An animal that eats both other animals and plants.
What is an omnivore?
The three macronutrients/macromolecules
What are carbohydrates, lipids/fats, and proteins?
What is predation?
The most specific classification group, below genus.
What is species?
The scientific name for a prediction about an experiment.
What is a hypothesis?
What is an apex predator?
During photosynthesis, plants take in carbon dioxide and water to make this energy source.
Name of the organism in/on which a parasite lives.
What is the host?
A visual tool for classifying organisms.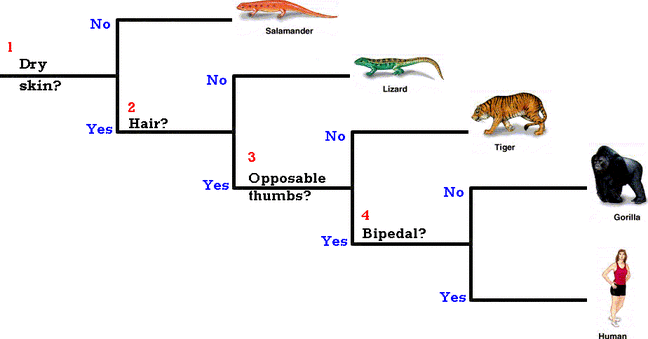
What is a dichotomous key?
What yeast needs to ferment.
What is sugar/glucose?
The primary consumer in each food chain.
What are the mouse, the rabbit, and the grasshopper?
This macronutrient is broken down into amino acids.
What is protein?
Name for all non-living things within an ecosystem.
What is abiotic factors?
An organism with cells that do not have a nucleus.
What is a prokaryote?
the variable we manipulate.
What is the independent variable?
The percentage of energy that is transferred from one trophic level to the next.
What is 10%
Chemical digestion takes place in this organ for carbohydrates and lipids.
What is the small intestine?
The type of mutualism where the species would die without one another.
What is obligate mutualism?
Name for an organism that can synthesize (create) its own food.
What is an autotroph?
Type of pollution that we modeled which kills aquatic wildlife and birds.
What is an oil spill?
The general name for a place on Earth where carbon is stored.
What is a reservoir?
The main enzyme that digests carbohydrates.
What is amylase?
The type of competition where the population of one prey species affects the population of another prey species.
What is apparent competition?
The six kingdoms of organisms.
What are animal, plant, fungi, protist, archaea, and eubacteria?
The maximum population an ecosystem can support.
What is carrying capacity?