What is a stimulus
Environmental change
what is thermoregulation
the regulation of body temperature
What does the endocrine system do?
Uses chemical messengers called hormones to regulate body functions.
What does the renal artery do
Carries blood from body to kidneys
Label 1-5

1: pulmonary artery
2: vena cava
3: pulmonary veins
4: right atrium
5: left atrium
What is negative feedback?
The response counteracts the stimulus
What is vasocontriction
When body temperature drops, blood vessels in the skin get narrower, reducing the volume of blood near the skin surface, and reduces heat loss.
What is adrenaline
It is the hormone that triggers the fight-or-flight response.
What is the difference between the small intestine and large intestine?
Large intestine: Removes water from undigested food
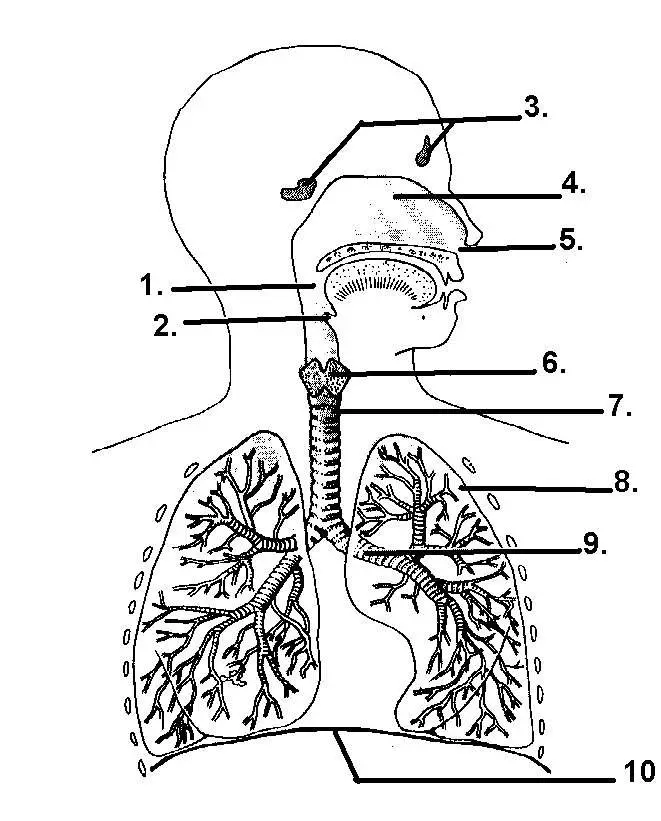
Label 6, 7, 8, 9
6: larynx
7: Trachea
8: alveoli
9: bronchus
Describe the components of a homeostatic loop
Receptor, Control Center, effector
How does sweat work to regulate body temperature?
Produced by sweat glands, sweat evaporates & takes heat away from the body.
compare motor neurons and sensory neurons
Sensory neurons carry impulse generates from stimulus to CNS, whereas motor neurons connect sensory neurons to motor neurons.
Substances the body needs such as glucose are reabsorbed in the bloodstream
Explain the function of the alveoli
Air sacs in the lungs that exchange carbon dioxide and oxygen in the blood.
What is positive feedback?
What occurs during hyperglycemia
Insulin is released to lower your blood sugar levels
What role does the CNS play in the nervous system?
The control center: Receives information and sends out messages
How does the appendix maintain homeostasis?
It doesn't
How is oxygen picked up in red blood cells?
Haemoglobin molecules inside red blood cells pick up and carry the oxygen.
State 2 things that is maintained in our body due to homeostatis.
Blood Glucose and temperature regulation.
When is glycogen released and what effects does it have on blood sugar levels?
Glycogen is released during hypoglycaemia (when your blood sugar is too low) When glycogen is released, your blood glucose levels increase.
What are some functions that hormones regulate?
(3 things)
-Level of glucose in blood and glucose breakdown
-water levels in body
-Heat production
- Sexual maturity
-Sperm and egg production
- growth of cells and tissues
How do kidneys maintain homeostasis?
Maintains the balance of vitamins, minerals, water and waste concentration.
Where does oxygenated blood travel to and which side of the heart is it pumped out from?
Oxygenated blood travels to the entire body and it is pumped out from the left side of the heart.