
You see this rhythm on an unresponsive patient. What is your FIRST step.


Your patient is deteriorating quickly. You place patient on portable monitor and see this. Which medication would you anticipate the MD to order?

Eliquis is what class of blood thinner?
You notice this on the monitor:

Which electrolyte would you suspect is abnormal? Too high or too low?

Your patient has a change of rhythm, noted by the MT. When you assess the rhythm, you see this:
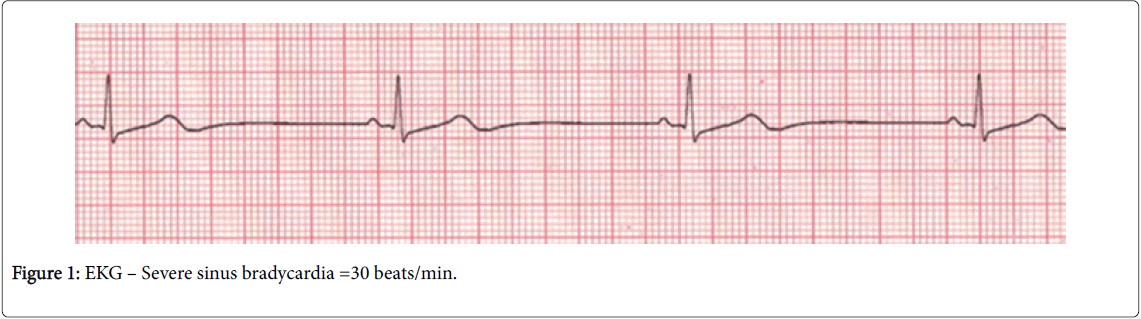
After obtaining VS and see the patient's BP is also now 84/52. Which medication and dosage would you anticipate being ordered by the MD?
True or False
Valium may be given on the Tele Floor as long as the medication is programmed into a locked PCA pump with no patient controlled bolus option and only a locked rate is ordered.


This mnemonic is used to help recall the major contributing factors to a pulseless arrest. Name each component of the mnemonic.
(Hint: Hs & Ts)
Can Eliquis and Plavix be taken together?
Why or why not?
Absolutely.
Eliquis and Plavix play 2 different roles in the clotting cascade. Eliquis is an anticoagulant and Plavix is an an anti-platelet.