CNS consists of what ?
Brain and spinal cord
What does the longitudinal fissure do ?
Separates two hemispheres
What is another name for the cerebral cortex ?
Executive suite
Photoreceptors respond to what
Light
Levels of neural integration
Receptor level , Circuit level , Perceptual level
What are the three primary vesicles ?
Prosencephalon , Mesencephalon , Rhombencephalon
Deep groves represents what surface marking ?
What are association areas ?
Integrate diverse information
Receptors have either
Nonencapsulated (free) nerve endings, Encapsulated nerve endings
What receptors adapts slowly or not at all
Tonic receptors
Telencephalon gives rise to two ______? And together makeup the __________?
Cerebral hemisphere , cerebrum
Sulci dived into five lobes
Frontal , parietal , temporal , occipital, insula
What’s the name of the highlighted blue area
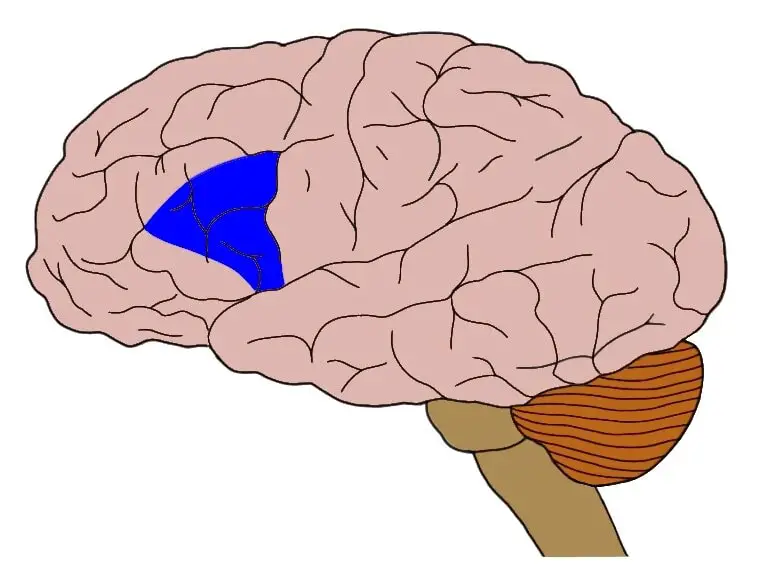
Broca’s area
Hair follicle receptors do what
free nerve endings that wrap around hair follicles
What gives you the ability to taste sweet and sour flavors
Quality discrimination
Myelencephalon becomes what ?
Medulla Oblongata
The basal nuclei is found where ?
Deep within white matter
Premotor cortex can be known for doing what
Helps plans movement
proprioceptors located in tendons that detect stretch also known as
Tendon organ
Visceral and referred pain
Visceral pain results from stimulation of visceral organ receptors
Forebrain moves toward what ?
Brain stem
What the name of the highlighted green area ?
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/10153/DMIAPl1Cx4EOfXKpNduhw_Insula_02.png)
Insula
Primary somatosensory cortex is located where
postcentral gyri of parietal lobe
Free nerve endings also known as ?
Thermoreceptors
the conscious interpretation of those stimuli
Perception