One small box on EKG corresponds to this amount of time (horizontally).
What is 40 milliseconds?
1 big box horizontally = 200 ms
1 small box vertically = 1 mm
1 big box vertically = 5 mm
This is the first-line antiplatelet therapy given in ACS unless contraindicated.
What is aspirin 325mg?
This is the spirometry ratio that is consistent with obstructive lung disease.
What is FEV1:FVC <0.7?
These symptoms associated with diabetes all start with P.
What is polydipsia, polyuria, and polyphagia?
The most common risk factor for COPD.
What is cigarette smoking?
A wide QRS is defined as a QRS interval greater than this number of milliseconds.
What is >120ms (0.12s) or 3 small boxes?
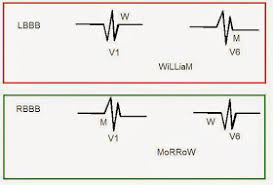
If you have a wide QRS, remember to then access for a bundle branch block.
The type of NSTEMI that occurs when there is supply/demand mismatch.
What is type 2 NSTEMI?
This is what is seen in the setting of demand ischemia, whereas type 1 is as spontaneous MI related to atherosclerotic plaque rupture, ulceration, erosion, or dissection.
This test should be checked, especially when the emphysema is panacinar and particularly affecting the lower lobes.
What is alpha-1 antitrypsin level?
This antibody should be checked if concerned for T1DM.
What is GAD 65 (glutamic acid decarboxylase)?
If negative, check additional antibodies: IA2 (the 40K fragment of tyrosine phosphatase), insulin, and ZnT8 (zinc transporter 8). Also consider checking insulin and C-peptide levels.
This is the inpatient glycemic target and outpatient Hgb A1c goal for well-controlled diabetes.
What is glucose <180 inpatient and Hgb A1c 7-8% outpatient?
These leads correspond with the septal area of the heart.
What is V1-V2?
I, aVL = lateral
II, III, aVF = inferior
V3-V4 = anterior
V5-V6 = apical (sometimes also referred to as lateral)
The EKG leads that correspond with an anterior MI?
What is V1-V4?
What are the two medications that people experiencing a COPD exacerbation should always receive (in addition to VTE prophylaxis)?
What are bronchodilators (ie, duonebs) and steroids (prednisone 40mg daily for 5 days)?
Additional considerations not always given: antibiotics, oseltamivir, NIPPV (BiPAP), intubation
This two symptoms are signs of a catabolic state, suggesting insulin deficiency and that you should start the patient on insulin.
What is weight loss and polyuria?
This blood gas finding suggests impending respiratory failure in severe COPD exacerbation.
What is respiratory acidosis (pH <7.35 and pCO2 >45)?
Remember to consider BiPAP if there is evidence of respiratory acidosis, severe dyspnea, increased work of breathing, or persistent hypoxemia!
This is the mm cutoff required to qualify as an ST depression.
What is >= 0.5mm?
Remember that this is reference to the baseline (PR segment), and needs to be present in 2 contiguous leads.
T wave inversions >= 1mm
ST elevations >= 1mm (except in V2-V3 where it depends on age/gender)
The medication that should be avoided/used cautiously in patients with inferior or right ventricular MI?
What is nitrate?
Also avoid use if SBP <100 or PDEi use in the last 48 hours.
These are the two symptom severity screening tools that, in addition to number of exacerbations, are used to help guide what pharmacologic treatment patients should be receiving.
What is mMRC (modified medical research council) and CAT (COPD assessment test)?
Unlike T2DM where screening for retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy starts at the time of diagnosis, it starts this many years after diagnosis in T1DM.
What is within 5 years after diagnosis?
Retinopathy screening = dilated and comprehensive eye examination
Kidney disease = eGFR and random urine albumin/Cr ratio
Distal symmetric polyneuropathy = assess skin and foot for deformities, pulses, and temperature/pain/vibration sensing
Autonomic neuropathy = evaluate for orthostasis, syncope, resting tachycardia, bowel/bladder dysfunction
This is a common dose at which to start weight-based dosing for basal insulin.
What is 0.25 units/kg/day?
Consider reducing to 0.15 units/kg/day if ESRD, low BMI, and/or elderly.
The axis that you would expect in right ventricular hypertrophy.
What is right axis deviation?
These EKG changes can be seen in Wellens syndrome.
What are biphasic or deeply inverted T waves in V2-V3?
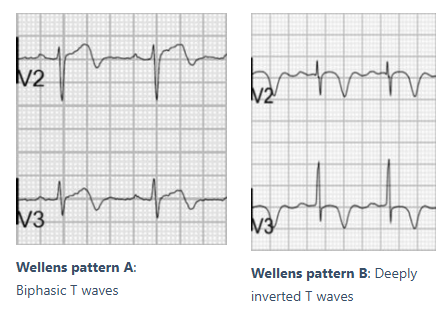
This is highly specific for critical stenosis of the left anterior descending (LAD) artery.
An ICS should be added to a patient's COPD treatment regimen when this finding is present.
What is blood eos >= 300?
Two options for basal insulin (name one that is dosed daily and one that is dosed twice daily)
What are glargine/detemir/degludec and NPH?
One of the EKG findings on a standard EKG that would make you concerned for a right ventricular MI (RVMI)?
What is:
- ST elevation in V1
- ST elevation in V1 and ST depression in V2 (highly specific for RV infarction)
- ST elevation in III>II?
Remember that patients with RVMI are preload-dependent so no nitrates!