The next level of organization in the list below.
Organism,______________, Community, Ecosystem
What is Population?
The name of this rock type.

What is obsidian?
The three subatomic particles found in atoms.
What are protons, neutrons, and electrons?
The next level of organization in the list below.
Atom, Molecule, Organelle, Cell,____________, Organ, Organ System, Organism
What is a tissue?
The name of this type of genotype (Aa).
What is heterozygous?
A definition and example of an abiotic factor.
What is a non-living part of an ecosystem and water?
Other examples: rocks, sun, win, gases, sand, etc.
WED stands for this.
What is weathering, erosion, and deposition?
Two examples of greenhouse gases.
What is carbon dioxide, water vapor, methane, nitrous oxide, HFCs, and PFCs?
This system is responsible for taking in oxygen and giving off carbon dioxide.
What is the respiratory system?
Two reasons for how asexual reproduction is different than sexual reproduction.
What is the offspring is genetically identical, happens fast, one parent, hard to evolve?
Two things that organisms might compete over.
What is food and habitat?
Other examples: mates, water, light (plants)
The current Geologic Time Scale Era that we are in from the options below.
A. Paleozoic
B. Precambrian
C. Mesozoic
D. Cenozoic
What is the Cenozoic Era?
Three examples of types of renewable energy.
What is solar, wind, hydropower, biomass, geothermal, tidal?
Four bones that are in the lower body (below the stomach).
What are the phalanges, metatarsals, tarsals, tibia, fibula, patella, femur, pelvis, sacrum, coccyx?
Mutations in DNA can be any of these three things to the organism.
What is positive/beneficial, negative/harmful, and neutral/no effect?
Two examples of invasive species in Maine.
What are Emerald Ash Borers and Green Crabs?
Other examples: Northern Pike, Purple Loosetrife, Spotted Lanternfly, Asian Shore Crab, Eurasian Milfoil, etc.
What is an igneous rock?
The number of neutrons that this element has.

What is 121 neutrons?
Gas exchange (oxygen <--> carbon dioxide) in the lungs happens where specifically?
hint: there are 2 parts that should be named
What are the capillaries and the alveoli?
From the list below, this shows an example of artificial selection.
A. Wolves evolving into different subspecies naturally
B. Farmers breeding cows that produce more milk
C. A scientist editing genes in a lab
D. A random mutation that helps potatoes resist drought
What is B. Farmers breeding cows that produce more milk?
What is increases?
The type of plate boundary when tectonic plates are pulling apart.
What are divergent plate boundaries?
Two pieces of evidence that a chemical change has taken place.
What is unexpected color change, new smell, burning/combustion, a gas is created, heat/light produced, change in temperature, a precipitate is formed?
What is it called when your body maintains stable and steady conditions?
What is homeostasis?
In the punnett square below, two heterozygous round pea plants are crossed. The percentage that you'd have any homozygous offspring is this. 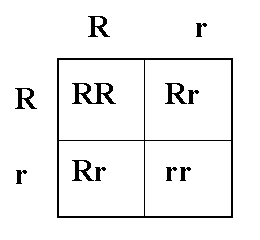
What is 50%?
25% homozygous dominant (RR)
25% homozygous recessive (rr)
50% chance of homozygous offspring