An educated guess that attempts to explain an observation or answer a question.
The age of an artifact as determined by a date printed on it or a reference to the artifact in a work of history.
What is known age.
The smallest unit of matter.
What is an atom?
The portion of the skeleton that supports and protects the head, neck, and trunk
Organisms that produce their own food.
What is producers.
Blood vessels that carry blood BACK TO the heart
A weakened or inactive version of a pathogen that stimulates the body's production of antibodies that can destroy the pathogen.
What is vaccine.
This nervous system structure that is composed of the brain and spinal cord.
What is Central Nervous System
This invention allows us to see the bones inside our body without surgery
What is the X-Ray
An aspect of an experiment that changes during the course of the experiment.
What is experimental variable.
The process of counting tree rings to determine the age of a tree.
What is dendrochronology.
Makes bones hard.
What are minerals.
The minimum amount of energy required by the body in a day.
What is Basal Metabolic Rate
Tiny thin-walled blood vessels that allow the exchange of gases and nutrients between the blood and cells and are located between the arteries and veins.
What is capillaries.
The system in the human body chiefly responsible for regulating water and chemical levels in the fluids of the body
What is the Urinary System
These nervous system structures that are sensitive to salty, bitter, sweet, sour, and umami.
What are taste buds.
This invention by Alexander Graham Bell was patented in 1876.
What is the telephone?
Experiments in which neither the participants NOR the people analyzing the results know who is in the control group.
What is Double-Blind Experiment
The view that most of earth's geological features are the result of large-scale catastrophes such as floods, volcanic eruptions, etc
The two DNA pairs.
What is .....
Adenine and Thymine
Cytosine and Guanine
What is symbiosis.
A chemical substance the body needs in small amounts to stay healthy
What is vitamin?
The chamber of the heart that deoxygenated blood leaves on its way to the lungs.
What is Right Ventricle.
The system in the body chiefly responsible for fighting disease.
What is Lymphatic System
The part of the autonomic nervous system that SLOWS the heart rate.
What is parasympathetic division.
This man invented the first practical incandescent light bulb.
Who was Thomas Edison?
The amount by which force or motion is magnified in a simple machine.
What is mechanical advantage
A layer of rock laid down by water.
What is sedimentary.
Item labeled number 2.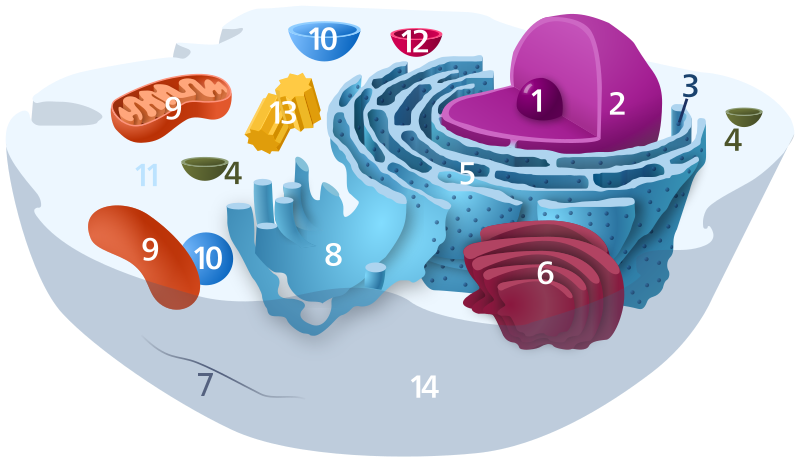
What is nucleus.
The more stable joint between one that has a large range of motion while the second has limited range of motion.
What is the second joint with less ROM.

The organ labeled by Number 4
What is liver
The process by which blood seals wounds to keep it from leaking out an injured artery.
This gland controls the pituitary gland.
What is the Hypothalamus
What is cerebrum.
This revolutionary product, released in 2007, reshaped mobile communications and technology.
What is the iPhone?
Mechanical Advantage of a block and tackle that uses two pulleys.
What is 2?
This pictures shows what?
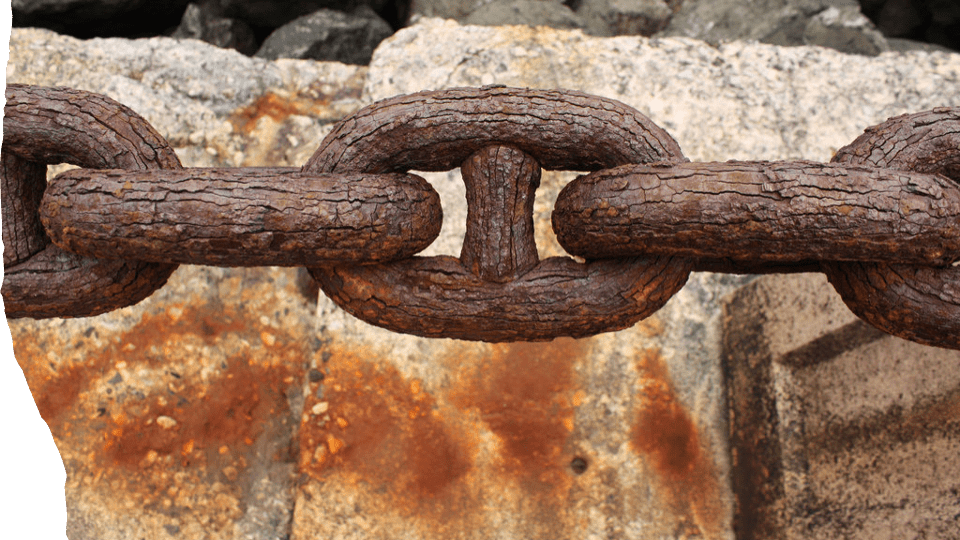

What is Chemical Weathering
 Item labeled 14
Item labeled 14
What is Cell Membrane.
Connects skeletal muscles to the skeleton.
What is tendon
The organ where most of the absorption of nutrients occurs.
What is the small intestine
The type of blood cells that contain hemoglobin.
What is Red Blood Cells
What is the adrenal gland.
The part of the autonomic nervous system that speeds up the heart rate.
What is sympathetic division
Known as the father of the computer, he conceptualized the first mechanical computer in the early 19th century.
Who was Charles Babbage?