Because one end of a water molecule is slightly positive and the other end is slightly negative, water molecules are __________.
Polar
What are the two main types of bonds that elements can form with other elements to make compounds?
Covalent and Ionic
What is the monomer of a carbohydrate called?
monosaccharide
Which of the four macromolecules are known as the primary component of cell membranes?
Lipids (phospholipids)
Define activation energy
The amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
The attraction between the oxygen of one water molecule to the hydrogen of a different water molecule is called a?
Hydrogen Bond
Define valence electrons
The electrons in an atom's outermost shell, determining its chemical properties and how it bonds with other atoms.
The monomer of a nucleic acid is called
a nucleotide
Amino acids are held together by this kind of bond, which is created by removing a H₂O molecule
Peptide bond
Enzymes speed up chemical reactions inside a cell by doing this
Lowering activation energy
The attraction between like molecules is called?
The attraction between unlike molecules is called?
Cohesion ; Adhesion
The number of protons in the nucleus determines what value on the periodic table?
The atomic number
What are the building blocks of proteins?
Amino acids
List three examples of carbohydrates
Simple Sugars: glucose, fructose, galactose
Compound: maltose, sucrose, lactose
Complex Carbohydrates: Starch, glycogen, cellulose
What happens to enzymes when they are affected by changes in pH, preventing it from binding to its substrate?
Denaturing
A mixture of water and undissolved particles that are so small that they do not settle out is called a?
Suspension
In an covalent bond, oxygen would be most likely to pair with which one of the following elements? Why?
a. Iron
b. Hydrogen
c. Argon
d. Aluminum
b. Hydrogen, in a covalent bond oxygen must bond with another nonmetal.
Complex organic compounds that store and transfer genetic information to the cell are called?
Nucleic acids
Identify the sugars found in the nucleotides for DNA and RNA
Deoxyribose & Ribose
The pocket or groove on the surface of an enzyme into which the substrate must fit.
Active site
Correctly draw a water molecule, including relative charges and the correct number of electrons
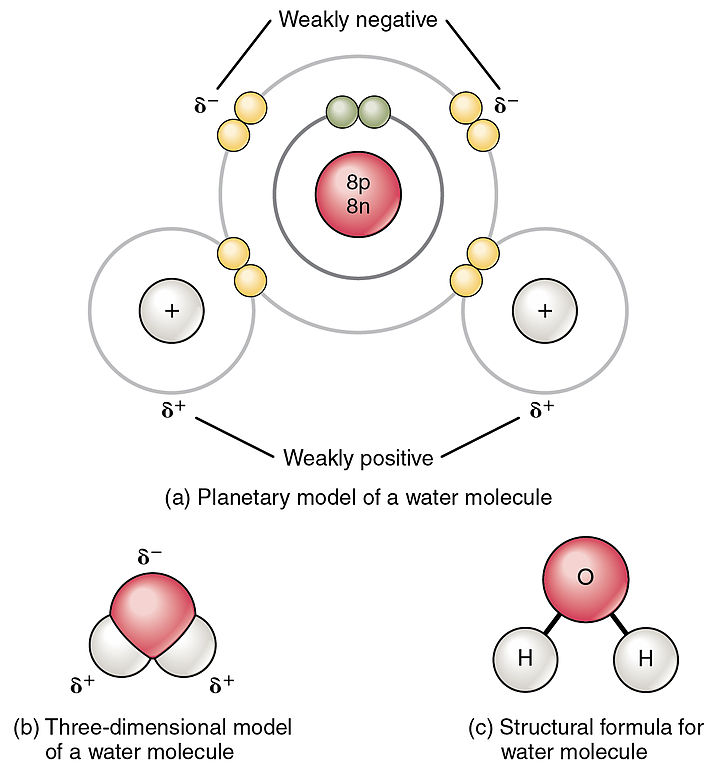
How many atoms would be found in this molecular compound?
3C₆H₁₂O₆
72 atoms
Name the two building blocks of lipids
Glycerol and Fatty Acids
If a fatty acid has one or more carbon to carbon double bonds, it is said to be?
Unsaturated
Name the type of chemical reaction: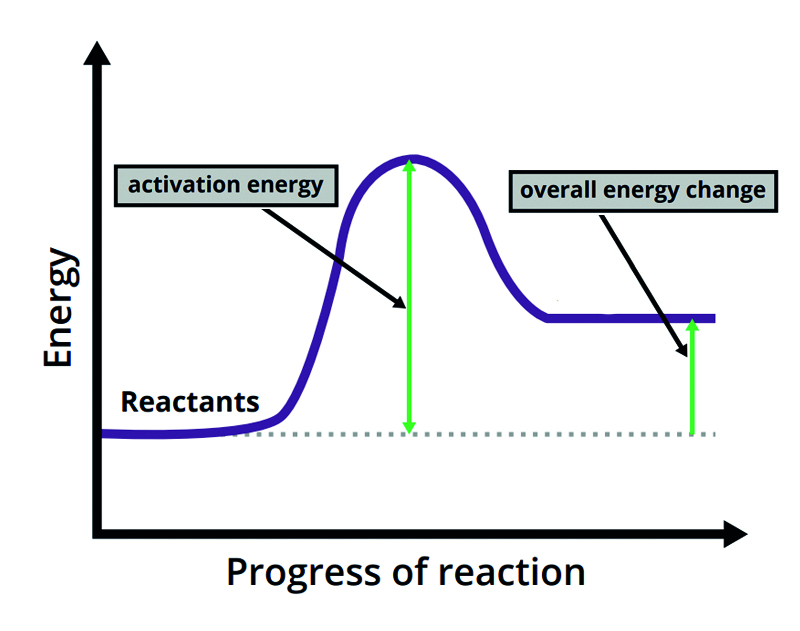
Endothermic reaction