Give an example of a physical change.
Example: Crumpling up a piece of paper.
This is the name of the temperature a substance melts (solid to liquid).
Melting point
This energy, also known as heat, energy that comes from the movement of atoms and molecules in a substance.
Thermal energy
This energy is stored energy energy that is ready to go.
Potential energy
Give an example of a chemical change.
Example: Cooking an egg.
A phase change on a heating curve is indicated by a _________.

flat line/plateau
This type of energy is energy stored in the bonds of atoms and molecules.
Chemical energy
True or false - as a pendulum moves from the bottom of its swing to the top of its swing, the potential energy decreases.
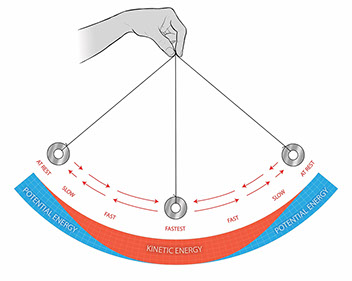
False - potential energy increases, kinetic energy decreases
Classify the following into physical and chemical changes (write P or C):
1) Melting an ice cube
2) Wood burning
3) Mixing milk into coffee
4) Shredding paper
1) P
2) C
3) P
4) P
True or false - if the boiling point of a substance is 200 degrees Fahrenheit, the condensation point of a substance is 200 degrees Fahrenheit.
True
This energy is energy stored in the movement of objects.
The law of conservation of energy states that __________________.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed.
True or false - during a chemical change, a new state of matter is always produced.
FALSE - A new material is formed.
As a substance is cooling and changes from gas to liquid and eventually solid, the molecule movement will ________.
decrease/slow down!
This energy is energy from moving electrons.
Electric energy
Which point has the greatest kinetic energy?
Point 3
True or false - All chemical reactions are reversible.
False - all chemical reactions are irreversible.
A substance has a melting point of 40.0°C and a boiling point of 65°C. What is nitrogen's state of matter at 70°C?
Gas
This energy is created by movement of energy through substances in waves.
Sound energy
Daily Double!!!!
Potential energy that is related to an object's height above the ground is known as ________ potential energy.
gravitational