Any change or signal in the environment that can make an organism react in some way.
Stimulus
Explain how asexual reproduction is different from sexual reproduction.
Asexual produces offspring identical to parent and requires 1 parent. Sexual produces offspring different from parents and requires 2 parents.
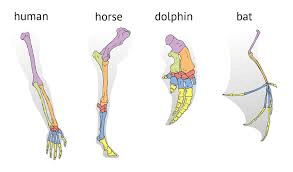 What describes this evidence that supports the theory of evolution?
What describes this evidence that supports the theory of evolution?
Homologous Structures
Describe the difference between biotic and abiotic factors in an ecosystem.
Biotic are living factors, abiotic are nonliving factors.
What is the role of a decomposer in a food chain?
They break down dead organisms and return nutrients back into the environment.
A substance that contains pathogens that have been weakened or killed but can still trigger the body to produce chemicals that destroy the pathogen.
Vaccine
What are the different forms of a gene called?
(For example R = dominant and r = recessive)
Alleles
What is a group of similar organisms that can mate and produce offspring capable of reproduction?
Species
Describe the difference between Immigration and Emigration in relation to a population.
Immigration is when new members move into a population, Emigration is when members leave a population.
Name 2 abiotic factors in an environment
Air, water, soil, sunlight, etc.
The mosquito Aedes aegypti is a carrier of the Zika virus. Aedes is the name of the mosquito's:
Genus
Explain the difference between genotype and phenotype.
Genotype is the actual genes an organism inherits and phenotype is the appearance (what traits are visible).
An organism with "high fitness" is described as having the ability to do what?
Survive and reproduce
What is the role of an organism in its habitat?
Niche
What are the levels of organization in living things?
Cell-tissue-organ-organ system-organism
Which cell structure breaks down sugar to provide ENERGY for the cell's activities?
Mitochondria (remember Mighty Mitochondria)
Which one is heterozygous?
Aa aa AA
Aa
Overproduction, variations, and competition are all things that affect:
Natural Selection
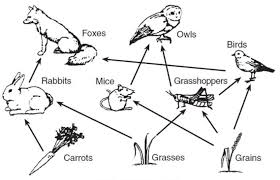 Name 2 secondary consumers in this food web.
Name 2 secondary consumers in this food web.
Owls and Foxes
What is the difference between a producer and a consumer?
Producer can make its own food (plant)
Consumer has to eat other organisms (animal)
Which system of the body is responsible for removing the carbon dioxide waste from the body?
Respiratory
What is the cause of genetic diseases?
Mutations
What happens to organisms that do not have the adaptations needed to survive a changing environment?
They become extinct.
What is the difference between Mutualism and Commensalism?
In mutualism, both organism benefit. In commensalism, one benefits and the other is not affected.
Explain how Dr. Francisco Redi helped to disprove the theory of spontaneous generation.
His experiment proved that living things do not appear from nonliving sources (flies don't come from rotting meat, they come from eggs laid on the meat).
What happens when a cell reproduces? (What is the end result?)
2 daughter cells are formed.
Two guinea pigs are Bb for fur color (B is black and b is white). What % of their offspring will have black fur?
25% or 1/4
What is the fossil record?
All the fossils that have been discovered so far and what we have learned from them.
What is a pioneer species?
The first species to populate an area.
Explain the difference between a dominant trait and a recessive trait.
The dominant trait will always appear, the recessive one will always be hidden.
State the 3 parts of the Cell Theory.
1. All living things are made of cells.
2. Cells come from other cells.
3. Cells are the basic unit of life.
What is a pedigree?
Used to trace the inheritance in a family of a particular trait. (Remember Queen Victoria an Hemophilia in her family!)

What type of fossil is pictured?
Body fossil, preserved remains
Any factor that causes a population to stop growing or decrease in size (such as a disease) is called a:
Limiting factor
What are omnivores, carnivores, and herbivores?
Omni - eat everything
Carn - eat meat
Herb - eat plants