Which pattern in a fetal heart rate signifies fetal well-being representing fetal alertness or arousal states
Acceleration
You are charge nurse and you notice that one of your nurses has been checking in on her patient who is in labor, but there is no documentation on that patient for this shift and it is already noon. What should you remind this nurse about documentation of observations of the laboring mother and baby?
Documentation of all observations (e.g., maternal vital signs, fetal heart rate and pattern, progress of labor) and nursing interventions, including the woman’s response, must be accurate, complete, timely, and according to agency policy.
What is the term for when the abdominal wall muscle separate in a pregnant woman?
muscles separate- diastasis recti abdominis
Which vegetable is said to be a treatment for engorgement?
Iceberg lettuce
Cabbage
collard greens
Romain lettuce
Cabbage
Name the 2 main patient teachings for rubella vaccine related to pregnancy
teratogenic, no pregnancy for 1 months after
is a type of body movement or behavior that provides the observer with cues.
Reciprocity
Mutuality
Synchrony
Engrossment
Reciprocity
Why do babies spit up so much?
cardiac sphincter
the ring of muscle between the esophagus and the stomach is not yet fully developed, why babies spit up
A baby at 11% percentile for gestational age would be considered
LGA
AGA
SGA
GGA
aga
LGA – large for gestational age, >90th %
AGA – appropriate for gestational age, 11th – 89th percentile
SGA – small for gestational age, <10th %
How often do newborns feed?
1-2 hours
2-3 hours
3-4 hours
4-5 hours
Feed approximately every 2–3 hours (8–12 feedings per 24 hours)
When is a biophysical profile done?
Biophysical profile (done for non-reactive NST)
noninvasive dynamic assessment of the fetus and its environment that is based on acute and chronic markers of fetal disease. It uses both real-time ultrasound and external fetal heart rate monitoring. This test includes assessment of five variables, namely fetal breathing movements, fetal body movements, fetal tone, non stress test (fetal heart rate reactivity), amniotic fluid volume.
What vaccine decreases the effects of the rubella vaccine?
Rhogam
Normal duration for a normal contraction
45 to 80 seconds, not generally exceeding 90 seconds.
What does a cervical exam of 9/90%/+1 mean
9cm
90% effaced
station +1
When can a non-lactating woman expect to resume menstruation after giving birth?
s early as 27 days after birth in nonlactating women, with a mean time of about 7 to 9 weeks. About 70% of nonlactating women resume menstruating by 12 weeks after birth
fertility returns
A nursing student would be incorrect if the following was selected as a risk for excessive bleeding:
Grand multiparity
Overdistention of uterus
Diabetes
Rapid labor
Prolonged labor
Diabetes
Grand multiparity
Overdistention of uterus (twins)
Rapid or prolonged labor
Retained placenta, placenta previa, or abruptio placentae
Medications (tocolytics, oxytocin)
Operative procedures (cesarean birth, vacuum extraction)
Preclampsia or coagulation defects
What does the coombs test look for?
(+ test = mother has Rh antibodies, - result would indicates no Rh antibodies)
The test is looking for "foreign" antibodies that are already adhered to the infant's red blood cells (rbcs), a potential cause of hemolysis.
refers to the "fit" between the infant's cues and the parent's responses.
Reciprocity
Mutuality
Synchrony
Engrossment
Synchrony
Which of the following is correct for a newborn
Pulse 190
RR 32
WBC 30,000/mm3
BGM 200
Vital signs
Pulse: 120 to 160 beats per minute
resp rate: 40 to 60 breaths per minut
Labs:
blood sugar- 70 and 150 mg/dL
Wbc- 9,000 to 30,000/mm3
Which of the following is not a medical benefits of circumcision?
Decreased UTIs
Decreased testicular torsion
Decreased STDs
Decreased cervical cancer
Decreased testicular torsion
Medical benefits
Decreased UTIs
Decreased STDs
Decreased cervical cancer
Which hormone stimulates the milk ejection reflex (MER)/ let down reflex?
Oxytocin
What kick count would warrant a Non- stress test
A count of fewer than:
3 kicks in 1 hour
10 kicks in 2 hours
warrants further evaluation by a nonstress test (NST)
Fetal alarm signal
What was the initial intention of fetal monitoring?
Decrease incidence of Cerebral Palsy
Which of the following may cause decreased oxygen in the fetus? Select all that apply
A maternal hypertension
B maternal hypotension
C compression of the umbilical cord
D expansion of the umbilical cord
E sleeping mother
F sleeping baby
maternal hypertension
maternal hypotension
compression of the umbilical cord
Maternal hyper/hypotention/ hypovolemia, Compression of umbilical cord, partial placental separation, complete abruption, head compression, ↓ blood flow intervillous in placenta (uterine hypertonus, deterioration of placental vasculature (DM or HTN))
What marks the beginning and end and the active phase of the first stage of labor?
onset of labor- 6 cm
6cm-10cm
10 cm- baby born
period of relative calm-
6cm-10cm
Your patient is 10 days postpartum. She is having bright red discharge. What should you tell her?
That is normal! It's called lochia rubia and it can last up to 14 days after birth
Go to the ER you should be having pinkish- brown discharge by now
Rub your belly to give yourself a fundal massage to slow the bleeding
You are just menstruating, make sure you use contraception if you don't want to get pregnant.
Go to the ER you should be having pinkish- brown discharge by now
Rubra- Bright red 1-3 days Blood from placental site; trophoblastic tissue debris, vernix, lanugo, meconium
Serosa- Pinkish-brown 4-10 days Blood, wound exudate, RBCs, WBCs, trophoblastic tissue debris, cervical mucus, microorganisms
alba - Whitish-yellow 10-14 days, can last 3-6 weeks WBCs, trophoblastic tissue debris
Which of the following would be allowed to go home before 24?
One successful feeding, 2 stools
uncomplicated delivery, with gestation diabetes
An infant who is term with a hr of 136 and rr of 42
A mother who has had an epidural and cannot walk on her own yet
An infant who is term with a hr of 136 and rr of 42
Mother recovered and able to care for self and baby
Uncomplicated pregnancy, delivery and pp period
Term infant; normal exam and VS
Two successful feeding
Voided and stooled
Your patient does not want to breast feed. How would she supress lactation?
well-fitted support bra first 72 hours
avoid breast stimulation, including running warm water over the breasts, newborn suckling, or expressing milk
For many men fatherhood begins at ____
birth
For many men, fatherhood begins at the moment of birth, whereas women are more likely to begin the journey toward motherhood when the pregnancy is confirmed.
Which of the following can be used to determine if a newborn has hip dysplasia? Select all the apply
Ortolani Maneuver
Leopold maneuver
Symmetry of Gluteal Folds
Babinski maneuver
Cobb Method
Ortolani Maneuver
Symmetry of Gluteal Folds
erythromycin 0.5% ophthalmic ointment is the recommended prophylactic medication to prevent infection from:
N. shigella
G. chancroid
N. gonorrhoeae
G. inguinale
syphilis
erythromycin 0.5% ophthalmic ointment is the recommended prophylactic medication to prevent infection from Neisseria gonorrhoeae
The infant you are taking care of is happily sitting in the bouncer. He begins sucking on his shirt, bringing his fist to his cheek, and smacking his lips. What would this be a sign of?
Feeding readiness cues
4 categories of risks to pregnancy
biophysical, psychosocial, sociodemographic, environmental
biochemical, psychosocial, sociodemographic, environmental
biophysical, psychosocial, socioeconomic, environmental
biophysical, psychoanalytic, socioeconomic, environmental
biophysical, psychosocial, sociodemographic, environmental
What conditions can be exacerbated after a mother has given birth and the weeks following after?
autoimmune conditions such as multiple sclerosis or lupus erythematosus
What type of fetal heart rate pattern is a deceleration that begins after contraction and is abnormal? It is associated with low apgar scores!
Late (utero-placental insufficiency)- The deceleration begins after the contraction has started, and the lowest point of the deceleration occurs after the peak of the contraction.
Abnormal pattern associated with fetal hypoxemia, acidemia, and low Apgar scores; considered ominous if persistent and uncorrected, especially when associated with absent or minimal baseline variability
More than 30 sec
A laboring mother is hesitant to go to the hospital due to her lack of insurance and the cost of a hospital stay. She wants to go, but is worried what will happen if she cannot pay the hospital. What should you tell her to reassure her?
Don't worry you can just give birth at home!
We can go to planned parenthood, they can treat you for free!
EMTALA is in place, the hospital will help you regardless of whether or not you can pay.
Maybe you should have gotten insurance before getting pregnant
Emergency Medical Treatment and Active Labor Act (EMTALA) considers active labor an emergency
a federal regulation enacted to protect pregnant women during an emergency regardless of their insurance status or ability to pay for care. According to the EMTALA, pregnant women who present with contractions or who may be in labor are considered unstable and must be assessed, stabilized, and treated at the hospital where they present regardless of their insurance status or ability to pay
Your patient delivered at home 48 hours ago. She is worried she might be sick. She does not have a fever or any symptoms other than profuse night sweats. Why might this be?
Profuse diaphoresis often occurs, especially at night, for the first 2 to 3 days after birth. Fluid loss through perspiration and increased urinary output accounts for a weight loss of 2 to 3 kg (5 to 6.6 lb) during the early puerperium
Which of the following increases risk of infection
Catheterization
Multiple cervical examinations
Obesity
Manual extraction of the placenta
Diabetes
Catheterization
Multiple cervical examinations
Prolonged labor / Prolonged rupture of membranes
Manual extraction of the placenta
Diabetes
What does Kleihauer-Betke detect
(determines presence of fetal blood in maternal circulation).
If more than 30 mL of fetal blood is present in the maternal circulation, the dosage of Rh immune globulin must be increased
What is the condition where after giving birth a mother is emotionally labile and often cries easily for no apparent reason? This lability seems to peak around the fifth day and subsides by the tenth day.
Postpartum blues
What is the optimal state of arousal for an infant
drowsy
quiet alert
active alert
crying
The optimal state of arousal is the quiet alert state
Why do we give newborns vitamin k shots?
Vitamin K promotes the formation of clotting factors in the liver and is used for the prevention and treatment of hemorrhagic disease in the newborn. Vitamin K is not produced in the intestinal tract of the newborn until after microorganisms are introduced. By day 8, normal newborns are able to produce their own vitamin K.
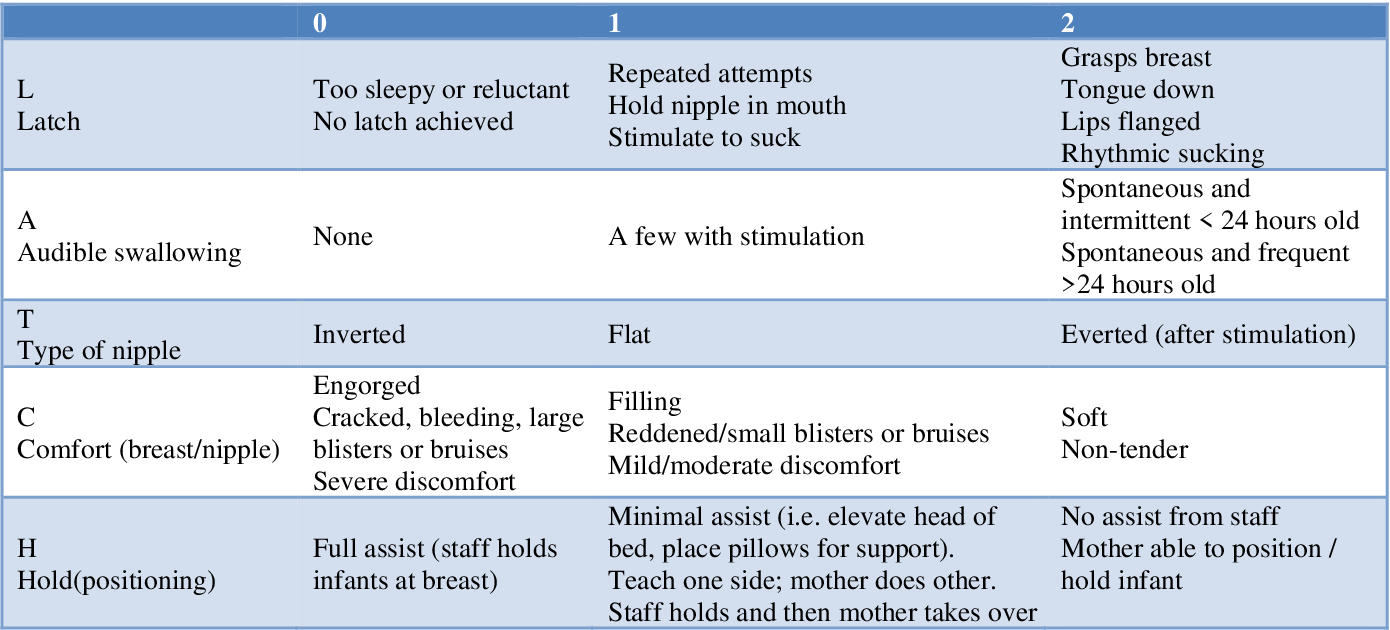
What is the highest latch score acheivable?
10!
Causes of intrauterine growth restriction
maternal hypertension
maternal hypotension
Genetic disorders in fetus
cigarette smoking
fetal hypotension
maternal hypertension, Genetic disorders in fetus, cigarette smoking
Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Maternal Causes
Hypertensive disorders
Pregestational diabetes
Cyanotic heart disease
Autoimmune disease
Restrictive pulmonary disease
Multifetal gestation
Malabsorptive disease/malnutrition
Living at a high altitude
Tobacco/substance abuse
Fetal Causes
Genetic disorders
Teratogenic exposure
Fetal infection
Name one of the 3 states that has the highest percentage of twins
Connecticut, Massachusetts, and New Jersey.
The baby's hr is 120 with moderate variability. absence of late or variable decelerations. Presence of early decelerations as well as accelerations. Which. category of pattern would this be an example of?
Category I (Abnormal pattern)
Category I (Normal pattern)
Category II (Intermediate pattern)
Category III (Abnormal pattern)
Normal pattern–Category 1
• Baseline rate 110-160 beats/min (bpm)
• Baseline FHR variability: moderate
• Late or variable decelerations: absent
• Early decelerations: either present or absent
• Accelerations: either present or absent
A nursing student is describing scenarios where a vaginal exam would be appropriate. Which statement would indicate further teaching is necessary?
admission to assess labor status
with rupture of membranes (ROM)
Prolonged ROM
maternal urge to bear down
*Prolonged ROM
Correct:
admission to assess labor status
with rupture of membranes (ROM)
maternal urge to bear down
before administration of analgesia/anesthesia
sudden decrease in FHR or sign of fetal distress).
Your patient is beside herself crying about how much she hates her body after giving birth. She is upset that she no longer has a flat stomach and that she has stretch marks. What should you tell her?
Hit the gym
Many women feel this way after giving birth (provide her with resources on how to accept the changes in her body as well as how to safely return to exercise to achieve the abdominal tone she is looking for.)
It is okay the stretch marks will go away and you'll be back in shape in no time!
Provider her with a weight watchers brochure
Many women feel this way after giving birth (provide her with resources on how to accept the changes in her body as well as how to safely return to exercise to achieve the abdominal tone she is looking for.)
Hypovolemic shock
Your patient is having a difficult time voiding. To avoid catheterization, what interventions may be used?
listen to running water, placing her hands in warm water, or pouring water from a squeeze bottle over her perineum, shower or sitz bath, relaxation techniques administering analgesics,
a sterile catheter may be inserted to drain the urine
What would a sign of postpartum depression be?
Changes in your feelings:
Feeling depressed most of the day every day
Feeling shame, guilt or like a failure
Feeling panicked or scared a lot of the time
Having severe mood swings
Changes in your everyday life:
Having little interest in things you normally like to do
Feeling tired all the time
Eating a lot more or a lot less than is normal for you
Gaining or losing weight
Having trouble sleeping or sleeping too much
Having trouble concentrating or making decisions
Changes in how you think about yourself or your baby:
Having trouble bonding with your baby
Thinking about hurting yourself or your baby
Thinking about suicide (killing yourself)
Which of the following is normal for the first 30 minutes after birth? Select all that apply
Hr 160
Fine crackles
Nasal flaring
RR 50
Retraction
Tremors
Regular respirations
Hr increases 160- 180 beats/min gradually falls 30 minutes to 100 - 120 beats/min.
Respirations are irregular, 60- 80 breaths/min
Fine crackles, grunting, nasal flaring, and retractions (cease within the first hour)
alert spontaneous startles, tremors, crying, and head movement
Bowel sounds and meconium
What is the most serious risk of a heelstick
necrotizing osteochondritis resulting from lancet penetration of the bone.
Which of the following would be a sign that an infant is not sufficiently breast feeding?
bursts of 15-20 sucks/ swallows
Audible swallowing
has 2 substantiative bowel movements and 5 wet diapers
easily releases the breast after feeding
Has at least three substantive bowel movements and six to eight wet diapers every
Which of the following are biochemical tests?
amniocentesis
ultrasonography
percutaneous umbilical blood sampling
chorionic villus sampling
Daily Fetal Movement Count (DFMC)
amniocentesis, percutaneous umbilical blood sampling, chorionic villus sampling, and maternal sampling
In 1879, the heaviest recorded baby was born, weighing in at
22 pounds