The (three!) continents on which Deciduous Forest Biomes are located
What are North America, Europe and Asia
The science and study of woody plants (trees & shrubs), specifically, their taxonomic classifications & leaf identification.
What is Dendrology

What is Platanus Occidentalis or American Sycamore
The continuous state of change in forests can be summarized with these two basic elements.
What are disturbance and succession
The typical structure of Deciduous forests includes four layers - name two
What are:
1. canopy composed of mature full-sized dominant species with a slightly lower layer of mature trees
2. the understory
3. a shrub layer
4. a ground layer of grasses and other herbaceous plants.
The name of Bud A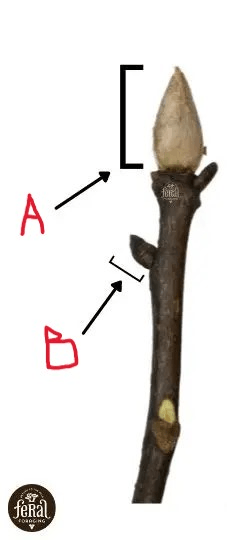
What is the terminal bud
The central, supporting pillar of the tree. Although dead, it will not decay or lose strength while the outer layers are intact.
What is heartwood
A distinguishable hole in the canopy of a forest as the result of a single tree or large tree branch falling, which allows light through to the understory or forest floor, where early-successional shade-intolerant species can colonize and maintain a population within the dominant forest.
What is a treefall gap
The purposeful clearing of forested land. Throughout history and into modern times, forests have been razed to make space for agriculture and animal grazing, and to obtain wood for fuel, manufacturing, and construction.

What is deforestation
A branching pattern where side branches, leaves and leaf scars grow from the stem directly across from each other.
What is opposite

What is Sequoia Sempervirens (or) Redwood
The temperature/water availability/wind affect/sunlight etc. within and under the forest canopy (as opposed to outside of it)
What is microclimate
This word refers to trees that lose their leaves seasonally
What is deciduous
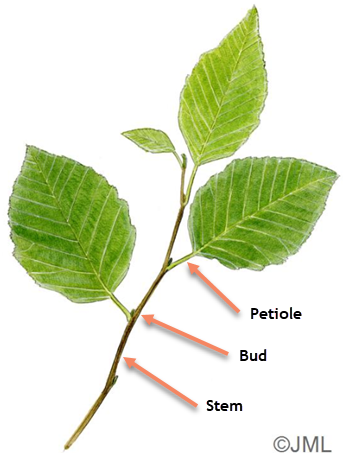
An embryonic shoot located in the axil of a leaf (not the tip of the branch, but the side)

What are axillary (or lateral) buds
The pipeline through which food is passed to the rest of the tree. It lives for only a short time, then dies and turns to cork to become part of the protective outer bark.
What is the inner bark or phloem
Name a common pioneer tree species in North American Deciduous Forests
red cedar, alder, black locust, most pines and larches, yellow poplar, aspen, etc
The primary consumer trophic level includes which of the following organisms?
A. Birds and squirrels.
B. Worms and fungi.
C. Carnivores.
D. Trees and flowers.
What is A. Birds and Squirrels

The stalk that joins a leaf to a stem (twig)
What is the petiole
The growing part of the trunk. It annually produces new bark and new wood in response to hormones that pass down through the phloem with food from the leaves. These hormones, called “auxins”, stimulate growth in cells. Auxins are produced by leaf buds at the ends of branches as soon as they start growing in spring.
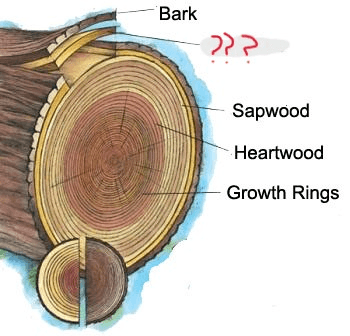
What is the Cambium
Forest disturbances can vary in frequency and intensity, and include natural disasters such as (name at least 2)
fire, landslides, wind, volcanic eruptions, rare meteor impacts, outbreaks of insects, fungi and other pathogens, animal clearing events, anthropogenic disturbances (logging, warfare, pollution, etc)