Greater inputs of capital + paid labor relative to the space being used
What is intensive agriculture?
divided land into irregularly shaped plots of land that were described using physical features
What is metes and bounds?
facilitated the global diffusion of plants, animals, diseases, human population, culture, technology, and ideas between Afro-Eurasia and the Americas
What is the Columbian Exchange?
improved methods of cultivation, harvesting, and storage of food that started in the 1700s and then benefited from the Industrial Revolution with the use of machines and new technology
What is the Second Agricultural Revolution?
biological engineering to change the DNA of a seed or animal
What are GMOs?
the agricultural practice located in the marked areas on the map
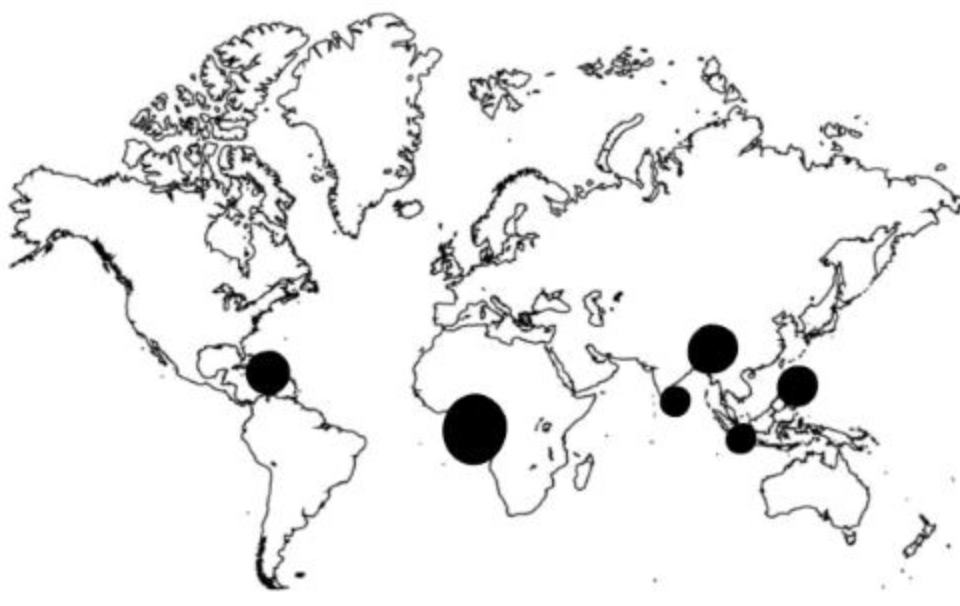
What is plantation agriculture?
a survey system found in the Midwest and Western USA and Canada.

What is township and range?
a location where plants and animals were first domesticated
What is an agricultural hearth?
the job of the majority of people before the 2nd Agricultural Revolution, but after the start of the Neolithic Revolution
What is farmer?
the cross breeding of two seeds, each with a particular desirable trait, to produce a single seed with both desirable traits
What is seed hybridization?
Mediterranean agricultural products produced in Greece.
What are olives, pita bread, cheese, figs, lamb, and wine?
US state and Canadian province where sections of land, perpendicular to river can be found (2 parts)
What are Louisiana and Quebec?
Maize cultivation diffused from here to here during this process beginning in the late-15th century. (3 parts)
What is the Americas to Afro-Eurasia due to the Columbian Exchange?
led to a reduced need for human labor
What is mechanized agriculture?
lack of infrastructure, diverse climate, and diverse soil types caused this agricultural revolution to be unsuccessful in this region (2 parts)
What is the Green Revolution/3rd Agricultural Revolution in Sub-Saharan Africa?
Horticulture agriculture and plantations would be considered this type of farming, while ranching and nomadic herding would be considered this type of farming. (2 parts)
What is intensive and extensive?
a type of land cover change that allows for agricultural production in areas with varying elevations
What is terracing?
hearth of early agriculture and early civilization most credited with Southwest Asia (Tigris and Euphrates floodplains)
What is Mesopotamia or the Fertile Crescent?
decreased need for human labor on farms led to former farmers migrating to work in these areas
What is urban?
two positive consequences of the Green Revolution
What are higher crop yields, increased nutritional value, and decrease in food prices?
the agricultural practice found in the shaded areas and the method often used with the practice (2 parts)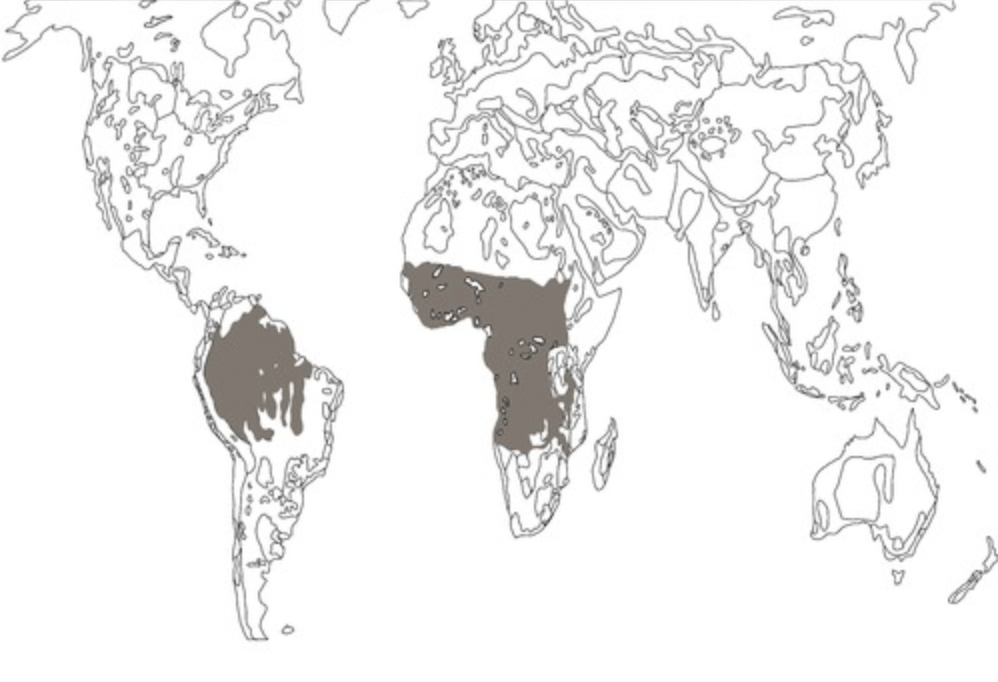
What is shifting cultivation and slash and burn?
Type of settlement pattern that was formed for safety and created a strong sense of community
What are clustered settlements?
two methods of trade that led to the diffusion of crops and animals
What are the Silk Road and the Columbian Exchange? (Will also accept Trans-Saharan Trade Routes)
two advancements of the Second Agricultural Revolution
What are the Iron/Steel Plough, Mechanized Seed Drilling, McCormick Reaper/Harvester, Grain Elevator, Barbed Wire, and Mixed Nitrogen and Nitric Acid Fertilizer?
two negative consequences of the Green Revolution
What are unemployment, environmental damage (chemical runoff ruins freshwater sources, loss of biodiversity, desertification, deforestation), dependence on chemicals, and population growth?