What is this physical exam finding and what disease?

Ulnar deviation in RA
What is the disease associated with the imaging?

OA
What does she have? What is the name of the rash?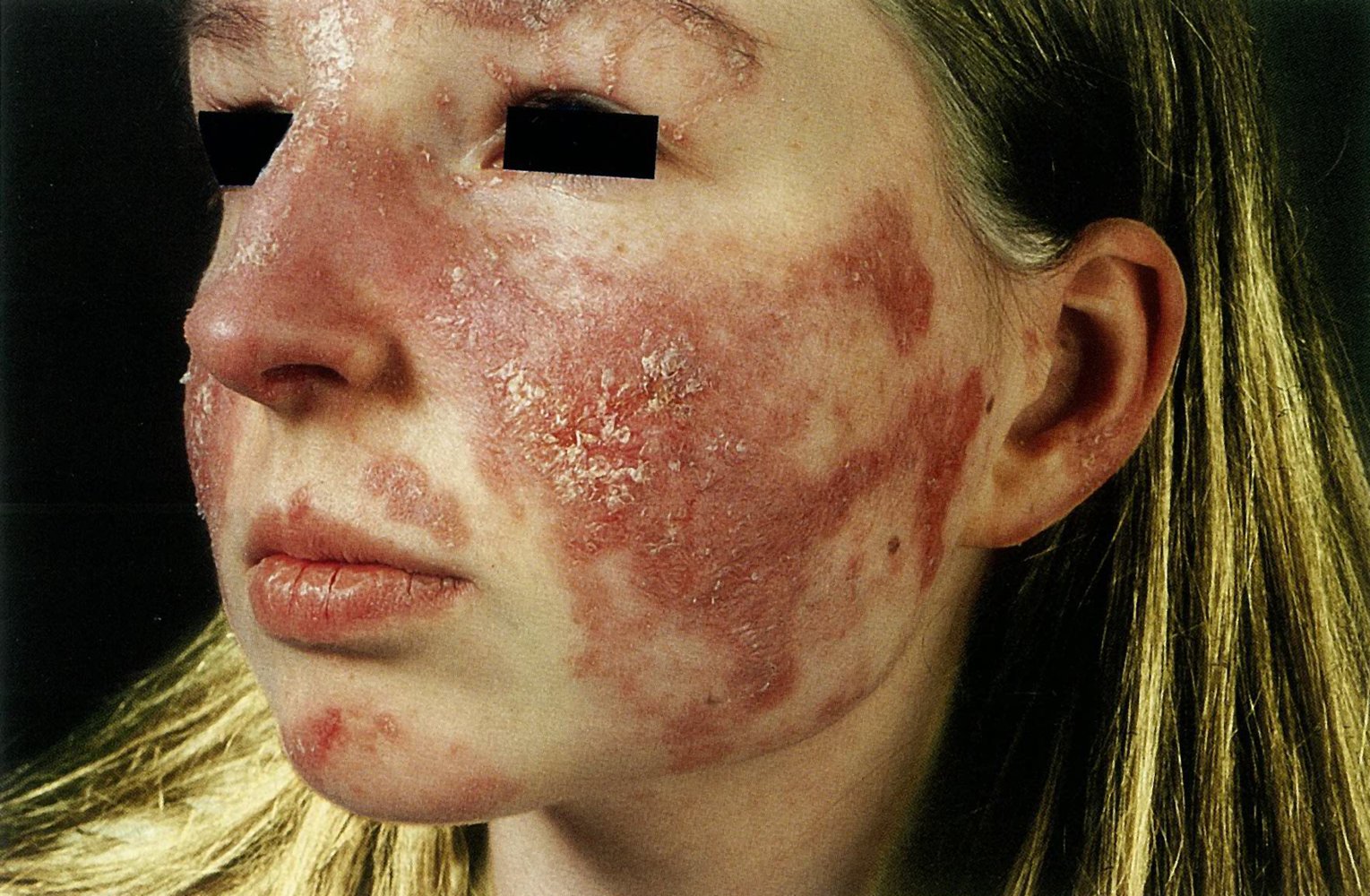
SLE, malar butterfly rash
What is this physical exam finding called and what disease is this present in?
Podagra, gout
This patient presented to the ER for new onset vision loss and headache over the temple. They have also been experiencing jaw pain with chewing, however this patient also has a history of TMJ and attributes it to that. Given these findings, what is next best step in management for this patient?
High dose prednisone
What is this deformity and in what disease?
Swan neck in RA
What are the common radiographic findings in OA?
- Joint space narrowing
- Osteophytes
- Subchondral sclerosis
- Subchondral bone cysts
What is the cornerstone of therapy (regardless of disease activity) in SLE?
Hydroxychloroquine
What is a first line agent for acute gout flare?
Prednisone x 5 days
This patient developed asymmetric arthritis and has a history of dysuria, frequency and mucopurulent urethral discharge. What is the diagnosis?
Gonoccocal arthritis
What is the cornerstone of therapy (regardless of disease activity) in RA?
Methotrexate - DMARD
What joints are commonly affected in OA?
- Predominantly weight-bearing joints (e.g., hip and knees)
- PIP and DIP joints(Bouchard nodes and Heberden nodesrespectively)
- First CMC joint
Which antigen specific ANAs are present in SLE?
Anti-dsDNA antibodies and Anti-Sm antibodies
Patient was started on a medication to treat their hypertension, however this precipitated a gout attack. What class of medication was initiated?
Thiazide
65 year old male is here because he has been experiencing nail pitting/onycholysis for quite some along with joint pain and rash on the dorsal surface of his hands. What is an appropriate topical treatment for this condition?
Clobetasol
Which serological marker is most specific in RA?
Anti-CCP
What are non pharmacological treatment options in OA?
Exercise, weight loss, physical therapy and occupational therapy
Which syndrome should all SLE patients be screened for and why?
Antiphospholipid syndrome, high risk of clotting
Should chronic urate lowering therapy be continued while being treated for an acute gout flare?
Yes
Which disease is associated this finding and what antibodies would you test for?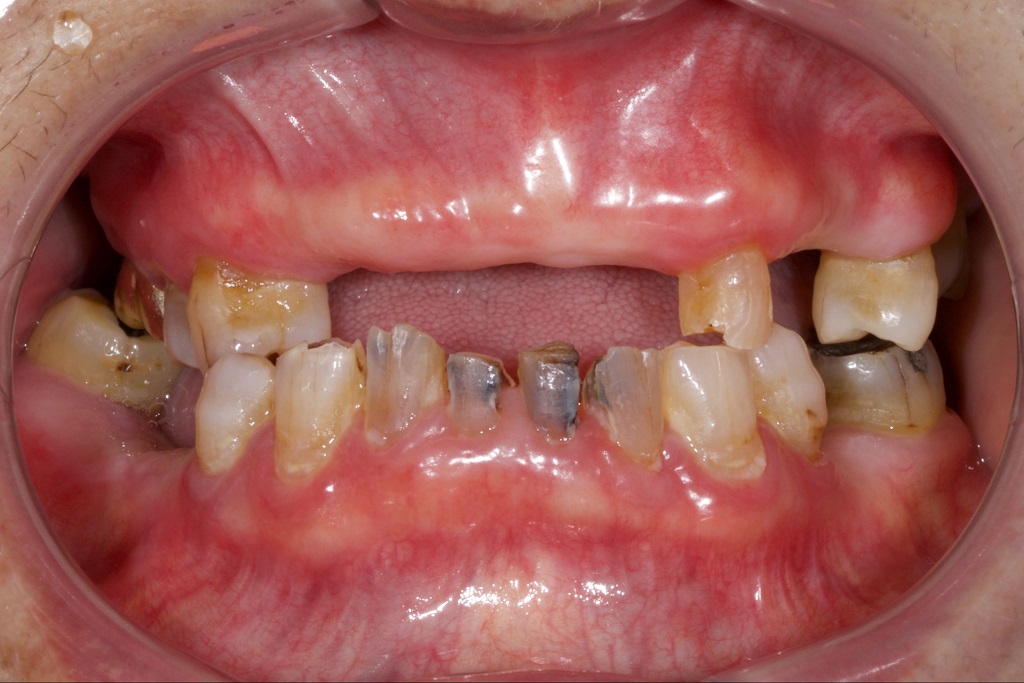
Sjogren syndrome, anti-Ro, anti-La
Which joints are spared in RA?
DIP
At what point do you refer patients with OA to orthopedic surgery for joint replacement?
Surgery is typically indicated if conservative measures fail
SLE patient is in the ED for hypertension, edema, hematuria. BMP is positive for AKI and UA demonstrates proteinuria, hematuria, cellular casts. What is this specific manifestation called?
Lupus nephritis
What is the gold standard for diagnosis of gout?
Arthrocentesis with synovial fluid analysis
This patient is complaining of foreign body sensation in their eye, dysuria and burning at the urethral meatus, and knee pain/swelling after experiencing diarrhea from food poisoning. What is the diagnosis?
Reactive arthritis
What is a complication of cervical HVLA in a patient with RA?
Atlantioaxial subluxation
How often are you able to administer joint injections?
Every 3 months
What is an associated complication of chronic hydroxychloroquine use?
Retinal toxicity
Are serum uric acid levels always elevated during an acute flare?
No
What is the disease and what is the radiographic finding called?

Ankylosing spondylitis, bamboo spine
Which joints are affected in RA?
- Frequently affected joints
- Metacarpophalangeal joints (MCP joints)
- Proximal interphalangeal joints (PIP joints)
- Wrist joints
- Knee joints
- Metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints)
What is a NSAID that can be prescribed with lower rates of gastroduodenal ulcers, GI complaints, and serious GI events?
Celebrex
Women with this disease may experience 3+ consecutive spontaneous abortions before 10 weeks, 1+ unexplained fetal death at or 10 weeks, or premature birth before 34 weeks due to severe PreE or placental insufficiency.
Antiphosphlipid syndrome
What type of crystals are these and is this positively or negatively birefringent?
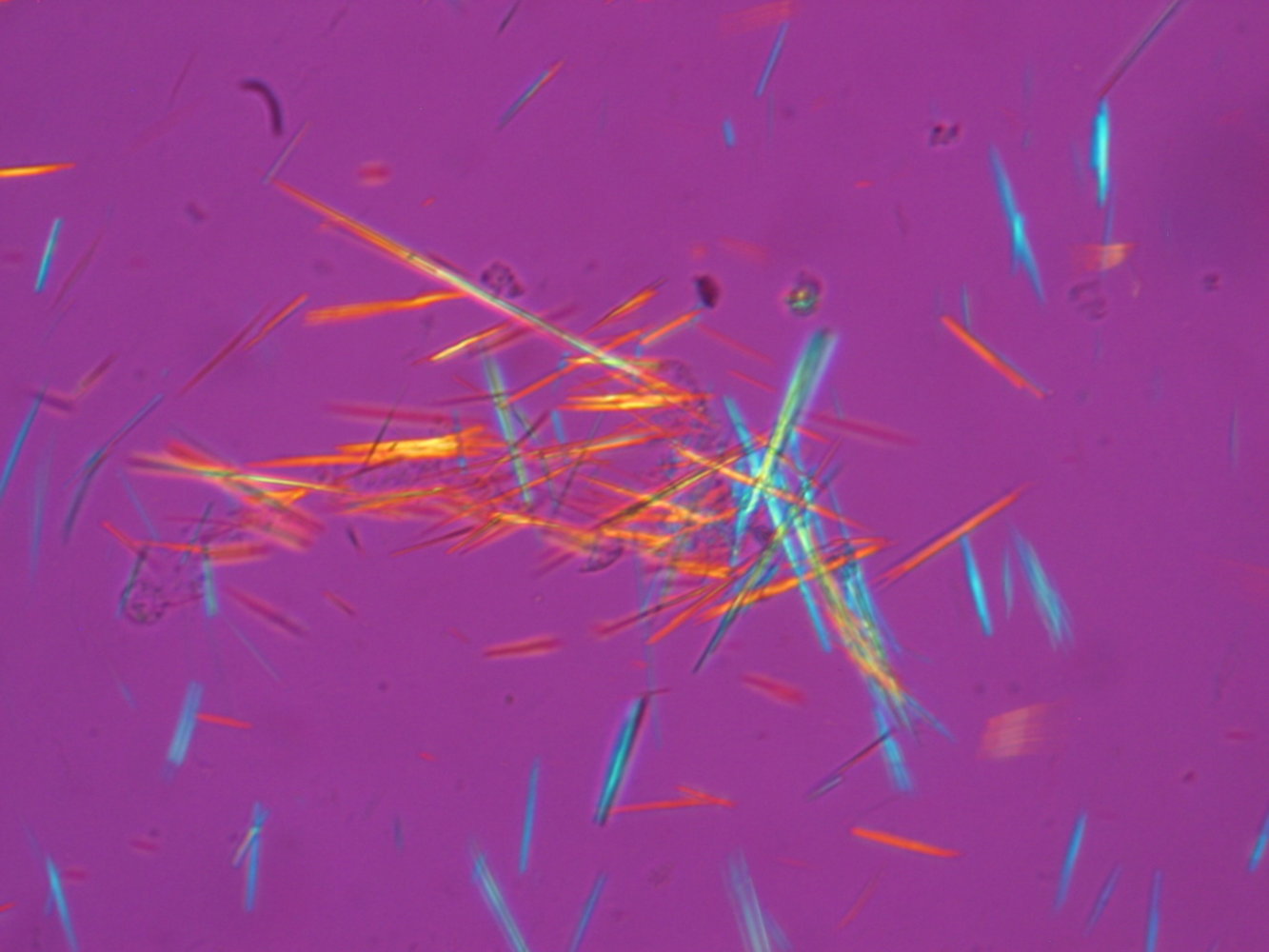
Monosodium urate crystals, negatively birefringent
What is the disease associated with this exam finding and can it lead to a nephritic or nephrotic syndrome?
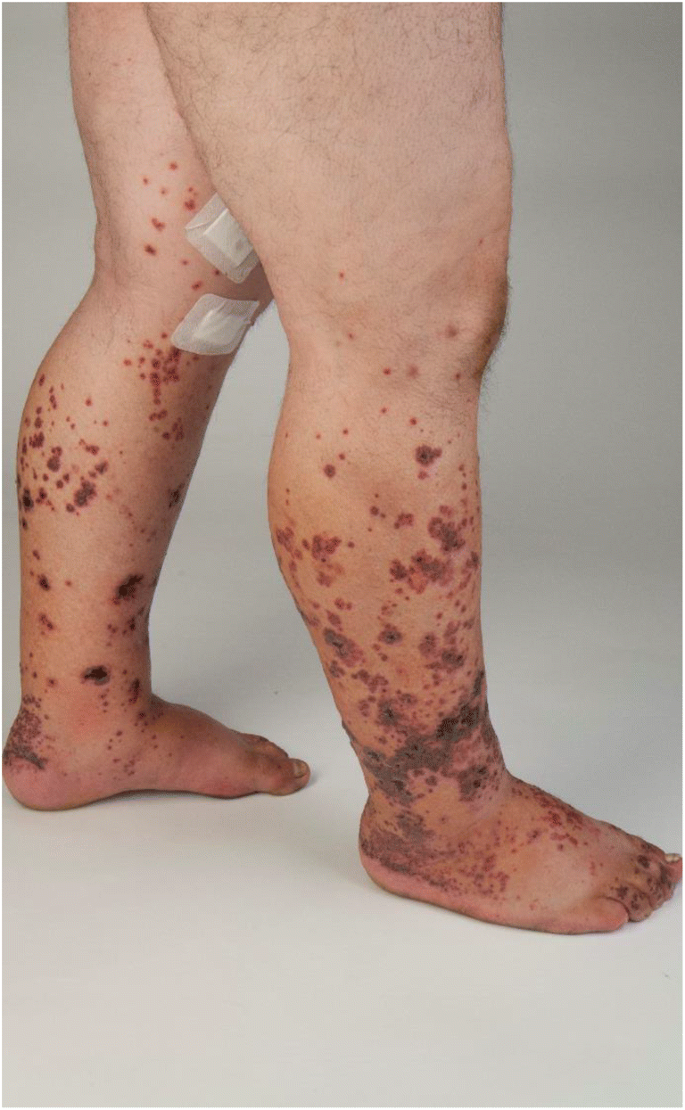
IgA vasculitis (HSP), Nephritic syndrome
What are the common radiographic findings in RA?
- Joint space narrowing
- Erosions
- Subchondral cysts
- Juxtaarticular demineralization
What is the name of the study that compared Celebrex with ibuprofen and naproxen's GI side effects?
PRECISION
What is this type of cutaneous lupus called?
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE), a chronic, scarring variant of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
What are the absolute indications for urate lowering therapy?
- Absolute indications
- Damage due to chronic gout seen on imaging
- Tophi development
- Frequent gout attacks (≥ 2 per year)
What is the syndrome associated with this exam finding? Which antibodies (100 point bonus)?

C - calcinosis
R - reynaud's
E - esophageal dysfunction
S - sclerodactyly
T - telangectasia
Antibodies - anti centromere antibodies
What is this exam finding called and in what disease?
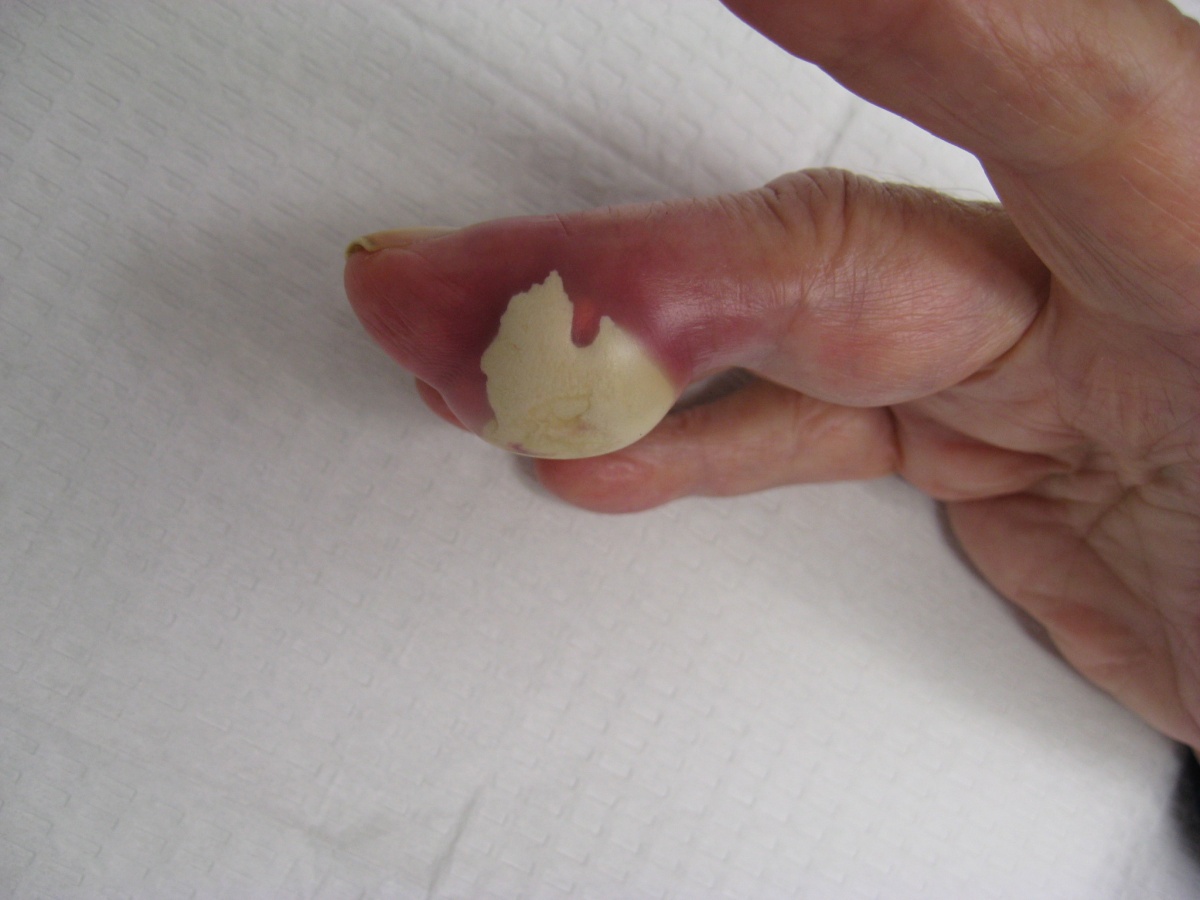
Tophi, gout
Which opioid is preferred for patient with OA of the knee?
Tramadol
What are the three most common causes of death in SLE?
Renal disease, Infections, and Cardiovascular complications
Should you initiate anti inflammatory prophylaxis before initiating urate lowering therapy?
Yes
Disease and crystal deposition

Calcific tendinitis, Basic calcium phosphate (BCP) crystals
Name the pathological process that is occurring and in what disease?
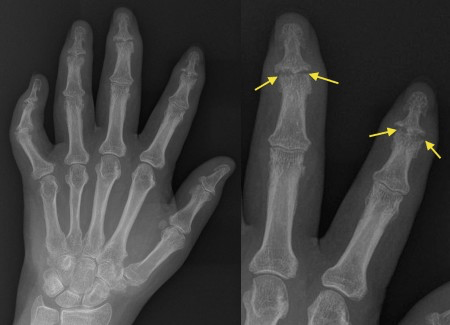
Psoriatic arthritis with marginal erosions of the distal interphalangeal joints. The bone gets eroded here first because the overlying cartilage is much thinner than in the centre of the joint. You will notice how the PIP and MCP joints are spared, whereas in the classical appearance of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) we see involvement of the MCP and PIP joints with sparing of the DIP joints.
What are the ingredients for a knee injection (include medications, their strength, dose in mL and needle specs) according to Dr. Kutsche's Injection Preparation. Where can this be found (100 point bonus)?
Kenalog (40 mg/ml) - 1 ml
Methylprednisolone (40 mg/ml) - 1 ml
Lidocaine (1% without epi) - 1 ml
Needle - 25 g, 1.5 inch
Bonus points - The lab
Which test can differentiate Discoid Lupus from SLE?
Lupus band test
What is this physical exam finding and in what disease?
Rheumatoid nodules in RA
Which rheumatological condition is scream cream most indicated in?
None