What is genetics?
The study of heredity.
What is heredity?
The passage of genetic instructions (traits) from parent to offspring.
Sexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically _____________ to the parents.
Similar (slightly different)
Some genes can be hidden or covered up by another. These are considered to be-
Recessive
What are two examples of genetic disorders we discussed in class?
Hemophilia, Sickle Cell Anemia, Down Syndrome, Cystic Fibrosis
What is the picture of all the chromosomes in an organism called?
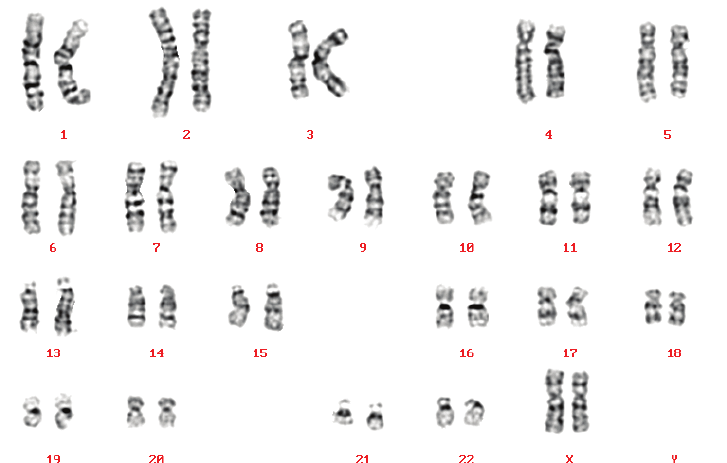
A Karyotype
What is it called when two organisms are chosen to mate together to achieve specific traits in the offspring?
Selective Breeding
What is the visual chart that shows specific traits through a family tree?
Pedigree Diagram
Where are genes located?
In the chromosomes
Who first studied heredity and the passage of traits from one generation to the next (Father of Modern Genetics)?
Gregor Mendel
Asexual reproduction produces offspring that are genetically ____________ to the parent.
Identical
What is the punnet square used for?
To determine the outcome of genetic crossings.
Name two traits that could be inherited from a parent?
Examples: hair color, eye color, height, skin color, freckles, etc...
How are the last chromosomes arranged for male and females?
Females= XX
Males= XY
What is it called when scientists take the DNA or gene out of an organism and put it into another?
Genetic Engineering (Recombinant DNA)
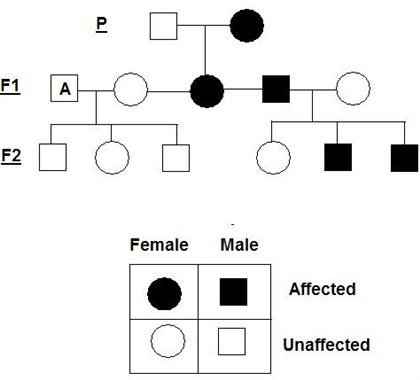
What are the shapes for male and female on a pedigree diagram?
Male: square
Female: circle
Homozygous
What type of organism did Gregor Mendel use to first study heredity?
Pea Plants
If you are studying a population of genetically identical individuals, you can conclude that these individuals reproduce how?
Asexually
A black chicken (BB) is crossed with a black chicken (BB). What percentage of offspring will be black?
100%
Why does a Punnet Square use capital and lowercase letters (what do they represent)?
Capital = Dominant Trait Lower Case = Recessive Trait
What is this diagram called?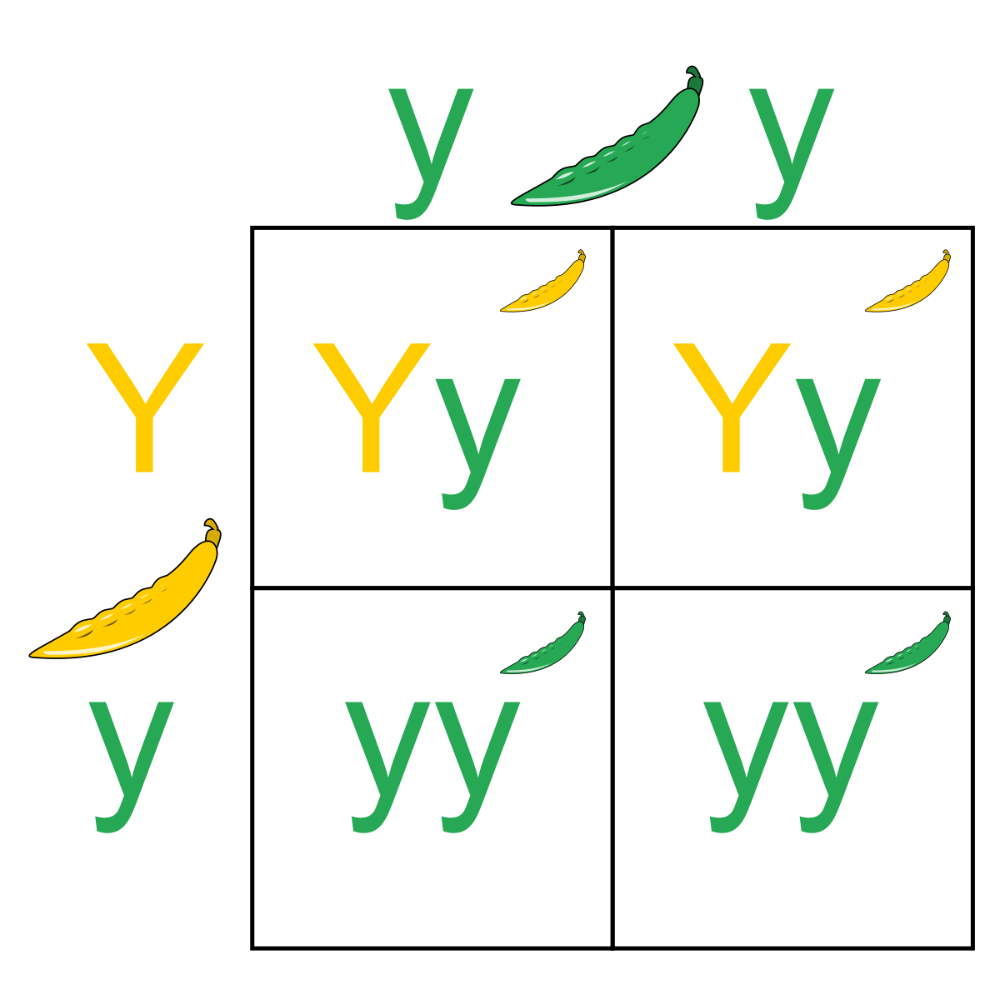
Punnett Square
Name two organisms that have been selectively bred?
Cows, Corn, Plants, Animals, Pigs, Horses, Dogs, etc.
Describe what a CARRIER looks like on a pedigree diagram?
Half-shaded shape
Two DIFFERENT copies of an allele?
Heterozygous
The physical trait observed in an offspring is known as it's -
Phenotype
For some traits, only one copy of a particular gene is needed to show a given trait. These genes are referred to as-
Dominant
Having dimples is dominant (D). Not having dimples is recessive. (d) Both parents are heterozygous for the dominant trait. What percentage of the children will NOT have dimples?
25%
How many parents are involved in asexual reproduction?
One
What is the name of this specific form of genetic engineering?
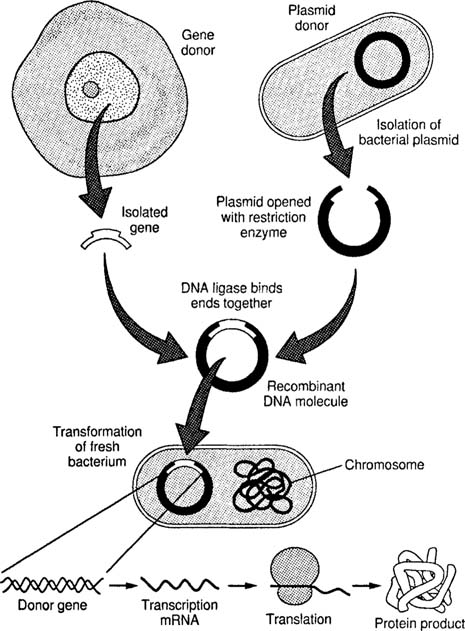
Recombinant DNA
Name one organism that scientists have use the technology of recombinant DNA on?
Glow in the dark cats, insect-resistant plants, human gene for insulin.
How can we figure out of a trait is dominant in a pedigree diagram?
There would only be fully shaded in shapes--no carriers.
What do we call the genetic make up of the individual, represented by a set of letters?
Genotype
How many chromomsomes do humans have?
46 or 23 pair
What is an example of a homozygous dominant genotype?
TT
Long ears are dominant (E) in rabbits. If one parent is homozygous dominant for the long ear trait and the other homozygours reccessive (e), what is the only possible genotype of the offspring?
Ee
Two dark brown rabbits have four offspring. Three of the offspring are dark and one is white. What does this tell you about the parents' genes for fur color?
Dark brown is dominant and white fur is recessive. Both parents are heterozygous.
What are two of the three ways that you can identify there is something wrong in a karyotype?
Missing, Extra, or Deletion in the Chromosomes
Explain one reason why people would use genetic engineering?
To benefit humans
What is the GENOTYPE of person A in this pedigree diagram? (You can use any letter)
Write out all the genotypes and phenotypes (with probabilities) of the following example:
The trait for a straight thumb (H) is dominant over the trait for a hitchhiker’s thumb (h).
Two people with straight thumbs (Hh x Hh) got married. Complete the diagram below to show the genes for their children.
Genotype: HH 25%, Hh 50%, hh 25%
Phenotype: Straight 75%, Hitchikers 25%