to the plane defined by two other axes in a Cartesian coordinate system.
What is the right-hand rule?
This is the vertical velocity of someone jumping at 5 m/s at an angle of 60 degrees.
What is 4.33 m/s?
The perpendicular distance between the joint's axis of rotation and the line of action of a muscle's force.
What is a moment arm?
sumF=m*a
What is the law of acceleration (Newton's Second Law)?
This quantity possess a magnitude and a particular direction associated with it.
What is a vector quantity?
The change in linear velocity over time.
What is the linear acceleration?
The type of acceleration of an athlete who is slowing down when moving towards the ground during a squat as depicted here:
What is positive acceleration?
The shoulder joint angle in the sagittal plane that would minimize the torque induced by the dumbbell.
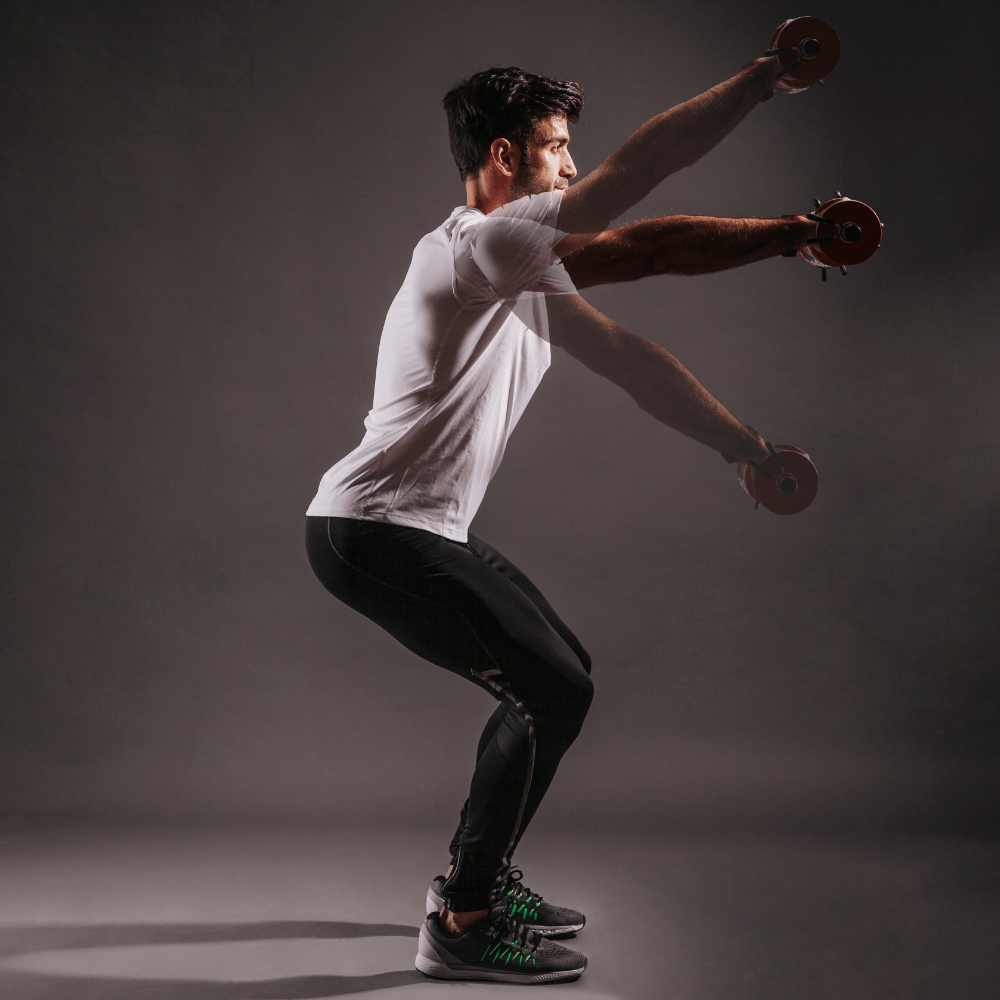
What is 0° flexion?
The point in this graph in which the vertical ground reaction force is equal to the jumper's weight.
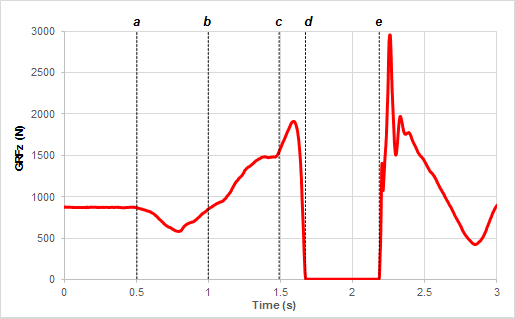
What is a?
Kicking a soccer ball is an example of this type of kinetic chain.
What is an open kinetic chain?
Parts of a resultant vector, two or more vectors that are acting in different directions
What are components?
The acceleration of an athlete who is moving towards the ground at a constant speed during a squat as depicted here:
What is zero acceleration?
This is minimized when a runner flexes her knee during the swing phase of running, thereby maximizing the acceleration induced by muscular torque (i.e., hip flexors).
What is the radius of gyration (or moment of inertia)?
The time interval in this graph in which the jumper's COG would have positive acceleration while moving away from the ground (before take-off).
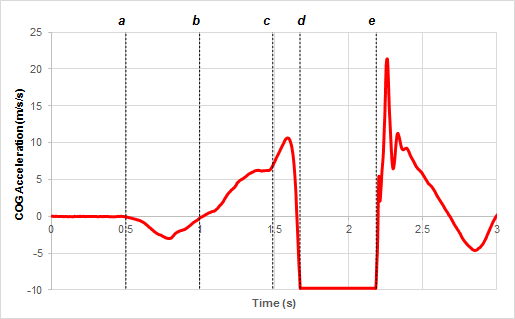
What is c and d?
The magnitude of the horizontal (compressive-distractive) component of a 100 N biceps force when the elbow is flexed at 90 degrees:
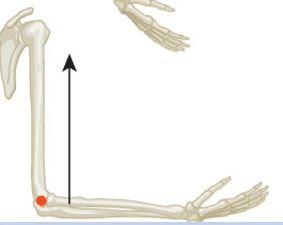
What is 0 N?
The horizontal component of the biceps force at this angle (<90 degrees).
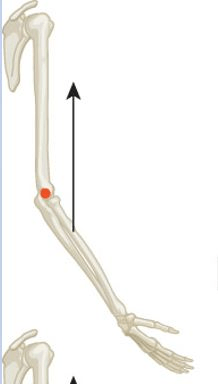
What is compressive?
The time interval in the following countermovement jump before take-off in which the athlete is speeding up in the downward direction (+ = up; - = down).
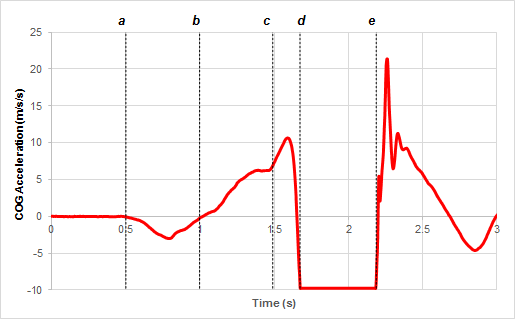
What is between a and b?
"Nursemaid's elbow" is a subluxation of the radial head caused by this center-seeking force when a child is swung in circles by their hands.
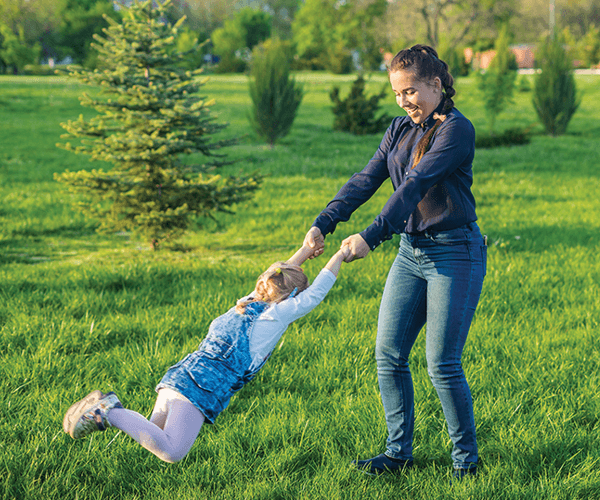
What is centripetal?
This law of motion states that forces work in pairs and provides the foundation on which the ground reaction force is described.
Newton's Third Law