Give one reason why biologists consider viruses to NOT be living things.
They are not made of cells.
They cannot reproduce on their own (need a host cell).
Nucleotides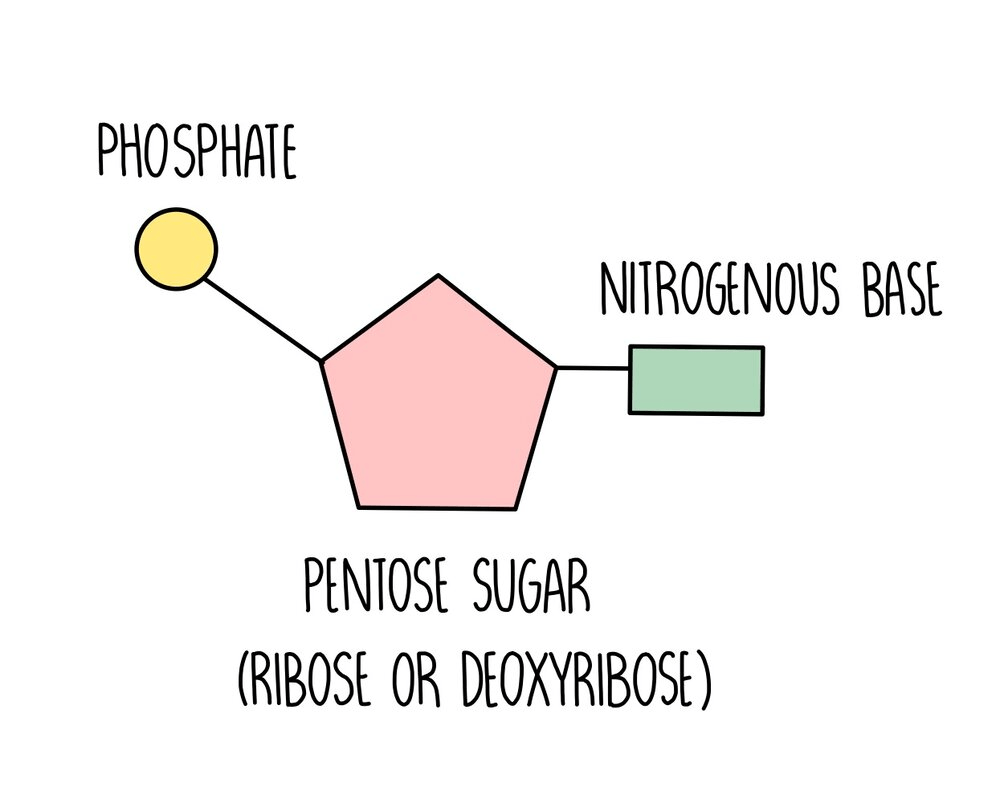
How are eukaryotes different from prokaryotes?
Eukaryotes DO have a nucleus. Prokaryotes have NO nucleus. 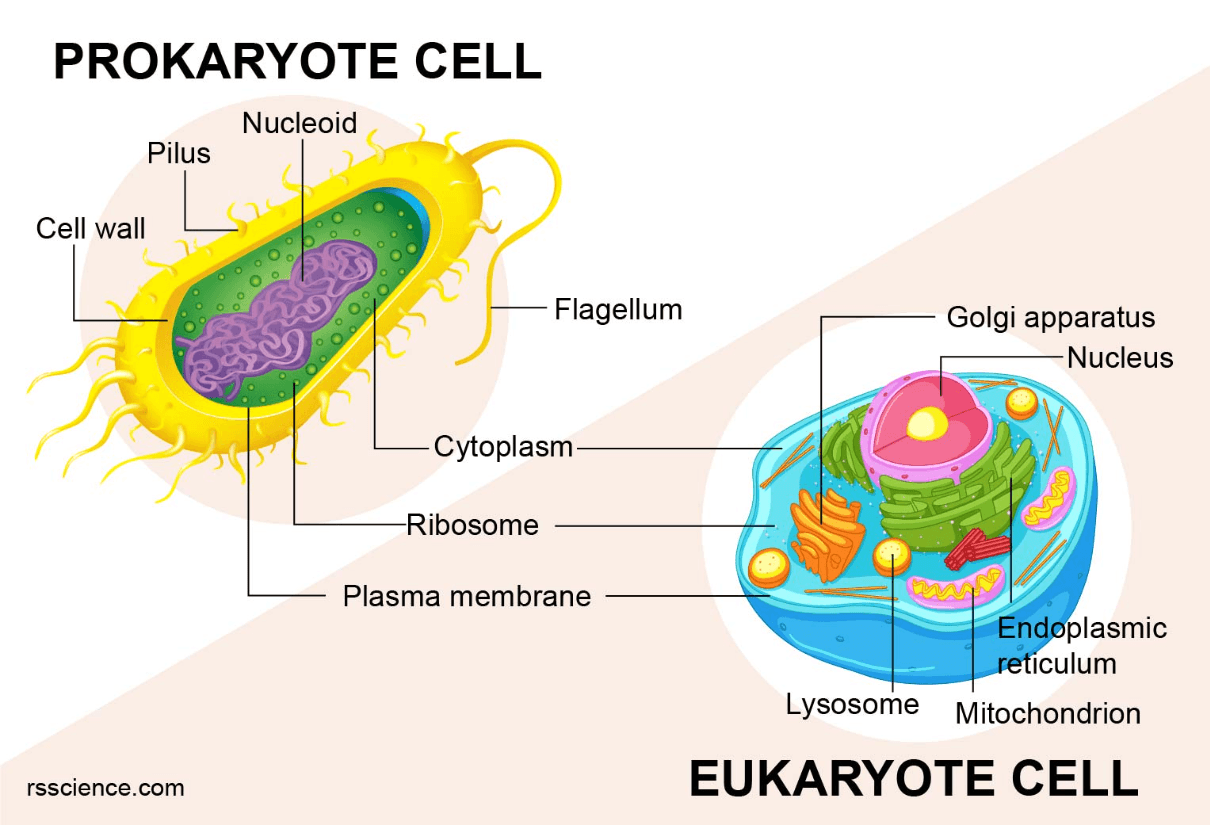
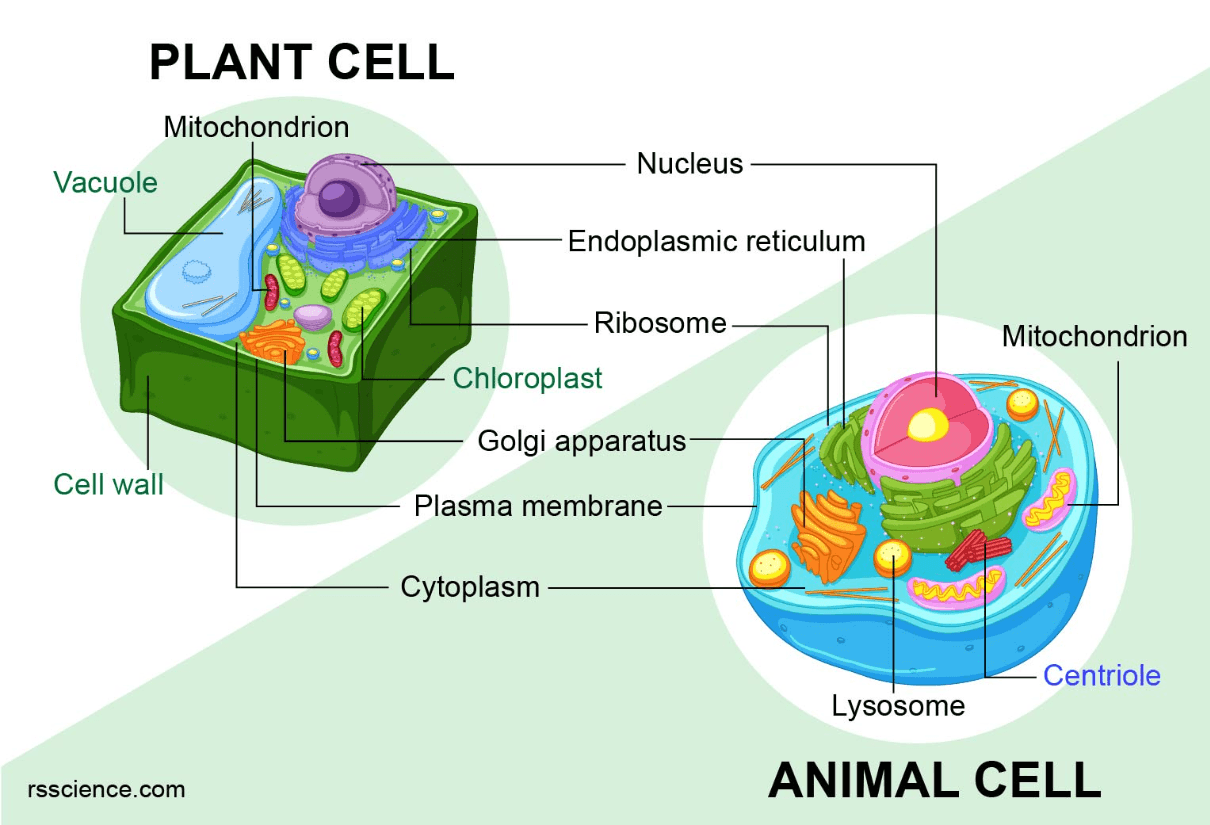
Tell at least one difference between plant cells and animal cells.
Only plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts.
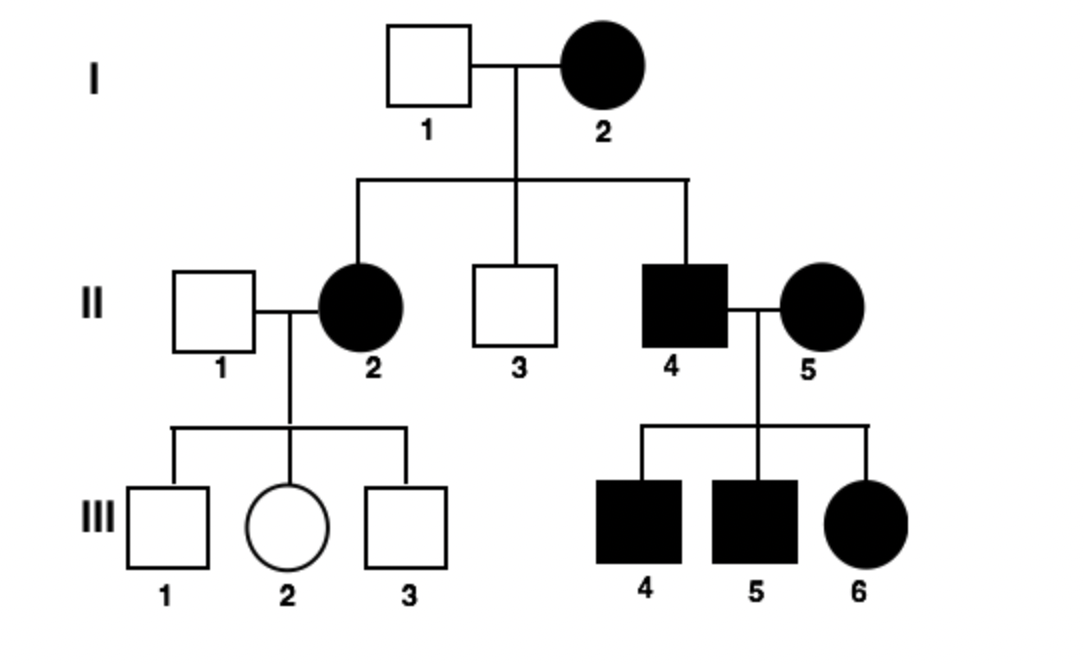
Based on what you know about pedigrees, tell the number of a person who is an affected male.
Numbers are written like this: I-1, I-2, II-1, etc.
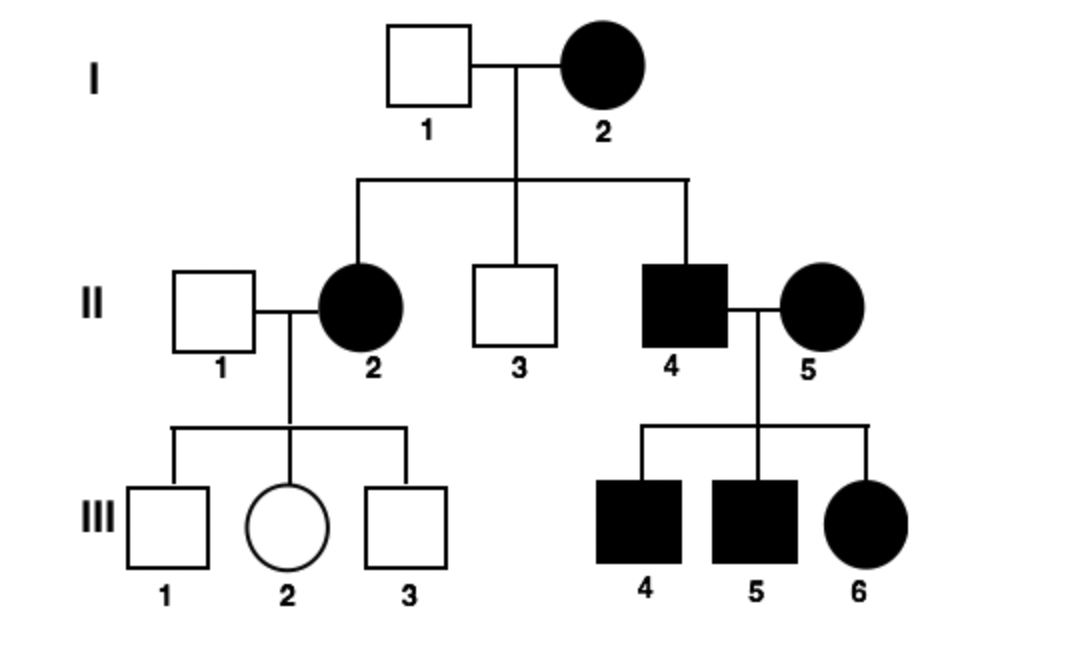
II-4, III-4, or III-5
One characteristic of life is that all living things respond to a stimulus. They do this in order to maintain a consistent (same) internal environment. What word means STAYING THE SAME?
Homeostasis
What is the purpose of enzymes?
Enzymes speed up reactions/lower the activation energy needed for a reaction.
Which enzyme UNZIPS DNA during DNA replication?
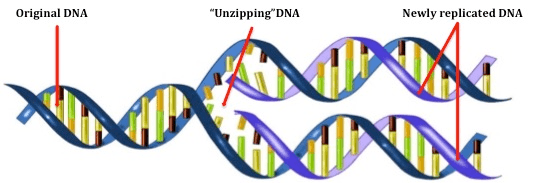
DNA Helicase. (DNA polymerase makes a POLYMER, or big molecule, by adding nucleotides to the original strand). 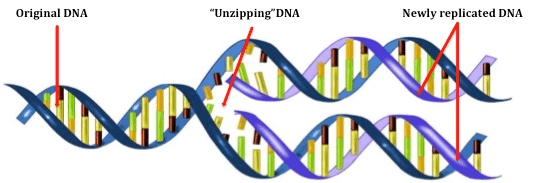
Give one example of ACTIVE TRANSPORT.
Active transport requires energy: protein pumps, exocytosis, endocytosis.
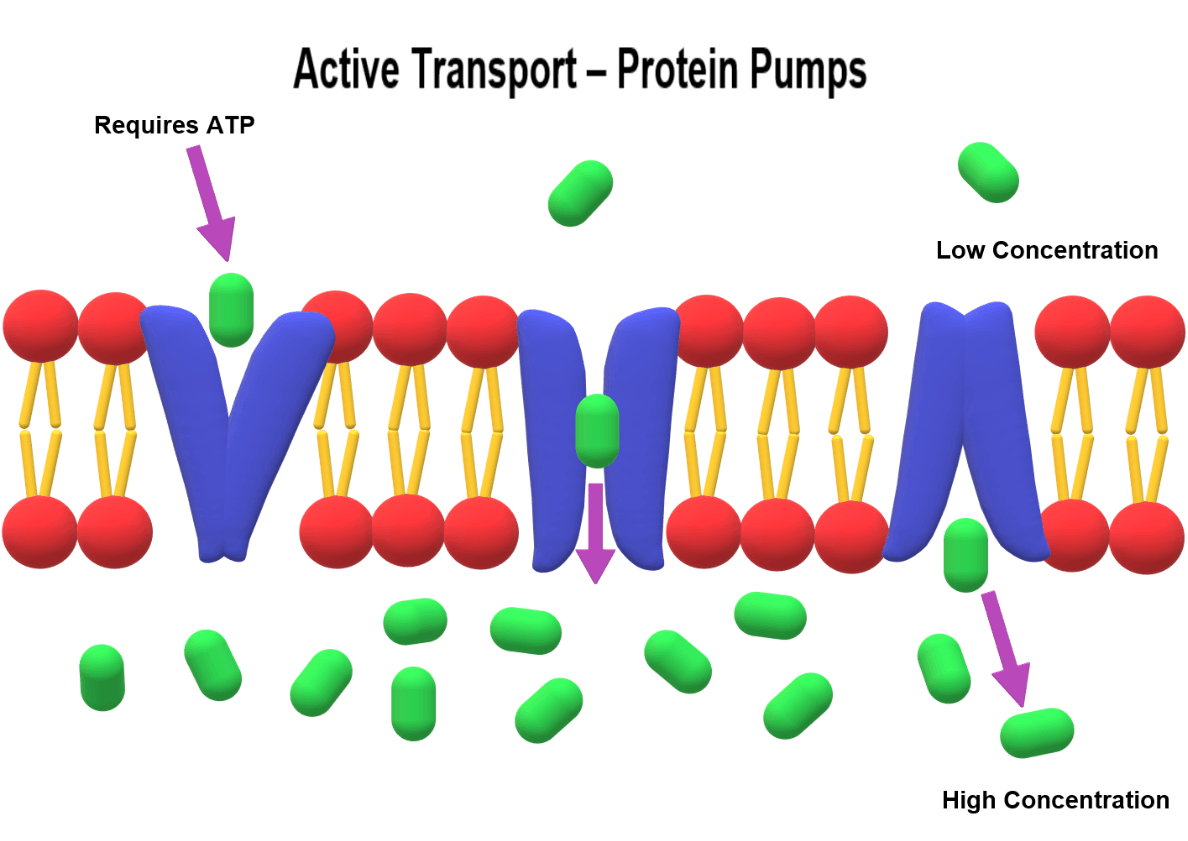
Describe what this picture is showing.
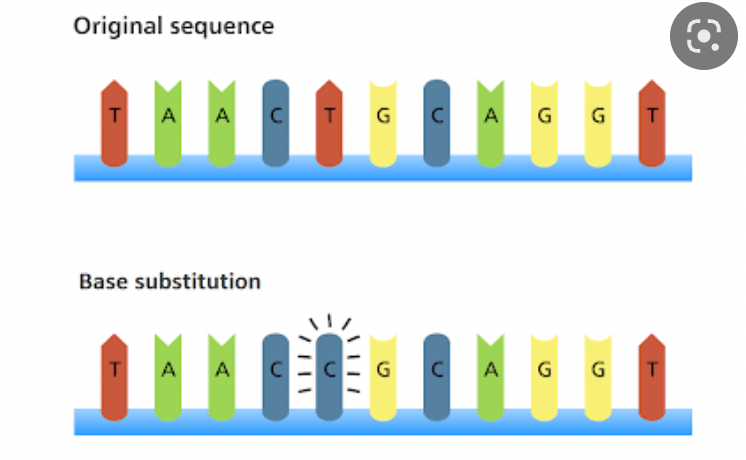
This picture is showing a point mutation, where ONE base is changed. This will change the protein that is made.
A scientist designed an experiment to test the effect of temperature on bacterial growth. He grew three different cultures of the bacterium E. coli under three heat lamps at different temperatures. What was the independent variable in this experiment?
The temperature
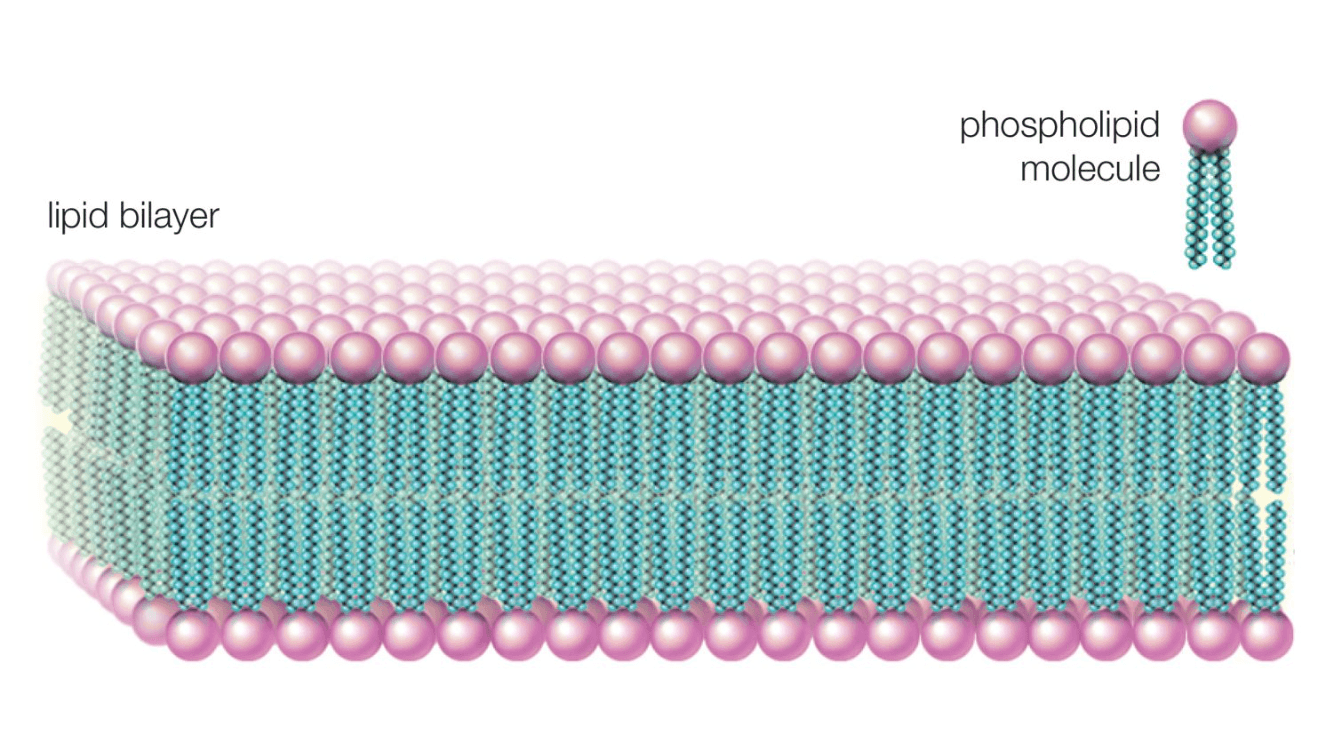
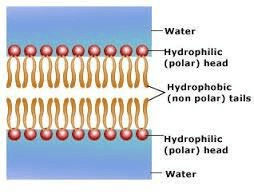
Which macromolecule makes up the largest part of the cell membrane?
Lipids (remember--phospholipid bilayer!)
A king crab has 208 chromosomes in its nerve cells. How many chromosomes are in a king crab sperm cell?
104! NERVE cells are diploid, so 208 = 2n. Sperm cells are haploid = n.To find the haploid number, we divide 208/2.
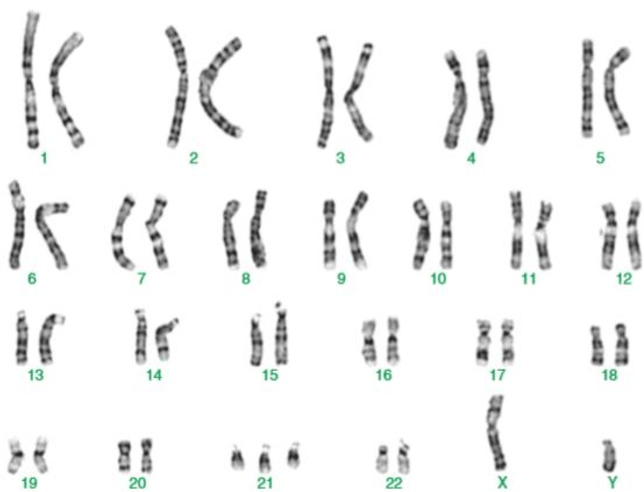
Tell TWO things you can say about this person based on this karyotype.
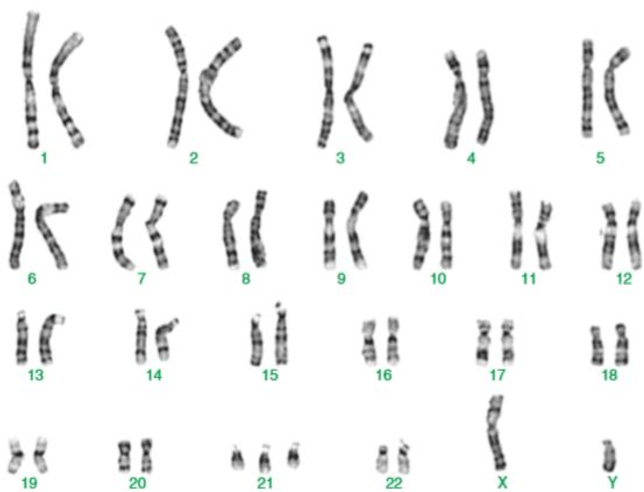
This person is a MALE (XY chromosomes) who has Down's Syndrome (three of chromosome #21).
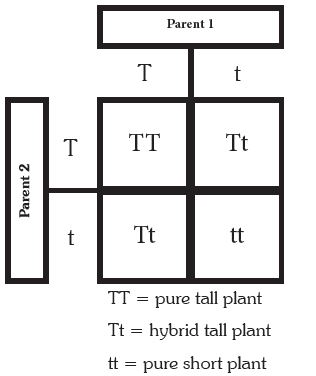
In pea plants, tall (T) is dominant to short (t). What would the phentoype ratio be for crossing two heterozygous tall plants?
75% tall, 25% short
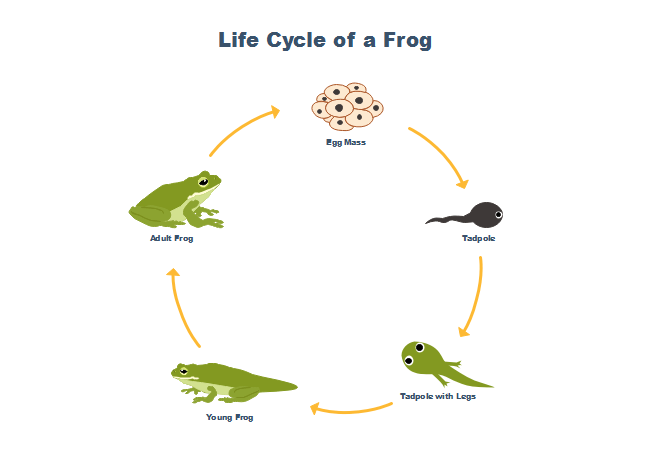 This frog changes from an egg to a tadpole, and finally to an adult frog. Which characteristic of life does this represent?
This frog changes from an egg to a tadpole, and finally to an adult frog. Which characteristic of life does this represent?
All living things grow and develop.
Give at least THREE functions of proteins.
1. Structure (muscles, bones, etc.), 2. Transport, 3. Movement, 4. Defense/immune, 5. Hormones, 6. Enzymes
An organism is unicellular, an autotroph, eukaryotic, and does NOT have a cell wall. Which kingdom does it belong in?
Protista! Almost all unicellular eukaryotes are in this kingdom, except for a few exceptions, like YEAST (which is a fungus, which are heterotrophic and have a cell wall).

The cell membrane is made of a PHOSPHOLIPID bilayer. The outside is POLAR phosphorus, the inside is NON-POLAR lipid.
Is it possible for a man with type B blood and a woman with type A blood to have a child with type O blood? Why or why not? A Punnett Square might help you!
Yes, it's possible! If the man is heterozygous (IBi) and the woman is also heterozygous (IAi), their child could be ii (Type O).
What is the name of #5?
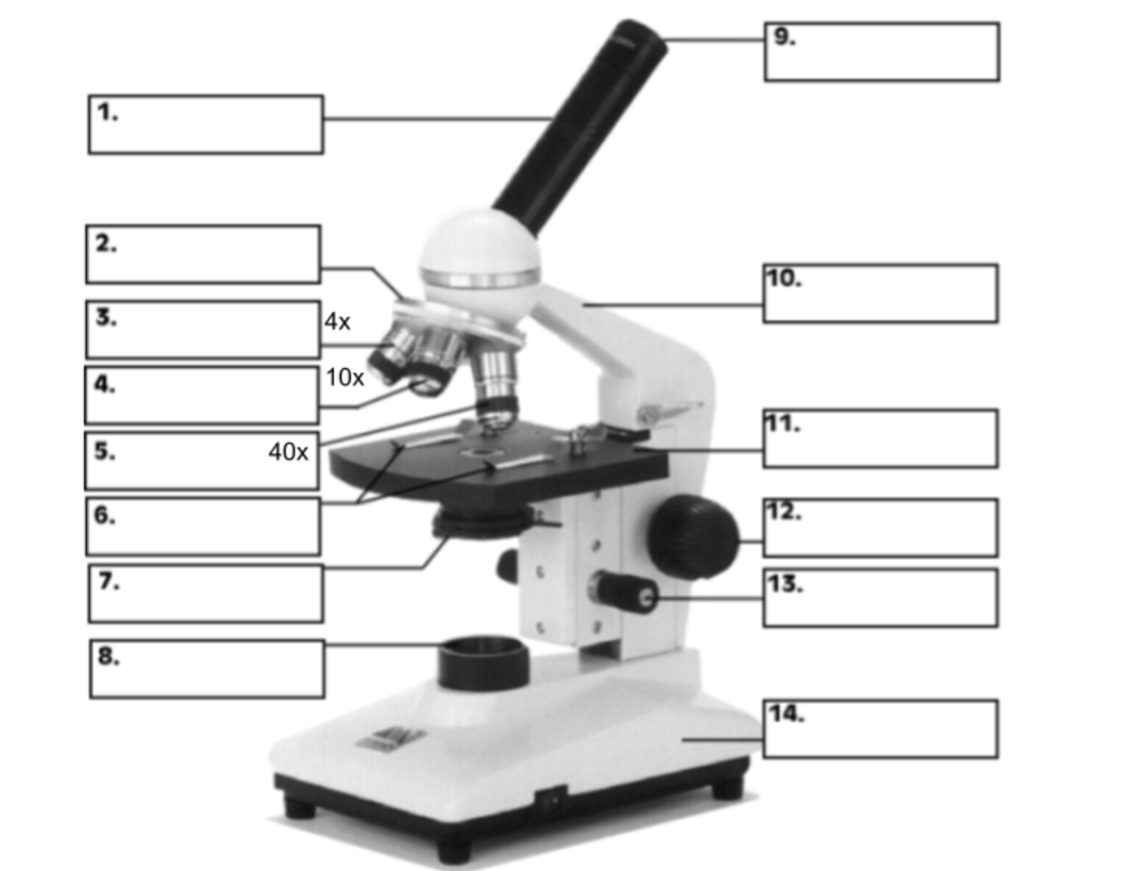
High power objective lens
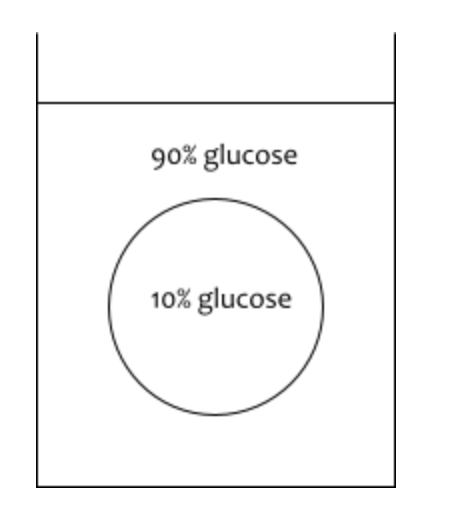 Look at the diagram of a cell in a solution. The cell membrane is permeable to water, but not glucose. Describe what would happen AND tell why.
Look at the diagram of a cell in a solution. The cell membrane is permeable to water, but not glucose. Describe what would happen AND tell why.
100-10% = 90% water INSIDE the cell. 100-90 = 10% water OUTSIDE the cell. Water will move OUT of the cell from high to low concentration. The cell will shrink.
Which phase of mitosis is this? Name the phase AND tell at least on reason why you know this is correct!
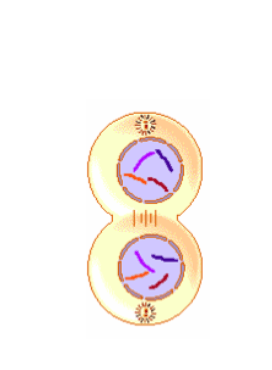
This is TELOPHASE. The sister chromatids have completely separated. The nuclear membrane is reforming.
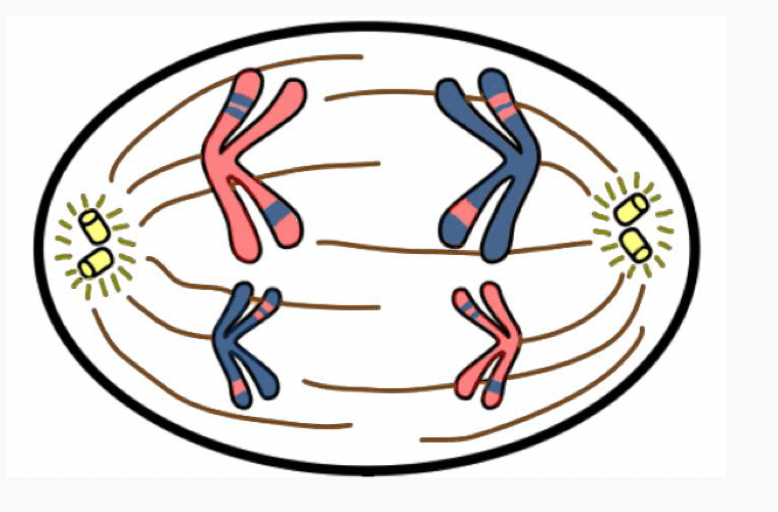
What phase of meiosis is this AND how do you know?
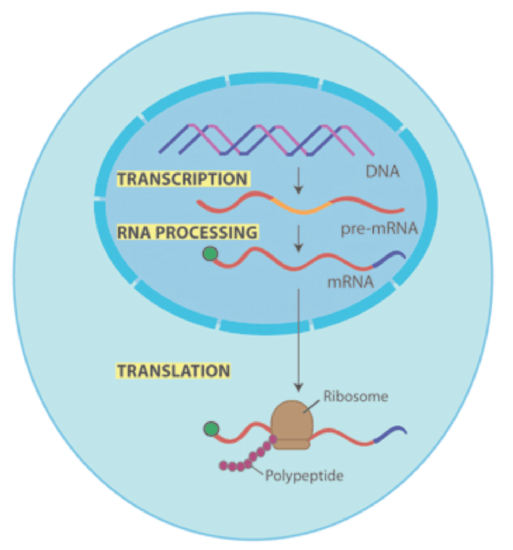
The DNA double helix is unzipped and a single-stranded mRNA copy is made. (Later this mRNA will be used to make an amino acid chain/protein during translation).