What is the law of conservation of energy?
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred to a new place or new type energy.
What are two types of waves that transfer energy?
transverse & longitudinal
What causes changes in seasons on Earth.
Earth revolving around the sun and its tilted axis.
What are the four main spheres of Earth?
biosphere, geosphere, atmosphere, and hydrosphere
What are the three main types of rocks?
Sedimentary, metamorphic, and igneous
Why is resource management important for global energy?
Limited resources and not available everywhere. Take care of them and don't pollute. We might run out.
How do transverse waves move?
Transverse waves perpendicular to the direction in which energy moves.
would also accept up and down

Describe how the tilt of the Earth affects the length of days and nights.
tilted toward the Sun- longer days and shorter nights. titled away - shorter daylight hrs
Describe one component of the biosphere.
All living organisms on Earth.
How are igneous rocks formed?
Igneous rocks form from cooled lava/magma.
How does energy transfer in a food web? Provide and example.
Energy sun (light) to plant (make sugar) herbiv eats (rabbit consumer), we eat to move
Describe how longitudinal waves transfer energy through a medium.
Particles compress and spread out and move parallel to the direction of moving energy.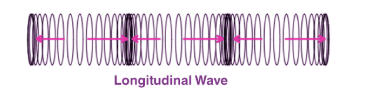
How do the positions of the Earth, Sun, and Moon impact ocean tides?
What is the atmosphere, and why is it important?
The atmosphere is the layer of gases surrounding the Earth. It provides breathable air and supports photosynthesis.
Describe the process of sedimentary rock formation.
Sediments accumulate and are buried deeply (W.E.D) where the pressure compacts and cements them together into layered rocks.
What role does resource management play in reducing pollution in water, air, and soil?
Manage with rules to protect air, water and soil. Give a hoot, don't pollute
Provide an example of a transverse wave and explain its characteristics.
Rope, light, radio (guitar string –not the sound from it) moves up and down, perpendicular to energy
What are spring and neap tides?
Spring tides occur when the sun, Earth, and moon are aligned causing the largest differences between high and low tide. Neap tides occur when the sun, moon, and Earth form a 90 degree angle causing the smallest difference between high and low tides.
Explain the role of the hydrosphere in Earth's systems.
Water for living organisms and impacts weather due to the water cycle. It also causes erosion which changes the geosphere.
What are metamorphic rocks, and how do they form?
Existing rocks are transformed by intense heat and pressure causing a change in their structure and texture.
Explain how energy is conserved on an amusement park ride.
When a roller coaster is at the top of a hill it has gravitational potential energy. When it begins to move downhill the potential energy is transformed into kinetic energy. This process continues throughout the ride. Some energy is transformed into heat or sound energy as well.
Explain the relationship between wave height and energy transfer.
More height, more energy.
How does the tilt of the Earth affect climate (temperature in seasons)
Tilt toward sun - direct rays and more daylight hrs higher temperatures year round.
How do the geosphere and biosphere interact?
The geosphere provides shelter to many animals and nutrients to plants. Minerals
Explain the rock cycle and how rocks can change from one type to another.
Shows how different types of rocks are formed.
Melt & Cool - Ign
Heat & Pressure - Met
WED then compact & Cement - Sediment