the solid, outer layer of Earth that consists of the crust and rigid upper part of the mantle
What is the lithosphere
the supercontinent that formed 300 million years ago and began to break up 200 million years ago
What is Pangea
a break in a body of rock along which one block moves relative to another
what is a fault
a block of lithosphere that consists of the crust and the rigid, outermost part of the mantle
what is a tectonic plate
a movement or trembling of the ground that is caused by a sudden release of energy when rocks along a fault move
what is an earthquake
Which of letter represents the mantle in the diagram below?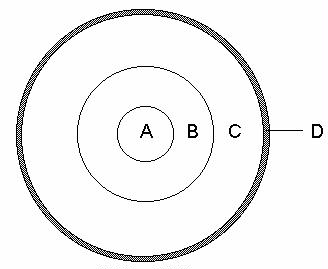
C
This underwater phenomena which occurs at mid-ocean ridges help to explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics
What is sea-floor spreading?
What is the difference between magma and lava?
Scientists use the term magma for molten rock that is underground and lava for molten rock that breaks through the Earth's surface.
Which letter in the image below represent the focus
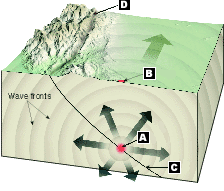
A- focus
This layer of the Earth is made mostly of iron and some nickel and makes up about 1/3 of the Earth's mass.
What is the core
Name the three plate boundaries depicted in the image below listed in order from top to bottom.
Divergent Plate Boundary
Convergent Plate Boundary
Transform Plate Boundary
In what type of fault does the hanging wall move up relative to the footwall?
Reverse fault
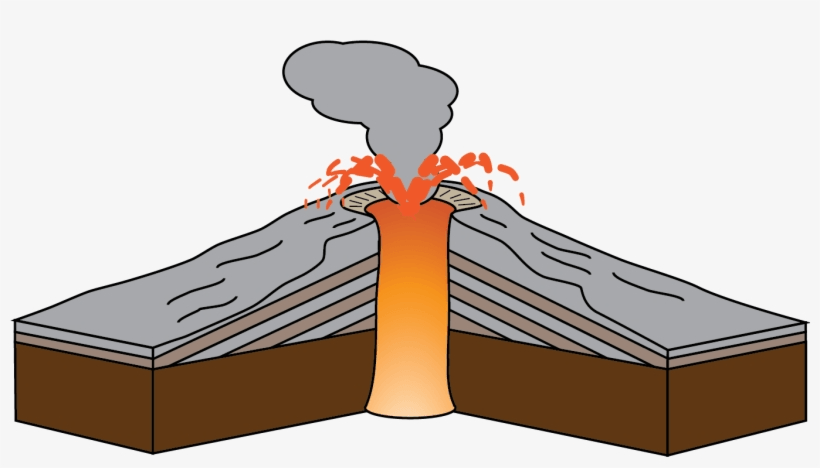
Name the volcano structure marked by the number ten in the image below.
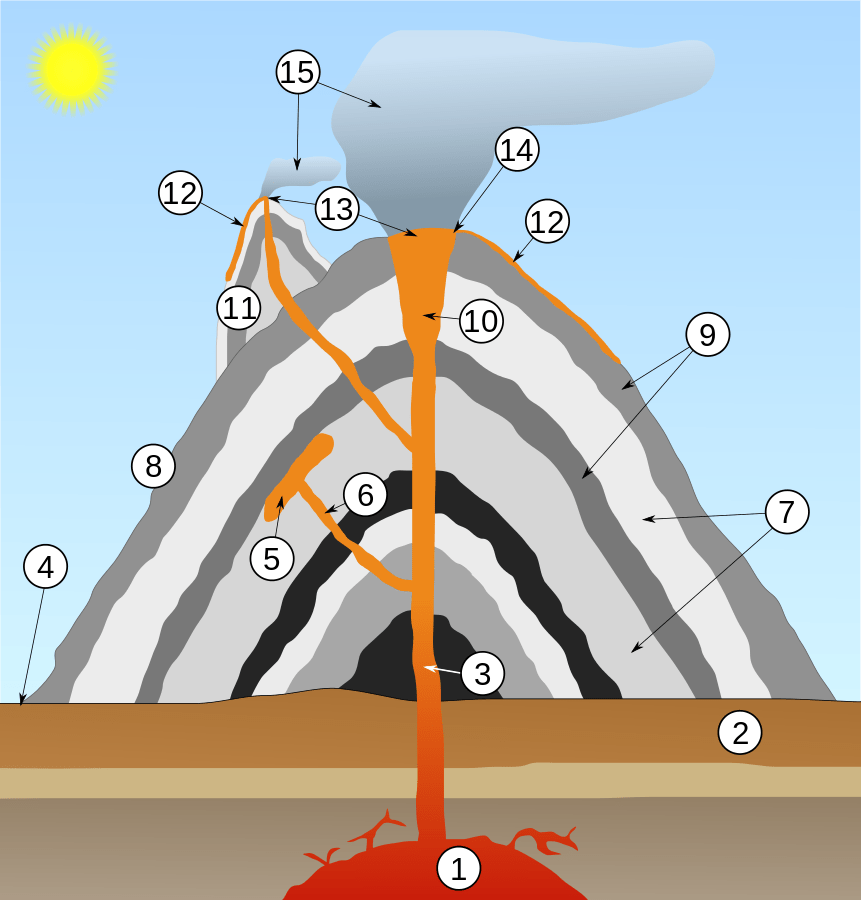
What is the vent
The data from the three sites depicted in the image below could be used to approximate the location of this feature of an earthquake.
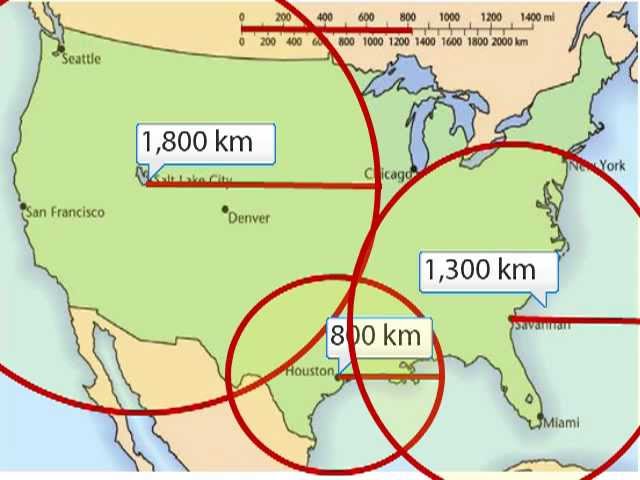
What is the epicenter
This physical layer of the Earth consists of the upper layer of the earth's mantle, and is located below the lithosphere
asthenosphere
Define the three major types of plate boundaries
Convergent Boundary- the boundary between tectonic plates that are colliding
Divergent Boundary- the boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other.
Transform Boundary- the boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally.
What kind of faults are represented in the following series of images (Match the letter with the fault type).
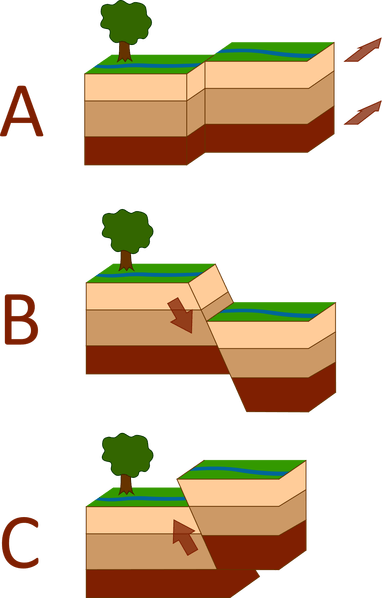
A- Strike-slip fault
B- Normal fault
C- Reverse fault
Name the three volcano types depicted below in order from top to bottom
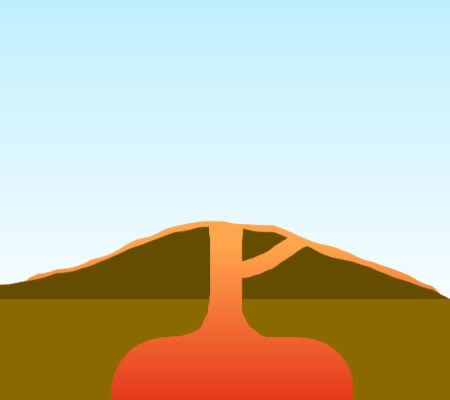
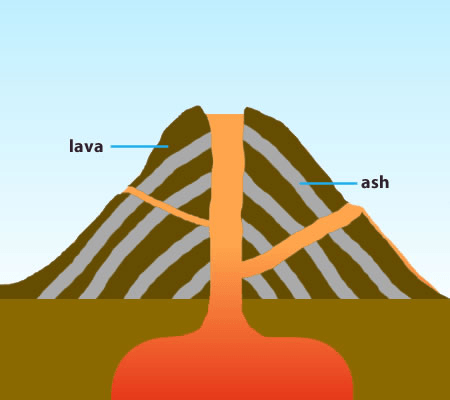

composite
shield
cinder cone
The phenomena that occurs is the result of the sudden return of elastically deformed rock to its un-deformed shape.
What is elastic rebound?
Name all three compositional layers of the Earth and all five physical layers
Compositional: crust, mantle core
Physical: lithosphere, asthenosphere, mesosphere, outer core, and inner core.
Name a landform that could be found at each of the three types of plate boundaries.
Convergent Boundary- mountain range, volcano
Divergent Boundary- rift valley, mid-ocean ridge, fissure eruption
Transform Boundary- valleys, trenches, scarps, and ridges
What type of stress is associated with the each of the three kinds of faults pictured below (match the stress type with the correct letter).
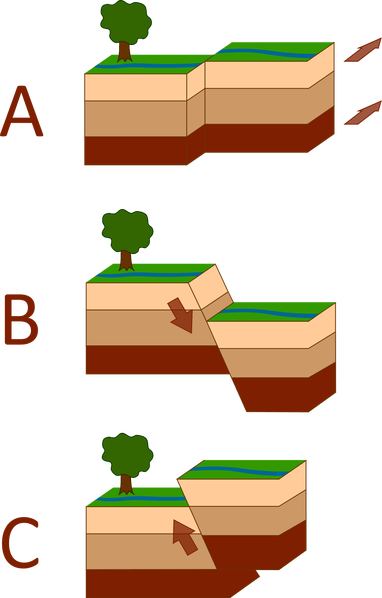
A- Shear stress
B- Tension
C- Compression
Name the three volcano types and describe how they form.
Cinder Cone Volcano- small volcanoes with steep slopes. They form from ash and pieces of solidified lava that fall around a small vent.
Composite Volcano- are built from alternating layers of hardened lava flows and pyroclastic material. They generally develop into large, steep mountains.
Shield Volcano- volcanoes with broad bases and gently sloping sides. They are the result of mild eruptions.
Which station is closest to the epicenter and how do you know?
Station C: the first spike occurs at station C indicating the arrival of the primary or p-wave. This means station C is closest because the seismic waves travel outward in all directions from the epicenter. They arrive sooner at stations which are closest.