Immunotherapy
Spill
Fatigue, bone pain, recurrent infections, and renal impairment.
What are the most common presenting symptoms of multiple myeloma?
Younger age, elevated WBC, frequent infections, petechiae, malaise
What are the most common presenting symptoms of leukemia?
Unexplained weight loss, high fever, and night sweats are characteristics of what in lymphoma patients.
What are B symptoms?
Essential for inducing a generic immune response to antigens.
What is innate immunity?
Type of PPE to be worn any time there is a risk of splashes or spills, including disposal of contaminated body fluids.
What is eye/face shields?
Class of drugs that can cause cardiac dysfunction and recommends an ECHO or MUGA prior to tx.
What are anthracyclines?
Renders compound inert or inactive.
What is deactivation?
Type of myeloid cell that is the root of the disease in multiple myeloma.
What is a plasma cell?
These are preferred access for a newly diagnosed leukemia patient.
What is a central line (DL PICC, Port a cath, etc)?
Swollen lymph nodes along your neck, armpits, or groin; rashes; fever; unexplained weight loss.
What are the most common symptoms of lymphoma?
Secondary line of defense and involves immunologic memory, specificity, and collaboration of B cells and T cells.
What is adaptive immunity?
When 2 chemotherapy competent RNs independently check multiple things prior to administering chemotherapy such as patient labs, MD orders, consent, integrity of drug, etc.
What is a double check/2 RN independent check?
This chemotherapy can cause ocular toxic reactions and requires steroid eye drops.
What is cytarabine?
A drug that meets one or more of the following: carcinogenicity, teratogenicity, reproductive toxicity, organ toxicity at low doses, genotoxicity, etc.
What is a hazardous drug?
Increasing age, Male gender, African-American race, Positive family history, MGUS
What are risk factors for developing multiple myeloma?
DIC and hyperfibrinolysis are risks for this patient population.
What is APL?
Exposure to Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV), AYA, male, Family HX, HIV or weakened immune system.
What are risk factors for developing Lymphoma?
Type of white blood cell that is the first line of defense in the immune system.
What is a neutrophil?
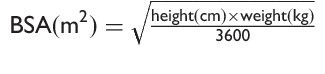
What is Mosteller formula?
Vesicant that is fatal if given intrathecally.
What is Vincristine?
Destroys microorganisms.
What is disinfection?
This side effect is common across most pharmaceutical drugs that are used to treat multiple myeloma.
What is peripheral neuropathy?
Advise patient to go to emergency department immediately, do not take acetaminophen at this time.
What is the preferred intervention a triage nurse will advise when a patient verbalizes having a fever of 100.4F, chills, and malaise?
B lymphocytes (B Cell), T lymphocytes (T Cell), and Natural Killer cells (NK)
What are the three major types of lymphocytes that lymphoma affect?
Elimination, Equilibrium, Escape
What is immunoediting?
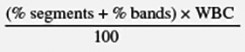
What is absolute neutrophil count formula?
Antitumor antibiotic that can cause pulmonary toxicities and recommends a PFT.
What is bleomycin?
Removes HD residue.
What is decontamination?
Criteria that is used for diagnosing multiple myeloma.
What is CRAB criteria?
This syndrome is described by unexplained fever, weight gain, respiratory distress, interstitial pulmonary infiltrates, hypotension, pleural or pericardial effusions and hepatic, renal, or multi organ failure.
What is Retinoic Acid Syndrome?
Fertility concerns/preservation, socio-economic status
What are nursing considerations for childbearing aged newly diagnosed lymphoma patients?
HSR, CRS, latent infection re-activation, infection, TLS
What are some general nursing considerations when you are taking care of a patient who is getting a mAb?
A device that mechanically prohibits the transfer of environmental containments into the system and the escape of HD or vapor concentrations outside of the system.
What is a closed system transfer device?
Alkylating agent that requires frequent bathing immediately following and during first 24 hours after administration as it is secreted through sweat/skin.
What is thiotepa?
Controlling body for occupational exposure to hazardous drugs.
What is OSHA?