What is the Sun?
The Sun is a STAR!
What two things do plants make in photosynthesis?
A. Water and sunlight
B. Sunlight and carbon dioxide
C. Sugar and carbon dioxide
D. Glucose and oxygen
Glucose (sugar) and oxygen
What happens the motion of an object when unbalanced forces act on that object?
A. The object does not move
B. Only object’s speed of motion will change
C. Only the object’s direction of motion will change
D. The object speed and/or direction of motion may change
The object speed and/or direction of motion may change
What do the arrows represent?
the transfer of energy
How many objects in our Solar System can be considered a Star?
a) 0
b) 1
c) 3
d) 9
1 (the Sun)
The Moon goes through different phases as it:
a) goes around the Sun
b) changes size
c) spins on its axis
d) revolves around the Earth
Revolves around the Earth
Leaves
Roots
Flower
Which arrow correctly portrays the direction of Earth’s gravity?
A
THE SUN!!!
Producer- Grass
Consumer- Caterpillar, Blue Jay
Decomposer- Mushroom
Explain the difference between Rotation and Revolution
Rotate- to spin around on an axis Example: the Earth rotates on it's axis
Revolve- a smaller object orbiting in a circle around a larger object. Example: the Earth revolves around the Sun
To make sugars so that the tree can grow
A book laying on a table has many forces acting on it. Why doesn’t it move?
A. each force has the same strength on the book, so the forces equal to zero
B. the force of the table is stronger
C. the book is stronger
D. gravity is stronger
Each force has the same strength on the book, so the forces equal to zero
In ecosystems, microbes and other decomposers:
a. Produce their own food
b. compete with plants
c. return matter to the ground
d. cause disease
Return matter to the ground
Which statement tells what causes the sun to appear to move across the sky?
a) Earth rotates on its axis
b) Earth is tilted on its axis
c) Earth revolves around the Sun
d) Earth has different time zones
The Earth rotates on its axis
What causes day and night?
a) the Earth’s rotation on its axis
b) the Moon’s orbit around the Earth
c) the Earth’s orbit around the Sun
d) the Sun’s rotation on its axis
Earth's Rotation on it's axis
What 3 things does a plant need for photosynthesis?
a. Carbon dioxide, sunlight, and soil
b. Carbon dioxide, sunlight, and oxygen
c. Water, sunlight, and oxygen
d. Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
Carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight
<-
Name a producer.
~Any plant~
A student wants to model what causes day and night on Earth, using a globe to represent Earth and a light bulb to represent the Sun. Images of the model are shown below.
How can the student use the globe and the light bulb to show what causes day and night on Earth?
a) by rotating the globe near the light bulb
b) by tilting the globe and rotating the light bulb
c) by turning the light bulb on and off near the globe
d) by moving the light bulb in a circle around the globe
By rotating the globe near the light bulb
What causes the seasons?
a) the Earth’s orbit and its tilt
b) the Moon’s orbit around Earth
c) the Northern and Southern Hemisphere
d) the Eastern and Western Hemisphere
Earth's orbit and tilt
What is photosynthesis?
a. When carbon dioxide comes out of a plant
b. The process of how a plant makes food
c. When sunlight and oxygen make food
d. When rain water enters a plant
The process of how a plant makes food
Draw two magnet examples (label the poles):
1. Attracting
2. Repelling
1. N-S, S-N
2. S-S, N-N
Name an example of a consumer that is affected by producers.
Rabbit, deer
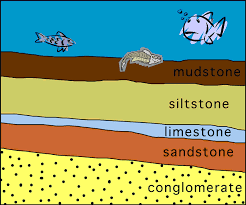
Which layer of rock is the oldest? Which layer is the youngest?
Oldest = Conglomerate
Youngest = Mudstone